<ctype.h>
int isalnum(int c);
int isalpha(int c);
int iscntrl(int c);
int isdigit(int c);
int isgraph(int c);
int islower(int c);
int isprint(int c);
int ispunct(int c);
int isspace(int c);
int isupper(int c);
int isxdigit(int c);
int tolower(int c);
int toupper(int c);
Include the standard header <ctype.h>
to declare several functions that are useful
for classifying and mapping codes from the
target character set. Every function that has a parameter of type
int can accept the value of the macro
EOF or any value
representable as type unsigned char. Thus, the argument can
be the value returned by any of the functions
fgetc,
fputc,
getc,
getchar,
putc,
putchar,
tolower,
toupper, and
ungetc.
You must not call these functions
with other argument values.
Other library functions use these functions. The function
scanf,
for example, uses the function
isspace
to determine valid white space within an input field.
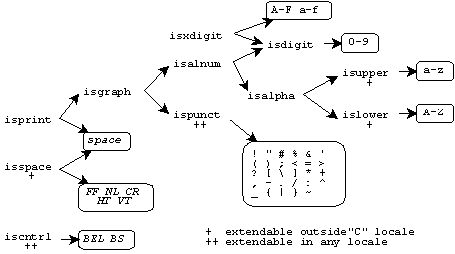
The character classification functions are strongly interrelated. Many are defined in terms of other functions. For characters in the basic C character set, here are the dependencies between these functions:

The diagram tells you that the function
isprint
returns nonzero for space or for
any character for which the function
isgraph returns nonzero.
The function
isgraph, in turn,
returns nonzero for any character for which either the function
isalnum or the function
ispunct
returns nonzero. The function
isdigit,
on the other hand, returns nonzero only for the digits
0-9.
An implementation can define additional characters that return nonzero for some of these functions. Any character set can contain additional characters that return nonzero for:
ispunct
(provided the characters cause
isalnum to return zero)
iscntrl
(provided the characters cause
isprint to return zero)
The diagram indicates with ++ those functions that can
define additional characters in any character set.
Moreover, locales other than the
"C" locale
can define additional characters that return nonzero for:
isalpha,
isupper, and
islower
(provided the characters cause
iscntrl,
isdigit,
ispunct, and
isspace to return zero)
isspace
(provided the characters cause
isprint to return zero)
The diagram indicates with + those functions that can
define additional characters in locales other than the
"C" locale.
Note that an implementation can define locales other than the
"C" locale
in which a character can cause
isalpha (and hence
isalnum)
to return nonzero, yet still cause
isupper and
islower to return zero.
isalnum
int isalnum(int c);
The function returns nonzero if c is any of:
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z o 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
or any other locale-specific alphabetic character.
isalpha
int isalpha(int c);
The function returns nonzero if c is any of:
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
or any other locale-specific alphabetic character.
iscntrl
int iscntrl(int c);
The function returns nonzero if c is any of:
BEL BS CR FF HT NL VT
or any other implementation-defined control character.
isdigit
int isdigit(int c);
The function returns nonzero if c is any of:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
isgraph
int isgraph(int c);
The function returns nonzero if c
is any character for which either
isalnum or
ispunct returns nonzero.
islower
int islower(int c);
The function returns nonzero if c is any of:
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
or any other locale-specific lowercase character.
isprint
int isprint(int c);
The function returns nonzero if c is
space or a character for which
isgraph returns nonzero.
ispunct
int ispunct(int c);
The function returns nonzero if c is any of:
! " # % & ' ( ) ; <
= > ? [ \ ] * + , -
. / : ^ _ { | } ~
or any other implementation-defined punctuation character.
isspace
int isspace(int c);
The function returns nonzero if c is any of:
CR FF HT NL VT space
or any other locale-specific space character.
isupper
int isupper(int c);
The function returns nonzero if c is any of:
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
or any other locale-specific uppercase character.
isxdigit
int isxdigit(int c);
The function returns nonzero if c is any of:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f A B C D E F
tolower
int tolower(int c);
The function returns the corresponding lowercase letter if one
exists and if
isupper(c);
otherwise, it returns c.
toupper
int toupper(int c);
The function returns the corresponding uppercase letter if one
exists and if
islower(c);
otherwise, it returns c.
See also the Table of Contents and the Index.
Copyright © 1989-1996 by P.J. Plauger and Jim Brodie. All rights reserved.