|
PLearn 0.1
|
|
PLearn 0.1
|
Enables embedded Python code to be called from PLearn/C++ code. More...
#include <PythonCodeSnippet.h>


Public Types | |
| typedef boost::function < PythonObjectWrapper(const TVec< PythonObjectWrapper > &args)> | StandaloneFunction |
| Typedef for an external C function that can be injected into the Python environment. | |
Public Member Functions | |
| PythonCodeSnippet (const string &code="", bool remap_python_exceptions=false) | |
| Default constructor. | |
| PythonCodeSnippet (const PythonObjectWrapper &instance, bool remap_python_exceptions=false) | |
| PythonObjectWrapper | getGlobalObject (const string &object_name) const |
| Default copy ctor, assignment op, dtor. | |
| void | setGlobalObject (const string &object_name, const PythonObjectWrapper &pow) |
| Set an object into the global environment. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | setGlobalObject (const string &object_name, const T &o) |
| bool | isInvokable (const char *function_name) const |
| Checks whether the specified function name is callable. | |
| PythonObjectWrapper | invoke (const char *function_name) const |
| Call the specified function taking 0 arguments. | |
| PythonObjectWrapper | invoke (const char *function_name, const TVec< PythonObjectWrapper > &args) const |
| Call the specified function taking n arguments. | |
| template<class T > | |
| PythonObjectWrapper | invoke (const char *function_name, const T &arg1) const |
| Call the specified function with 1 argument. | |
| template<class T , class U > | |
| PythonObjectWrapper | invoke (const char *function_name, const T &arg1, const U &arg2) const |
| Call the specified function with 2 arguments. | |
| template<class T , class U , class V > | |
| PythonObjectWrapper | invoke (const char *function_name, const T &arg1, const U &arg2, const V &arg3) const |
| Call the specified function with 3 arguments. | |
| template<class T , class U , class V , class W > | |
| PythonObjectWrapper | invoke (const char *function_name, const T &arg1, const U &arg2, const V &arg3, const W &arg4) const |
| Call the specified function with 4 arguments. | |
| template<class T , class U , class V , class W , class X > | |
| PythonObjectWrapper | invoke (const char *function_name, const T &arg1, const U &arg2, const V &arg3, const W &arg4, const X &arg5) const |
| Call the specified function with 5 arguments. | |
| template<class T , class U , class V , class W , class X , class Y > | |
| PythonObjectWrapper | invoke (const char *function_name, const T &arg1, const U &arg2, const V &arg3, const W &arg4, const X &arg5, const Y &arg6) const |
| Call the specified function with 6 arguments. | |
| template<class T , class U , class V , class W , class X , class Y , class Z > | |
| PythonObjectWrapper | invoke (const char *function_name, const T &arg1, const U &arg2, const V &arg3, const W &arg4, const X &arg5, const Y &arg6, const Z &arg7) const |
| Call the specified function with 7 arguments. | |
| void | inject (const char *python_name, StandaloneFunction function_ptr) |
| Inject into the Python code the specified stand-alone function object under the given name. | |
| template<class T > | |
| void | inject (const char *python_name, const T *object, PythonObjectWrapper(T::*)(const TVec< PythonObjectWrapper > &) const) |
| Inject a bound C++ member function into the Python code under the given name (const version). | |
| template<class T > | |
| void | inject (const char *python_name, T *object, PythonObjectWrapper(T::*)(const TVec< PythonObjectWrapper > &)) |
| Inject a bound C++ member function into the Python code under the given name (non-const version). | |
| void | dumpPythonEnvironment () |
| Produces a dump of the Python compiled code object to stderr; for debugging purposes. | |
| virtual string | classname () const |
| virtual OptionList & | getOptionList () const |
| virtual OptionMap & | getOptionMap () const |
| virtual RemoteMethodMap & | getRemoteMethodMap () const |
| virtual PythonCodeSnippet * | deepCopy (CopiesMap &copies) const |
| virtual void | build () |
| Post-constructor. | |
| virtual void | makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy (CopiesMap &copies) |
| Transforms a shallow copy into a deep copy. | |
| virtual void | run () |
| Override this for runnable objects (default method issues a runtime error). | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static string | _classname_ () |
| static OptionList & | _getOptionList_ () |
| static RemoteMethodMap & | _getRemoteMethodMap_ () |
| static Object * | _new_instance_for_typemap_ () |
| static bool | _isa_ (const Object *o) |
| static void | _static_initialize_ () |
| static const PPath & | declaringFile () |
Public Attributes | |
| string | m_code |
| Python statement list that should be compiled at build time to provide the desired functions (defined by the client code to PythonCodeSnippet) and otherwise set up the Python global namespace. | |
| bool | m_remap_python_exceptions |
| If true, Python exceptions raised during function execution are mapped to a C++ exception. | |
| map< string, string > | m_instance_params |
| parameters to the python ctor | |
| PythonObjectWrapper | m_instance |
| the python object instance | |
| PythonObjectWrapper | m_compiled_code |
| Compiled Python code module and global environment. | |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static const char * | InjectSetupSnippet = "__injected__ = {}\n" |
| The snippet prepended to 'code' option for the injections to behave properly. | |
| static const char * | SetCurrentSnippetVar = "_inject_import_.setCurrentSnippet(%p)\n" |
| Used to (un)set CURRENT_SNIPPET in Python. | |
| static const char * | ResetCurrentSnippetVar = "_inject_import_.resetCurrentSnippet()\n" |
| static StaticInitializer | _static_initializer_ |
Protected Member Functions | |
| PythonObjectWrapper | compileGlobalCode (const string &code) |
| Compile a code block into a new environment and return it. | |
| void | setCurrentSnippet (const void *handle) const |
| void | resetCurrentSnippet () const |
| void | handlePythonErrors (const string &extramsg="") const |
| If no Python error, do nothing. | |
| void | injectInternal (const char *python_name, StandaloneFunction *function_ptr) |
| This performs the low-level injection into the compiled Python code. | |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static void | declareOptions (OptionList &ol) |
| Declares this class' options. | |
| static PyObject * | pythonTrampoline (PyObject *self, PyObject *args) |
| This is the trampoline function actually called by Python. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| void * | m_handle |
| The Python handle for *this* instance. | |
| PObjectPool< StandaloneFunction > | m_injected_functions |
| Functions to be injected into the compiled Python code. | |
| PObjectPool< PyMethodDef > | m_python_methods |
| Injected Python method definitions. | |
Private Types | |
| typedef Object | inherited |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | build_ () |
| This does the actual building. | |
Enables embedded Python code to be called from PLearn/C++ code.
This class enables an embedded Python code snippet to be compiled and called back later. It is not designed to be used by itself, but rather in conjunction with specific PLearn objects that understand the PythonCodeSnippet calling protocol.
Note that global variables can be used, in the Python code, to keep a "living state", used to carry information across calls to Python functions.
A note on exception behavior within the PythonCodeSnippet:
The current implementation of the PythonCodeSnippet is designed to be thread-safe, i.e. the Python Global Interpreter Lock is always acquired before sensitive operations are carried out.
Definition at line 110 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
typedef Object PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::inherited [private] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Reimplemented in PLearn::TestSnippet.
Definition at line 112 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
| typedef boost::function<PythonObjectWrapper ( const TVec<PythonObjectWrapper>& args)> PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::StandaloneFunction |
Typedef for an external C function that can be injected into the Python environment.
Definition at line 120 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
| PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::PythonCodeSnippet | ( | const string & | code = "", |
| bool | remap_python_exceptions = false |
||
| ) |
Default constructor.
Note that "build" IS NOT CALLED from the constructor and must be called manually after all external functions have been injected (if necessary).
Definition at line 110 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
: inherited(), m_code(code), m_remap_python_exceptions(remap_python_exceptions), m_instance_params(), m_instance(), m_handle(this), m_compiled_code(), m_injected_functions(4), m_python_methods(4) { // NOTE: build() not called }
| PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::PythonCodeSnippet | ( | const PythonObjectWrapper & | instance, |
| bool | remap_python_exceptions = false |
||
| ) |
Definition at line 126 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::getPyObject(), m_compiled_code, m_instance, and PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::transfer_ownership.
: inherited(), m_code(""), m_remap_python_exceptions(remap_python_exceptions), m_instance_params(), m_instance(instance), m_handle(this), m_compiled_code(), m_injected_functions(4), m_python_methods(4) { PyObject* compiled_code= PyObject_GetAttrString(m_instance.getPyObject(), const_cast<char*>("__dict__")); m_compiled_code= PythonObjectWrapper(compiled_code, PythonObjectWrapper::transfer_ownership); // NOTE: build() not called }

| string PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::_classname_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 107 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
| OptionList & PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::_getOptionList_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 107 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::_getRemoteMethodMap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 107 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 107 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
| Object * PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::_new_instance_for_typemap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 107 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
| StaticInitializer PythonCodeSnippet::_static_initializer_ & PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::_static_initialize_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 107 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::build | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Post-constructor.
The normal implementation should call simply inherited::build(), then this class's build_(). This method should be callable again at later times, after modifying some option fields to change the "architecture" of the object.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Reimplemented in PLearn::TestSnippet.
Definition at line 209 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLearn::Object::build(), and build_().
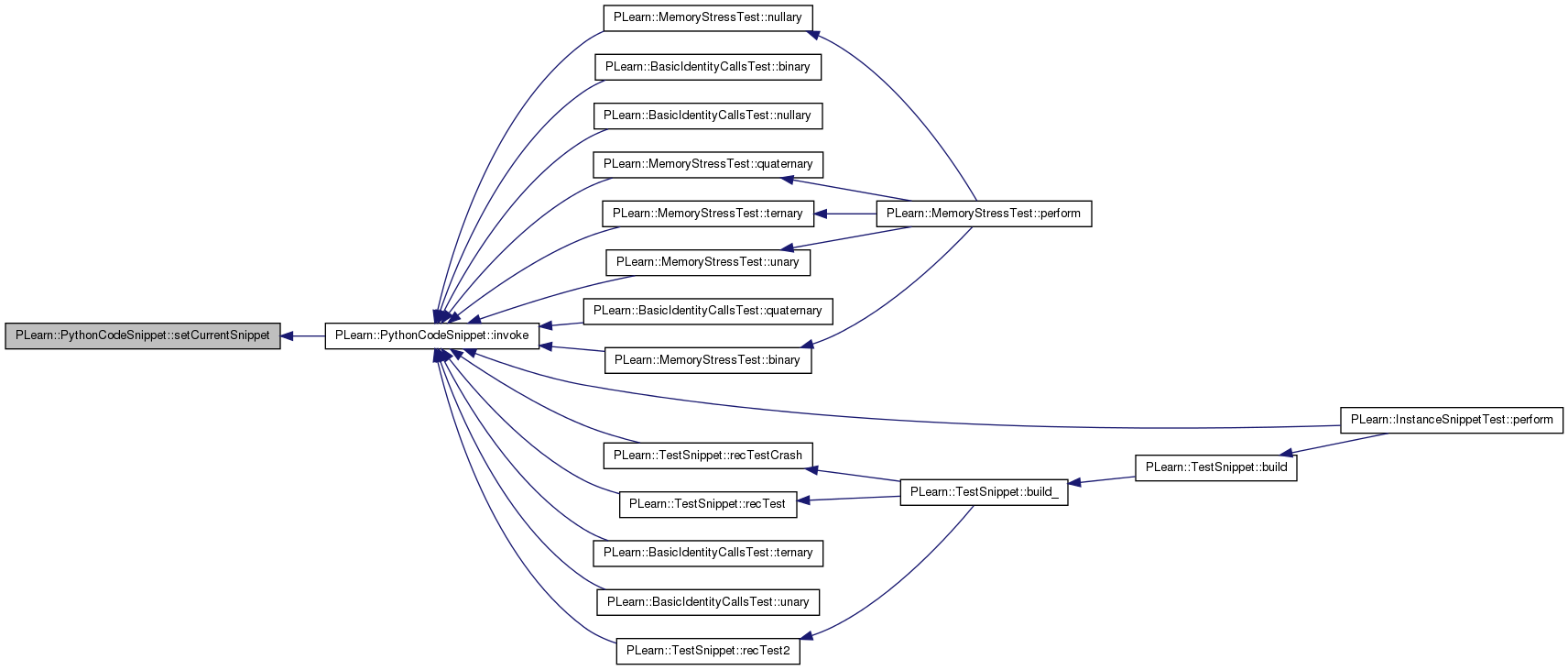
Referenced by PLearn::TestSnippet::build(), and PLearn::InstanceSnippetTest::perform().
{
inherited::build();
build_();
}


| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::build_ | ( | ) | [private] |
This does the actual building.
This is where the Python code is in fact compiled
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Reimplemented in PLearn::TestSnippet.
Definition at line 176 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References compileGlobalCode(), PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::initializePython(), InjectSetupSnippet, PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::isNull(), m_code, m_compiled_code, m_handle, m_injected_functions, m_instance, m_python_methods, PLearn::PMemPool::purge_memory(), resetCurrentSnippet(), and SetCurrentSnippetVar.
Referenced by build().
{
static PythonEmbedder python;
static bool numarray_initialized = false;
if (! numarray_initialized) {
// must be in each translation unit that makes use of libnumarray;
// weird stuff related to table of function pointers that's being
// initialized into a STATIC VARIABLE of the translation unit!
import_libnumarray();
numarray_initialized = true;
PythonObjectWrapper::initializePython();
}
// Compile code into global environment
if (m_code != ""){
// Here we don't call setCurrentSnippet() because it has to be called
// between the setup and the m_code... Still have to call
// resetCurrentSnippet() afterwards though.
char set_current_snippet[100];
sprintf(set_current_snippet, SetCurrentSnippetVar, m_handle);
m_compiled_code = compileGlobalCode(InjectSetupSnippet+
string(set_current_snippet)+m_code);
if(m_instance.isNull())
resetCurrentSnippet();
}
// Forget about injected functions
m_injected_functions.purge_memory();
m_python_methods.purge_memory();
}
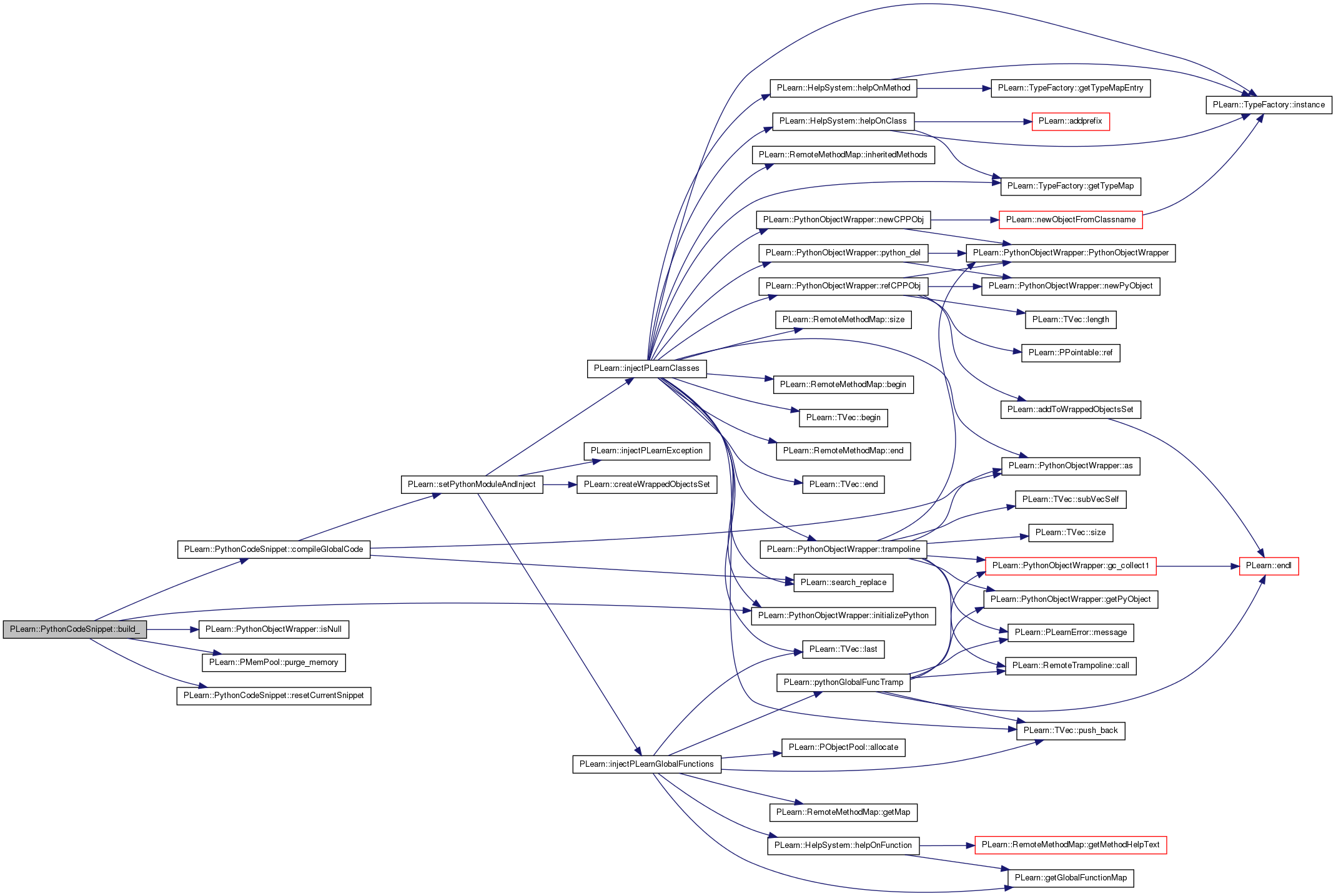

| string PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::classname | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 107 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
| PythonObjectWrapper PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::compileGlobalCode | ( | const string & | code | ) | [protected] |
Compile a code block into a new environment and return it.
Call PLERROR if the code contains an error.
Definition at line 544 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::as(), PLERROR, PLearn::search_replace(), and PLearn::setPythonModuleAndInject().
Referenced by build_(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
{
PythonGlobalInterpreterLock gil; // For thread-safety
PyObject* globals = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(globals, "__builtins__", PyEval_GetBuiltins());
//always include EmbeddedCodeSnippet to check for an object to instantiate
string extracode= "\nfrom plearn.pybridge.embedded_code_snippet "
"import EmbeddedCodeSnippet\n"
"from plearn.pybridge import pl_global_funcs\n";
if (code != "") {
#ifdef WIN32
// Under Windows, it appears the Python code will not execute with
// Windows carriage returns. Thus we first make a copy of the code and
// replace any carriage return by a Unix one.
string code_copy = code;
PLearn::search_replace(code_copy, "\r\n", "\n");
#else
const string& code_copy = code;
#endif
PyObject* res= PyRun_String((code_copy+extracode).c_str(),
Py_file_input /* exec code block */,
globals, globals);
Py_XDECREF(res);
if (PyErr_Occurred()) {
Py_XDECREF(globals);
PyErr_Print();
PLERROR("in PythonCodeSnippet::compileGlobalCode : error compiling "
"Python code contained in the 'code' option.");
}
}
//get the global env. as an stl map
PythonObjectWrapper wrapped_globals(globals);
Py_XDECREF(globals);
map<string, PyObject*> global_map=
wrapped_globals.as<map<string, PyObject*> >();
//inject global funcs, if not already done
static bool global_funcs_injected= false;
if(!global_funcs_injected)
{
map<string, PyObject*>::iterator it=
global_map.find("pl_global_funcs");
if(it == global_map.end())
PLERROR("in PythonCodeSnippet::compileGlobalCode : "
"plearn.pybridge.pl_global_funcs not present in global env!");
setPythonModuleAndInject(it->second);
global_funcs_injected= true;
}
//try to find an EmbeddedCodeSnippet to instantiate
PyObject* snippet_found= 0;
map<string, PyObject*>::iterator it_id=
global_map.find("pl_embedded_code_snippet_type");
if(it_id != global_map.end())
snippet_found= it_id->second;
else //check for a single class deriving from EmbeddedCodeSnippet
{
list<pair<string, PyObject*> > classes_found;
//iter (find)
PyTypeObject* embedded_code_snippet_type=
(PyTypeObject*)global_map["EmbeddedCodeSnippet"];
//find all classes deriving from EmbeddedCodeSnippet
for(map<string, PyObject*>::iterator it= global_map.begin();
it != global_map.end(); ++it)
{
if(PyType_Check(it->second)
&& 0 != PyObject_Compare(it->second,
(PyObject*)embedded_code_snippet_type)
&& PyType_IsSubtype((PyTypeObject*)it->second,
embedded_code_snippet_type))
{
classes_found.push_back(*it);
}
}
int nclasses= classes_found.size();
list<pair<string, PyObject*> >::iterator jt= classes_found.begin();
if(nclasses > 1)
{
string classes_list= jt->first;
for(++jt; jt != classes_found.end(); ++jt)
classes_list+= string(", ") + jt->first;
PLERROR("in PythonCodeSnippet::compileGlobalCode : "
"more than one class derives from EmbeddedCodeSnippet "
"and pl_embedded_code_snippet_type is not defined. "
"classes= [%s]",
classes_list.c_str());
}
if(nclasses == 1)
snippet_found= jt->second;
}
if(snippet_found)
{//instantiate object of appropriate type
PyObject* pyparams= PyDict_New();
if(!pyparams)
handlePythonErrors();
for(map<string, string>::const_iterator it= m_instance_params.begin();
it != m_instance_params.end(); ++it)
{// fill kwargs
PyObject* val= PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str());
PyDict_SetItemString(pyparams, it->first.c_str(), val);
Py_DECREF(val);
}
if(!PyCallable_Check(snippet_found))
PLERROR("in PythonCodeSnippet::compileGlobalCode : "
"found something that is not callable [not a class?]");
PyObject* pargs= PyTuple_New(0);
PyObject* the_obj= PyObject_Call(snippet_found, pargs, pyparams);
Py_DECREF(pyparams);
Py_DECREF(pargs);
if(!the_obj)
{
if (PyErr_Occurred())
PyErr_Print();
PLERROR("in PythonCodeSnippet::compileGlobalCode : "
"found subclass of EmbeddedCodeSnippet, but can't "
"call constructor with given params. "
"class='%s', params=%s",
((PyTypeObject*)snippet_found)->tp_name,
tostring(m_instance_params).c_str());
}
m_instance= PythonObjectWrapper(the_obj);
}
return wrapped_globals;
}


| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::declareOptions | ( | OptionList & | ol | ) | [static, protected] |
Declares this class' options.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 144 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLearn::OptionBase::buildoption, PLearn::declareOption(), PLearn::Object::declareOptions(), m_code, m_instance_params, and m_remap_python_exceptions.
{
declareOption(
ol, "code", &PythonCodeSnippet::m_code,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Python statement list that should be compiled at build time to provide\n"
"the desired functions (defined by the client code to PythonCodeSnippet)\n"
"and otherwise set up the Python global namespace. Note that the Python\n"
"'__builtins__' module is always injected into the global namespace.\n"
"You should also add the statement\n"
"\n"
" from numarray import *'\n"
"\n"
"to manipulate PLearn Vec and Mat.\n");
declareOption(
ol, "remap_python_exceptions", &PythonCodeSnippet::m_remap_python_exceptions,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"If true, Python exceptions raised during function execution are mapped\n"
"to a C++ exception. If false, then a normal Python stack dump is\n"
"output to stderr and a PLERROR is raised. Default=false.");
declareOption(
ol, "instance_params", &PythonCodeSnippet::m_instance_params,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"If this snippet represents a python object, these are the\n"
"parameters passed to the object's constructor.");
// Now call the parent class' declareOptions
inherited::declareOptions(ol);
}

| static const PPath& PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::declaringFile | ( | ) | [inline, static] |
| PythonCodeSnippet * PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::deepCopy | ( | CopiesMap & | copies | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 107 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::dumpPythonEnvironment | ( | ) |
Produces a dump of the Python compiled code object to stderr; for debugging purposes.
Definition at line 800 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
{
PyObject_Print(m_compiled_code.getPyObject(), stderr, 0);
}
| PythonObjectWrapper PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::getGlobalObject | ( | const string & | object_name | ) | const |
Default copy ctor, assignment op, dtor.
Return an object from the global environment. Return None if the object cannot be found.
Definition at line 232 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::getPyObject(), PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::isNull(), m_compiled_code, and m_instance.
Referenced by injectInternal().
{
PythonGlobalInterpreterLock gil; // For thread-safety
PyObject* pyobj;
if(!m_instance.isNull())
pyobj= PyObject_GetAttrString(m_instance.getPyObject(),
const_cast<char*>(object_name.c_str()));
else
pyobj= PyDict_GetItemString(m_compiled_code.getPyObject(),
object_name.c_str());
if (pyobj) {
// pyobj == borrowed reference
// Increment refcount to keep long-lived reference
Py_XINCREF(pyobj);
return PythonObjectWrapper(pyobj);
}
return PythonObjectWrapper(); // None
}


| OptionList & PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::getOptionList | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 107 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
| OptionMap & PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::getOptionMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 107 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::getRemoteMethodMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 107 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::handlePythonErrors | ( | const string & | extramsg = "" | ) | const [protected] |
If no Python error, do nothing.
If an error occurred, convert the Python Exception into a C++ exception if required, or otherwise print a traceback and abort
Definition at line 735 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLERROR.
Referenced by invoke().
{
PythonGlobalInterpreterLock gil; // For thread-safety
if (PyErr_Occurred()) {
if (m_remap_python_exceptions) {
// format using cgitb, throw as PythonError (PLearnError)
PyObject *exception, *v, *traceback;
PyErr_Fetch(&exception, &v, &traceback);
PyErr_NormalizeException(&exception, &v, &traceback);
if(!traceback)
{
//perr << "$$$$ before print" << endl;
PyErr_Print();
//perr << "$$$$ after print" << endl;
throw PythonException(string("PythonCodeSnippet: encountered Python "
"exception but there is no traceback.\n")
+ extramsg);
}
PyObject* tbstr=
PyString_FromString("plearn.utilities.pltraceback");
PyObject* tbmod= PyImport_Import(tbstr);
Py_XDECREF(tbstr);
if(!tbmod)
throw PythonException("PythonCodeSnippet::handlePythonErrors :"
" Unable to import cgitb module.");
PyObject* tbdict= PyModule_GetDict(tbmod);
Py_XDECREF(tbmod);
PyObject* formatFunc= PyDict_GetItemString(tbdict, "text");
if(!formatFunc)
throw PythonException("PythonCodeSnippet::handlePythonErrors :"
" Can't find cgitb.text");
PyObject* args= Py_BuildValue(const_cast<char*>("((OOO))"),
exception, v, traceback);
if(!args)
throw PythonException("PythonCodeSnippet::handlePythonErrors :"
" Can't build args for cgitb.text");
PyObject* pystr= PyObject_CallObject(formatFunc, args);
Py_XDECREF(args);
if(!pystr)
throw PythonException("PythonCodeSnippet::handlePythonErrors :"
" call to cgitb.text failed");
string str= PyString_AsString(pystr);
Py_XDECREF(pystr);
PyErr_Clear();
Py_XDECREF(exception);
Py_XDECREF(v);
Py_XDECREF(traceback);
throw PythonException(str+extramsg);
}
else {
PyErr_Print();
PyErr_Clear();
PLERROR("PythonCodeSnippet: encountered Python exception.\n%s",
extramsg.c_str());
}
}
}

| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::inject | ( | const char * | python_name, |
| T * | object, | ||
| PythonObjectWrapper(T::*)(const TVec< PythonObjectWrapper > &) | member_function | ||
| ) |
Inject a bound C++ member function into the Python code under the given name (non-const version).
Definition at line 500 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
{
StandaloneFunction func = boost::bind(member_function, object, _1);
inject(python_name, func);
}
| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::inject | ( | const char * | python_name, |
| StandaloneFunction | function_ptr | ||
| ) |
Inject into the Python code the specified stand-alone function object under the given name.
Note that the function must take accept a TVec of PythonObjectWrapper (the arguments) and return a PythonObjectWrapper. The return value needs to have controlled ownership (the default). You can use the Boost bind library in order to transform a class member function into such a stand-alone function. Note that the PythonCodeSnippet must have been compiled (with build) BEFORE injecting the desired functions. A typical idiom would be :
PP<PythonCodeSnippet> python = new PythonCodeSnippet(my_code); python->build(); python->inject("func1", my_func1); python->inject("func2", my_func2); // ...
Note that a new call to build() would have the effect of "forgetting" the injections, so they have to be carried out again.
Definition at line 533 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLearn::PObjectPool< T >::allocate(), injectInternal(), and m_injected_functions.
Referenced by PLearn::TestSnippet::build_().
{
StandaloneFunction* pfunc = m_injected_functions.allocate();
new(pfunc) StandaloneFunction(function_ptr); // In-place copy constructor
injectInternal(python_name, pfunc);
}
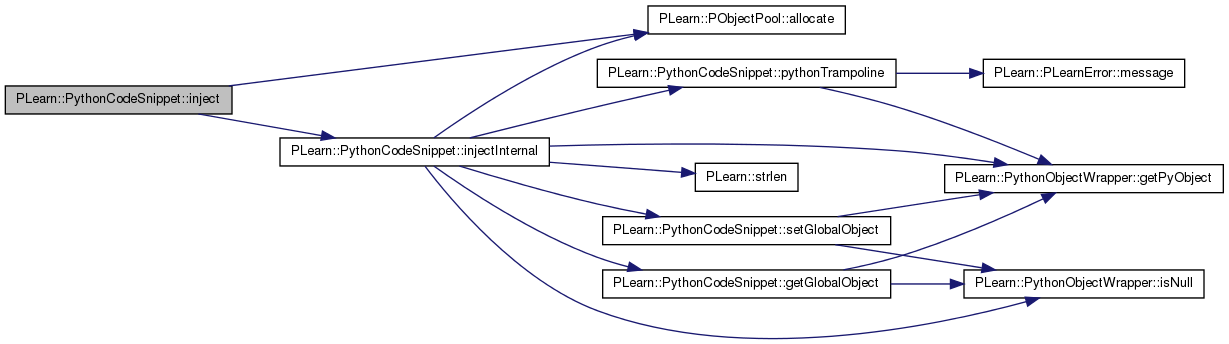

| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::inject | ( | const char * | python_name, |
| const T * | object, | ||
| PythonObjectWrapper(T::*)(const TVec< PythonObjectWrapper > &) const | member_function | ||
| ) |
Inject a bound C++ member function into the Python code under the given name (const version).
Definition at line 491 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
{
StandaloneFunction func = boost::bind(member_function, object, _1);
inject(python_name, func);
}
| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::injectInternal | ( | const char * | python_name, |
| StandaloneFunction * | function_ptr | ||
| ) | [protected] |
This performs the low-level injection into the compiled Python code.
Note that the pointer to StandaloneFunction must remain valid for the entire duration of the compiled code validity.
Definition at line 485 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLearn::PObjectPool< T >::allocate(), getGlobalObject(), PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::getPyObject(), PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::isNull(), m_instance, m_python_methods, PLERROR, pythonTrampoline(), setGlobalObject(), and PLearn::strlen().
Referenced by inject().
{
PythonGlobalInterpreterLock gil; // For thread-safety
// Wrap the function_ptr into a PyCObject
PyObject* self = PyCObject_FromVoidPtr(function_ptr, NULL);
// Create a Python Function Object
PyMethodDef* py_method = m_python_methods.allocate();
py_method->ml_name = const_cast<char*>(python_name);
py_method->ml_meth = pythonTrampoline;
py_method->ml_flags = METH_VARARGS;
py_method->ml_doc = const_cast<char*>("injected-function-from-PythonCodeSnippet");
PyObject* py_funcobj = PyCFunction_NewEx(py_method,
self /* info for trampoline */,
NULL /* module */);
if (py_funcobj) {
// Inject into the running snippet. Note that when a
// PythonObjectWrapper is constructed from a PyObject, it steals the
// refcount, so we don't need to perform a Py_XDECREF on py_funcobj.
this->setGlobalObject(python_name, py_funcobj);
if(!m_instance.isNull())
{
char* fn= new char[strlen(python_name)+1];
strcpy(fn, python_name);
PyObject_SetAttrString(m_instance.getPyObject(),
fn, py_funcobj);
delete[] fn;
}
else
{
// Publish the injection in the '__injected__' dictionary for imported modules
PythonObjectWrapper inj_dict = this->getGlobalObject("__injected__");
PyDict_SetItemString(inj_dict.getPyObject(), python_name, py_funcobj);
Py_XDECREF(self);
}
}
else
PLERROR("PythonCodeSnippet::injectInternal: failed to inject "
"Python function '%s'", python_name);
}


| PythonObjectWrapper PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::invoke | ( | const char * | function_name | ) | const |
Call the specified function taking 0 arguments.
Definition at line 307 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::getPyObject(), handlePythonErrors(), PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::isNull(), m_compiled_code, m_handle, m_instance, PLERROR, resetCurrentSnippet(), setCurrentSnippet(), and PLearn::strlen().
Referenced by PLearn::MemoryStressTest::binary(), PLearn::BasicIdentityCallsTest::binary(), PLearn::BasicIdentityCallsTest::nullary(), PLearn::MemoryStressTest::nullary(), PLearn::InstanceSnippetTest::perform(), PLearn::MemoryStressTest::quaternary(), PLearn::BasicIdentityCallsTest::quaternary(), PLearn::TestSnippet::recTest(), PLearn::TestSnippet::recTest2(), PLearn::TestSnippet::recTestCrash(), PLearn::MemoryStressTest::ternary(), PLearn::BasicIdentityCallsTest::ternary(), PLearn::BasicIdentityCallsTest::unary(), and PLearn::MemoryStressTest::unary().
{
PythonGlobalInterpreterLock gil; // For thread-safety
PyObject* pFunc= 0;
bool instance_method= false;
if(!m_instance.isNull())
{
char* fn= new char[strlen(function_name)+1];
strcpy(fn, function_name);
if(PyObject_HasAttrString(m_instance.getPyObject(), fn))
pFunc= PyObject_GetAttrString(m_instance.getPyObject(), fn);
delete[] fn;
}
if(pFunc)
instance_method= true;
else
pFunc= PyDict_GetItemString(m_compiled_code.getPyObject(),
function_name);
// pFunc: Borrowed reference if not instance_method
PyObject* return_value = 0;
if (pFunc && PyCallable_Check(pFunc)) {
if(!instance_method)
setCurrentSnippet(m_handle);
return_value = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, NULL);
if (! return_value)
{
if(instance_method){
Py_DECREF(pFunc);
}
handlePythonErrors(string("Error while calling function '")
+ function_name
+ "' with no params.");
}
if(!instance_method)
resetCurrentSnippet();
}
else
{
if(instance_method) {Py_DECREF(pFunc);}
PLERROR("PythonCodeSnippet::invoke: cannot call function '%s' (not callable).",
function_name);
}
if(instance_method) {Py_DECREF(pFunc);}
//return PythonObjectWrapper(return_value);
PythonObjectWrapper r(return_value);
Py_DECREF(return_value);
return r;
}
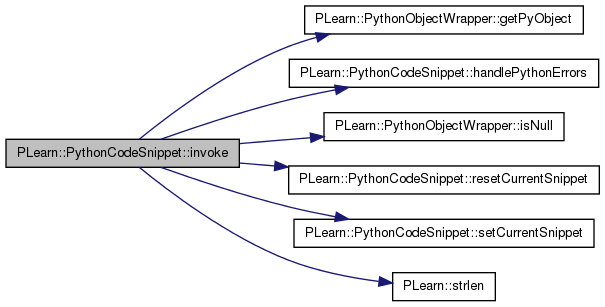

| PythonObjectWrapper PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::invoke | ( | const char * | function_name, |
| const T & | arg1, | ||
| const U & | arg2, | ||
| const V & | arg3, | ||
| const W & | arg4, | ||
| const X & | arg5 | ||
| ) | const |
Call the specified function with 5 arguments.
Definition at line 428 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
{
TVec<PythonObjectWrapper> args(5);
args[0]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg1);
args[1]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg2);
args[2]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg3);
args[3]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg4);
args[4]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg5);
return invoke(function_name, args);
}
| PythonObjectWrapper PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::invoke | ( | const char * | function_name, |
| const T & | arg1, | ||
| const U & | arg2 | ||
| ) | const |
Call the specified function with 2 arguments.
Definition at line 384 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
{
TVec<PythonObjectWrapper> args(2);
args[0]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg1);
args[1]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg2);
return invoke(function_name, args);
}
| PythonObjectWrapper PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::invoke | ( | const char * | function_name, |
| const T & | arg1, | ||
| const U & | arg2, | ||
| const V & | arg3 | ||
| ) | const |
Call the specified function with 3 arguments.
Definition at line 397 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
{
TVec<PythonObjectWrapper> args(3);
args[0]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg1);
args[1]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg2);
args[2]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg3);
return invoke(function_name, args);
}
| PythonObjectWrapper PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::invoke | ( | const char * | function_name, |
| const T & | arg1 | ||
| ) | const |
Call the specified function with 1 argument.
Definition at line 373 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
{
TVec<PythonObjectWrapper> args(1);
args[0]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg1);
return invoke(function_name, args);
}
| PythonObjectWrapper PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::invoke | ( | const char * | function_name, |
| const T & | arg1, | ||
| const U & | arg2, | ||
| const V & | arg3, | ||
| const W & | arg4, | ||
| const X & | arg5, | ||
| const Y & | arg6, | ||
| const Z & | arg7 | ||
| ) | const |
Call the specified function with 7 arguments.
Definition at line 467 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
{
TVec<PythonObjectWrapper> args(7);
args[0]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg1);
args[1]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg2);
args[2]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg3);
args[3]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg4);
args[4]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg5);
args[5]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg6);
args[6]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg7);
return invoke(function_name, args);
}
| PythonObjectWrapper PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::invoke | ( | const char * | function_name, |
| const T & | arg1, | ||
| const U & | arg2, | ||
| const V & | arg3, | ||
| const W & | arg4, | ||
| const X & | arg5, | ||
| const Y & | arg6 | ||
| ) | const |
Call the specified function with 6 arguments.
Definition at line 446 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
{
TVec<PythonObjectWrapper> args(6);
args[0]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg1);
args[1]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg2);
args[2]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg3);
args[3]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg4);
args[4]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg5);
args[5]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg6);
return invoke(function_name, args);
}
| PythonObjectWrapper PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::invoke | ( | const char * | function_name, |
| const TVec< PythonObjectWrapper > & | args | ||
| ) | const |
Call the specified function taking n arguments.
NOTE: the PythonObjectWrapper passed as arguments MUST be created with the 'transfer_ownership' option.
Definition at line 365 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::getPyObject(), handlePythonErrors(), i, PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::isNull(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), m_compiled_code, m_handle, m_instance, n, PLERROR, resetCurrentSnippet(), setCurrentSnippet(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::strlen(), and PLearn::tostring().
{
PythonGlobalInterpreterLock gil; // For thread-safety
PyObject* pFunc= 0;
bool instance_method= false;
if(!m_instance.isNull())
{
char* fn= new char[strlen(function_name)+1];
strcpy(fn, function_name);
if(PyObject_HasAttrString(m_instance.getPyObject(), fn))
pFunc= PyObject_GetAttrString(m_instance.getPyObject(), fn);
delete[] fn;
}
if(pFunc)
instance_method= true;
else
pFunc= PyDict_GetItemString(m_compiled_code.getPyObject(),
function_name);
// pFunc: Borrowed reference if not instance_method
PyObject* return_value = 0;
if (pFunc && PyCallable_Check(pFunc)) {
if(!instance_method)
setCurrentSnippet(m_handle);
// Create argument tuple. Warning: PyTuple_SetItem STEALS references.
PyObject* pArgs = PyTuple_New(args.size());
for (int i=0, n=args.size() ; i<n ; ++i)
{
PyTuple_SetItem(pArgs, i, args[i].getPyObject());
Py_INCREF(args[i].getPyObject());
}
return_value = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, pArgs);
Py_DECREF(pArgs);
if (! return_value)
{
if(instance_method)
{Py_DECREF(pFunc);}
handlePythonErrors(string("Error while calling function '")
+ function_name
+ "' with "
+ tostring(args.length())
+ " params.");
}
if(!instance_method)
resetCurrentSnippet();
}
else
{
if(instance_method)
{Py_DECREF(pFunc);}
PLERROR("PythonCodeSnippet::invoke: cannot call function '%s'",
function_name);
}
if(instance_method)
{Py_DECREF(pFunc);}
//return PythonObjectWrapper(return_value);
PythonObjectWrapper r(return_value);
Py_DECREF(return_value);
return r;
}

| PythonObjectWrapper PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::invoke | ( | const char * | function_name, |
| const T & | arg1, | ||
| const U & | arg2, | ||
| const V & | arg3, | ||
| const W & | arg4 | ||
| ) | const |
Call the specified function with 4 arguments.
Definition at line 412 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
{
TVec<PythonObjectWrapper> args(4);
args[0]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg1);
args[1]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg2);
args[2]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg3);
args[3]= PythonObjectWrapper(arg4);
return invoke(function_name, args);
}
| bool PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::isInvokable | ( | const char * | function_name | ) | const |
Checks whether the specified function name is callable.
Definition at line 279 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::getPyObject(), PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::isNull(), m_compiled_code, m_instance, and PLearn::strlen().
Referenced by PLearn::BasicIdentityCallsTest::nullary().
{
PythonGlobalInterpreterLock gil; // For thread-safety
PyObject* pFunc= 0;
bool instance_method= false;
if(!m_instance.isNull())
{
char* fn= new char[strlen(function_name)+1];
strcpy(fn, function_name);
if(PyObject_HasAttrString(m_instance.getPyObject(), fn))
pFunc= PyObject_GetAttrString(m_instance.getPyObject(), fn);
delete[] fn;
}
if(pFunc)
instance_method= true;
else
pFunc= PyDict_GetItemString(m_compiled_code.getPyObject(),
function_name);
// pFunc: Borrowed reference if not instance_method
bool ret= pFunc && PyCallable_Check(pFunc);
if(instance_method) {Py_DECREF(pFunc);}
return ret;
}


| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy | ( | CopiesMap & | copies | ) | [virtual] |
Transforms a shallow copy into a deep copy.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 215 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References compileGlobalCode(), m_code, m_compiled_code, m_injected_functions, m_python_methods, PLearn::Object::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), and PLearn::PMemPool::purge_memory().
{
inherited::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(copies);
// Compile fresh code into global environment
m_compiled_code = compileGlobalCode(m_code);
// Forget about injected functions (not necessarily the correct thing to do...)
m_injected_functions.purge_memory();
m_python_methods.purge_memory();
}

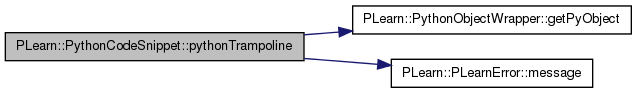
| PyObject * PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::pythonTrampoline | ( | PyObject * | self, |
| PyObject * | args | ||
| ) | [static, protected] |
This is the trampoline function actually called by Python.
Definition at line 438 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::getPyObject(), i, PLearn::PLearnError::message(), and PLERROR.
Referenced by injectInternal().
{
PythonGlobalInterpreterLock gil; // For thread-safety
try {
// Transform the args tuple into a TVec of not-owned PythonObjectWrapper
if (! PyTuple_Check(args))
PLERROR("PythonCodeSnippet.cc:python_trampoline: the Python interpreter "
"did not pass a Tuple as the arguments object.");
int size = PyTuple_GET_SIZE(args);
TVec<PythonObjectWrapper> args_tvec(size);
for (int i=0 ; i<size ; ++i) {
args_tvec[i]=
PythonObjectWrapper(PyTuple_GET_ITEM(args,i));
}
// Now get the void* stored within the PyCObject of self
StandaloneFunction* func =
static_cast<StandaloneFunction*>(PyCObject_AsVoidPtr(self));
PythonObjectWrapper returned_value = (*func)(args_tvec);
PyObject* to_return = returned_value.getPyObject();
Py_XINCREF(to_return);
return to_return;
}
// Catch PLERROR and such
catch (const PLearnError& e) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_Exception,
(string("PLearn Error: ")+e.message()).c_str());
return NULL;
}
// Catch C++ stdlib exceptions
catch (const std::exception& e) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_Exception,
(string("C++ stdlib error: ")+e.what()).c_str());
return NULL;
}
// Catch any other unexpected exceptions
catch (...) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_Exception,
"Caught unknown C++ exception while executing injected function "
"inside a PythonCodeSnippet");
return NULL;
}
}

| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::resetCurrentSnippet | ( | ) | const [protected] |
Definition at line 718 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLERROR.
Referenced by build_(), and invoke().
{
PythonGlobalInterpreterLock gil; // For thread-safety
PyObject* res= PyRun_String(ResetCurrentSnippetVar,
Py_file_input /* exec code block */,
m_compiled_code.getPyObject(),
m_compiled_code.getPyObject());
Py_XDECREF(res);
if (PyErr_Occurred()) {
Py_XDECREF(m_compiled_code.getPyObject());
PyErr_Print();
PLERROR("PythonCodeSnippet::resetCurrentSnippet: error compiling "
"Python code contained in the 'ResetCurrentSnippetVar'.");
}
}

| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::run | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Override this for runnable objects (default method issues a runtime error).
Runnable objects are objects that can be used as *THE* object of a .plearn script. The run() method specifies what they should do when executed.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 681 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLERROR.
{
if(m_instance.isNull())
PLERROR("in PythonCodeSnippet::run : this snippet is not "
"an instance of EmbeddedCodeSnippet");
if(!PyCallable_Check(m_instance.getPyObject()))
PLERROR("in PythonCodeSnippet::run : this instance of "
"EmbeddedCodeSnippet is not callable.");
PyObject* pargs= PyTuple_New(0);
PyObject* res= PyObject_Call(m_instance.getPyObject(), pargs, 0);
Py_DECREF(pargs);
if(!res) handlePythonErrors();
Py_XDECREF(res);
}
| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::setCurrentSnippet | ( | const void * | handle | ) | const [protected] |
Definition at line 697 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLERROR.
Referenced by invoke().
{
PythonGlobalInterpreterLock gil; // For thread-safety
char set_current_snippet[100];
sprintf(set_current_snippet, SetCurrentSnippetVar, handle);
PyObject* res= PyRun_String(set_current_snippet,
Py_file_input /* exec code block */,
m_compiled_code.getPyObject(),
m_compiled_code.getPyObject());
Py_XDECREF(res);
if (PyErr_Occurred()) {
Py_XDECREF(m_compiled_code.getPyObject());
PyErr_Print();
PLERROR("PythonCodeSnippet::setCurrentSnippet: error compiling "
"Python code contained in the 'SetCurrentSnippetVar'."
"\n\t'%s'", set_current_snippet);
}
}
| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::setGlobalObject | ( | const string & | object_name, |
| const PythonObjectWrapper & | pow | ||
| ) |
Set an object into the global environment.
Definition at line 251 of file PythonCodeSnippet.cc.
References PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::getPyObject(), PLearn::PythonObjectWrapper::isNull(), m_compiled_code, m_instance, and PLERROR.
Referenced by injectInternal().
{
PythonGlobalInterpreterLock gil; // For thread-safety
// Note that PyDict_SetItemString increments the reference count for us
int non_success = 0;
if(!m_instance.isNull())
non_success= PyObject_SetAttrString(m_instance.getPyObject(),
const_cast<char*>(object_name.c_str()),
pow.getPyObject());
else if (! pow.isNull())
non_success = PyDict_SetItemString(m_compiled_code.getPyObject(),
object_name.c_str(),
pow.getPyObject());
else
non_success = PyDict_SetItemString(m_compiled_code.getPyObject(),
object_name.c_str(),
Py_None);
if (non_success)
PLERROR("PythonCodeSnippet::setGlobalObject: error inserting a global Python \n"
"object under the name '%s'", object_name.c_str());
}


| void PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::setGlobalObject | ( | const string & | object_name, |
| const T & | o | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 179 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
{
setGlobalObject(object_name, PythonObjectWrapper(o));
}
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 310 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
const char * PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::InjectSetupSnippet = "__injected__ = {}\n" [static] |
The snippet prepended to 'code' option for the injections to behave properly.
Definition at line 123 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
Referenced by build_().
Python statement list that should be compiled at build time to provide the desired functions (defined by the client code to PythonCodeSnippet) and otherwise set up the Python global namespace.
Note that the Python '__builtins__' module is always injected into the global namespace. You should also add the statement
from numarray import *'
to manipulate PLearn Vec and Mat.
Definition at line 141 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
Referenced by build_(), declareOptions(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Compiled Python code module and global environment.
Definition at line 350 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
Referenced by build_(), getGlobalObject(), invoke(), isInvokable(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), PLearn::InstanceSnippetTest::perform(), PythonCodeSnippet(), and setGlobalObject().
void* PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::m_handle [protected] |
The Python handle for *this* instance.
Definition at line 346 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
Functions to be injected into the compiled Python code.
Definition at line 354 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
Referenced by build_(), inject(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
the python object instance
Definition at line 154 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
Referenced by build_(), getGlobalObject(), injectInternal(), invoke(), isInvokable(), PLearn::InstanceSnippetTest::perform(), PythonCodeSnippet(), and setGlobalObject().
| map<string, string> PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::m_instance_params |
parameters to the python ctor
Definition at line 151 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
Referenced by declareOptions().
PObjectPool<PyMethodDef> PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::m_python_methods [protected] |
Injected Python method definitions.
Definition at line 357 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
Referenced by build_(), injectInternal(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
If true, Python exceptions raised during function execution are mapped to a C++ exception.
If false, then a normal Python stack dump is output to stderr and a PLERROR is raised. Default=false
Definition at line 148 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
Referenced by declareOptions().
const char * PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::ResetCurrentSnippetVar = "_inject_import_.resetCurrentSnippet()\n" [static] |
Definition at line 127 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
const char * PLearn::PythonCodeSnippet::SetCurrentSnippetVar = "_inject_import_.setCurrentSnippet(%p)\n" [static] |
Used to (un)set CURRENT_SNIPPET in Python.
Definition at line 126 of file PythonCodeSnippet.h.
Referenced by build_().
 1.7.4
1.7.4