|
PLearn 0.1
|
|
PLearn 0.1
|
#include <StatsCollector.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual string | classname () const |
| virtual OptionList & | getOptionList () const |
| virtual OptionMap & | getOptionMap () const |
| virtual RemoteMethodMap & | getRemoteMethodMap () const |
| virtual StatsCollector * | deepCopy (CopiesMap &copies) const |
| StatsCollector (int the_maxnvalues=0) | |
| real | n () const |
| number of samples seen with update (length of VMat for ex.) | |
| real | nmissing () const |
| real | nnonmissing () const |
| real | sumsquarew () const |
| real | sum () const |
| real | sumsquare () const |
| real | min () const |
| real | max () const |
| real | agemin () const |
| real | agemax () const |
| real | range () const |
| real | mean () const |
| real | variance () const |
| The normalization for variance (nnonmissing_ - sumsquarew_/nnonmissing_) is defined so that the estimator is unbiased. | |
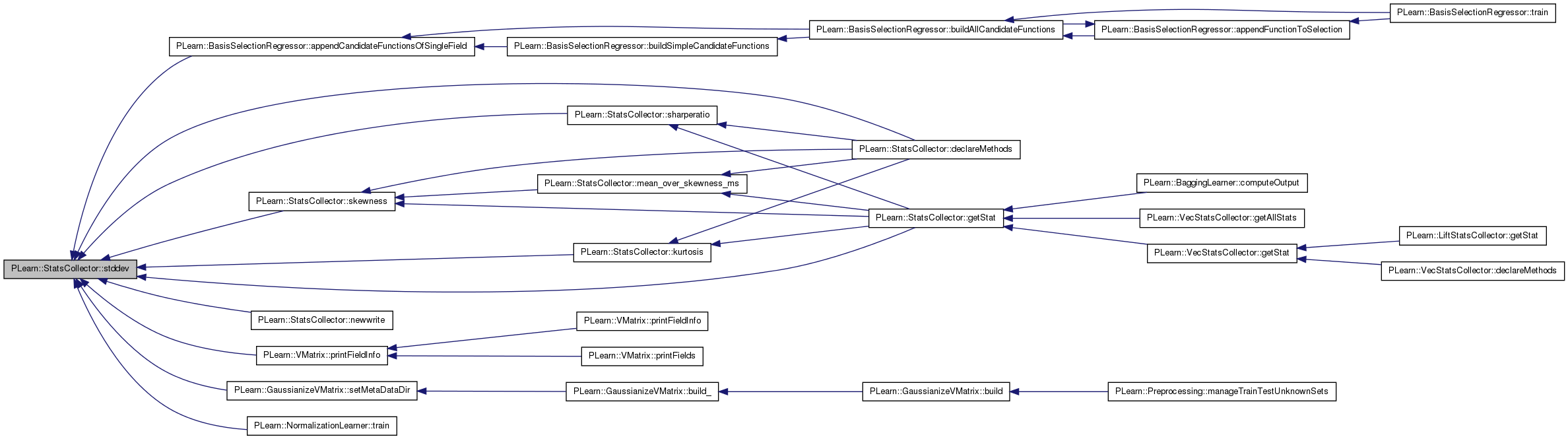
| real | stddev () const |
| real | skewness () const |
| real | kurtosis () const |
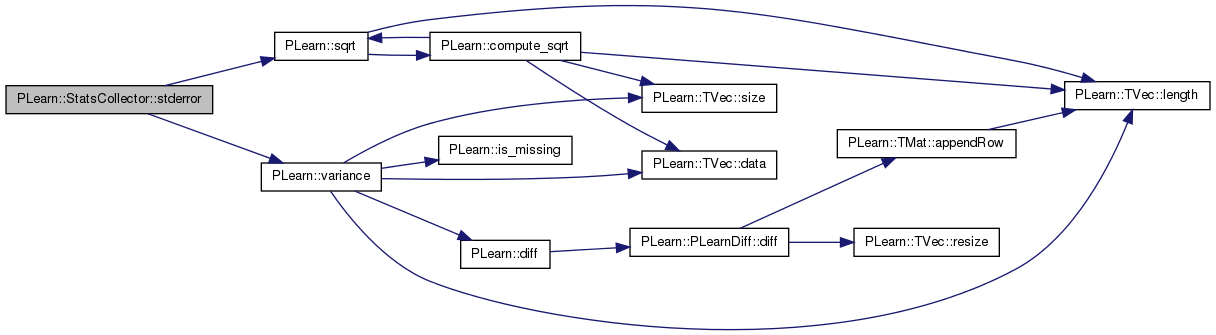
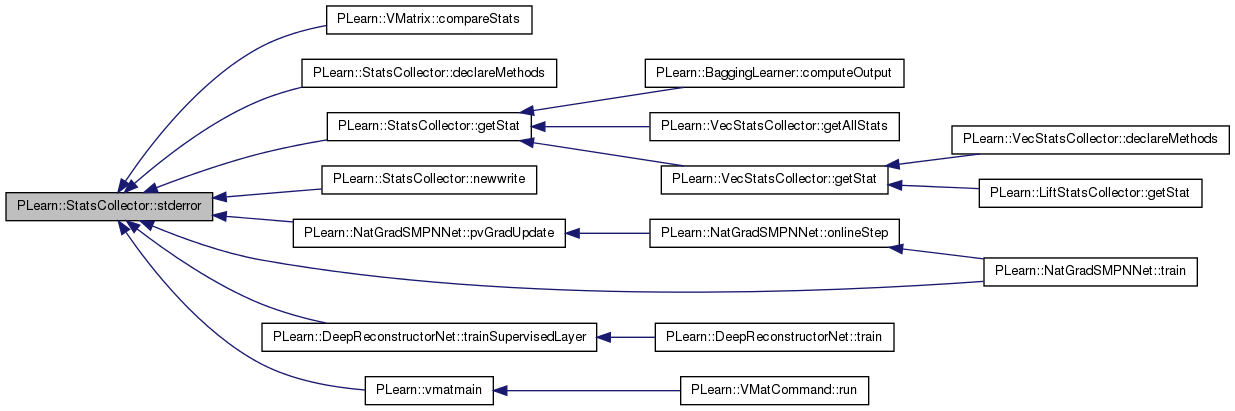
| real | stderror () const |
| real | first_obs () const |
| real | last_obs () const |
| real | sharperatio () const |
| real | mean_over_skewness () const |
| real | mean_over_skewness_ms () const |
| Special version for model selection. | |
| real | mean_over_kurtosis () const |
| real | zstat () const |
| real | zpr1t () const |
| one-tailed P(zstat()) | |
| real | zpr2t () const |
| two-tailed P(zstat()) | |
| real | iqr () const |
| real | prr () const |
| real | lift (int k, int &n_pos_in_k, int n_pos_in_k_minus_1=-1, real pos_fraction=-1) const |
| Return LIFT(k/n). | |
| real | nips_lift () const |
| NIPS_LIFT statistic (see help). | |
| real | mean_lift (real *pos_fraction=NULL) const |
| MEAN_LIFT statistic (see help). | |
| real | prbp () const |
| PRBP statistic (see help). | |
| real | dmode () const |
| discrete distribution mode | |
| Vec | dmodes () const |
| real | getStat (const string &statname) const |
| Compute a given statistic. | |
| virtual void | build () |
| simply calls inherited::build() then build_() | |
| void | forget () |
| clears all statistics, allowing to restart collecting them | |
| void | update (real val, real weight=1.0) |
| update statistics with next value val of sequence | |
| void | remove_observation (real val, real weight=1.0) |
| update statistics as if an observation of value val was removed of the observation sequence. | |
| void | finalize () |
| finishes whatever computation are needed after all updates have been made | |
| map< real, StatsCollectorCounts > * | getCounts () |
| Return the mapping from encountered real values to StatsCollectorCounts. | |
| map< real, StatsCollectorCounts > * | getApproximateCounts () |
| Same as getCounts(), except that the map that is returned has been transformed so that no two keys are equal, where equality is defined as the result of the PLearn function 'is_equal'. | |
| int | getMaxNValues () |
| Mat | cdf (bool normalized=true) const |
| returns a Mat with x,y coordinates for plotting the cdf only if normalized will the cdf go to 1, otherwise it will go to nsamples | |
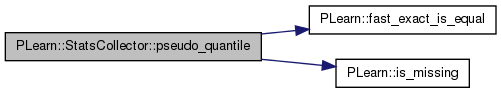
| real | pseudo_quantile (real q) const |
| Return the position of the pseudo-quantile Q. | |
| RealMapping | getBinMapping (double discrete_mincount, double continuous_mincount, real tolerance=.1, TVec< double > *fcount=0) const |
| DEPRECATED: DO NOT SORT IDs -xsm ! fix 'id' attribute of all StatCollectorCounts so that increasing ids correspond to increasing real values ! *** NOT TESTED YET void sortIds();. | |
| RealMapping | getAllValuesMapping (TVec< double > *fcount=0) const |
| RealMapping | getAllValuesMapping (TVec< bool > *to_be_included, TVec< double > *fcount=0, bool ignore_other=false, real tolerance=0) const |
| Same as getAllValuesMapping, except we can specify a bool vector, that indicates whether the k-th range should be included or not. | |
| virtual void | oldwrite (ostream &out) const |
| virtual void | newwrite (PStream &out) const |
| Overridden to have a fancy output for raw_ascii and pretty_ascii modes. | |
| virtual void | merge (const StatsCollector &other) |
| merge another StatsCollector into this one | |
| bool | isbinary () |
| bool | isinteger () |
| Vec | getCount (real value) |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static string | _classname_ () |
| static OptionList & | _getOptionList_ () |
| static RemoteMethodMap & | _getRemoteMethodMap_ () |
| static Object * | _new_instance_for_typemap_ () |
| static bool | _isa_ (const Object *o) |
| static void | _static_initialize_ () |
| static const PPath & | declaringFile () |
Public Attributes | |
| double | epsilon |
| Small regularizing value to be added to the variance (V) estimator (and indirectly, to standard deviation (STDDEV)). | |
| int | maxnvalues |
| Maximum number of different values to keep track of in counts. | |
| bool | no_removal_warnings |
| If the remove_observation mecanism is used and the removed value is equal to one of first_, last_, min_ or max_, the default behavior is to warn the user. | |
| double | nmissing_ |
| (weighted) number of missing values | |
| double | nnonmissing_ |
| (weighted) number of non missing value | |
| double | sumsquarew_ |
| sum of square of all weights | |
| double | sum_ |
| sum of all (values-first_) | |
| double | sumsquare_ |
| sum of square of all (values-first_) | |
| double | sumcube_ |
| sum of cube of all (values-first_) | |
| double | sumfourth_ |
| sum of fourth-power of all (values-first_) | |
| real | min_ |
| the min | |
| real | max_ |
| the max | |
| real | agemin_ |
| how many observations ago the min was observed | |
| real | agemax_ |
| how many observations ago the max was observed | |
| real | first_ |
| first encountered nonmissing observation | |
| real | last_ |
| last encountered nonmissing observation | |
| bool | more_than_maxnvalues |
| int | binary_ |
| true if all seen variable are 0 or 1, -1 in some case | |
| int | integer_ |
| true if all seen variable are integer, -1 in some case | |
| map< real, StatsCollectorCounts > | counts |
| map< int, real > | count_ids |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static StaticInitializer | _static_initializer_ |
Protected Member Functions | |
| void | sort_values_by_magnitude () const |
| Sort values stored in 'counts' by magnitude, so as to fill 'sorted_values'. | |
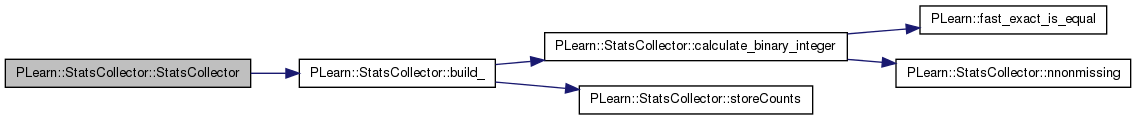
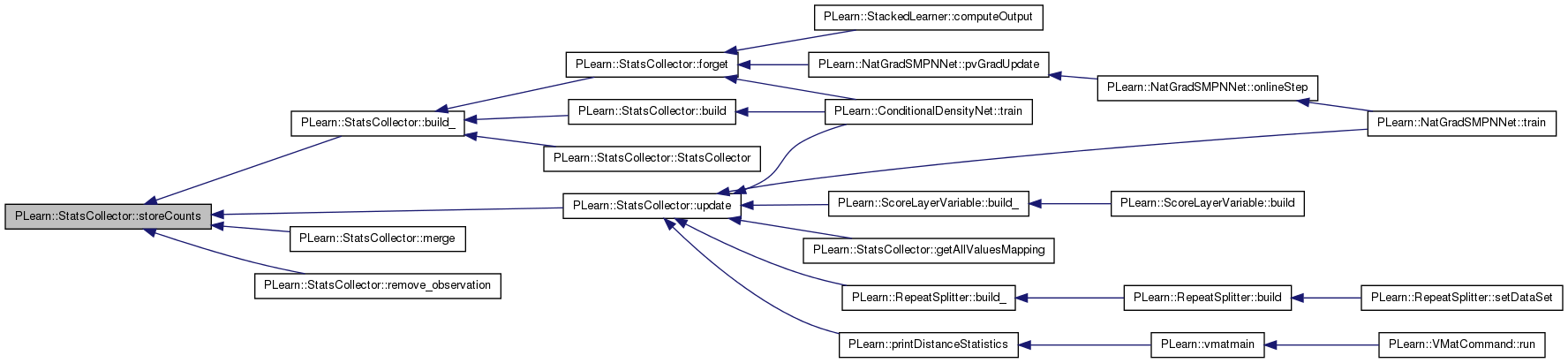
| bool | storeCounts () |
| Return 'true' iff this StatsCollector needs to fill the 'counts' map, i.e. | |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static void | declareOptions (OptionList &ol) |
| Declares this class' options. | |
| static void | declareMethods (RemoteMethodMap &rmm) |
| Declare the methods that are remote-callable. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| map< real, StatsCollectorCounts > | approximate_counts |
| This map is only created when getApproximateCounts() is called. | |
| Mat | sorted_values |
| Used to store the sorted values (after taking their absolute value), with their target value (1 or 0) in the second column. | |
| bool | sorted |
| Set to 1 when the values stored in 'counts' are sorted and stored in 'sorted_values'. | |
Private Types | |
| typedef Object | inherited |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | build_ () |
| This does the actual building. | |
| void | calculate_binary_integer () |
| used to calculate binary_ and integer_ if we reload an old version | |
Definition at line 134 of file StatsCollector.h.
typedef Object PLearn::StatsCollector::inherited [private] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 136 of file StatsCollector.h.
| PLearn::StatsCollector::StatsCollector | ( | int | the_maxnvalues = 0 | ) |
Definition at line 154 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References build_().
: epsilon(0.0), maxnvalues(the_maxnvalues), no_removal_warnings(false), nmissing_(0.), nnonmissing_(0.), sumsquarew_(0.), sum_(0.), sumsquare_(0.), sumcube_(0.), sumfourth_(0.), min_(MISSING_VALUE), max_(MISSING_VALUE), agemin_(MISSING_VALUE), agemax_(MISSING_VALUE), first_(MISSING_VALUE), last_(MISSING_VALUE), more_than_maxnvalues(false), binary_(-1), integer_(-1), sorted(false) { build_(); }
| string PLearn::StatsCollector::_classname_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 151 of file StatsCollector.cc.
| OptionList & PLearn::StatsCollector::_getOptionList_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 151 of file StatsCollector.cc.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::StatsCollector::_getRemoteMethodMap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 151 of file StatsCollector.cc.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 151 of file StatsCollector.cc.
| Object * PLearn::StatsCollector::_new_instance_for_typemap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 151 of file StatsCollector.cc.
| StaticInitializer StatsCollector::_static_initializer_ & PLearn::StatsCollector::_static_initialize_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 151 of file StatsCollector.cc.
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::agemax | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 249 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareMethods(), and getStat().
{ return agemax_; }
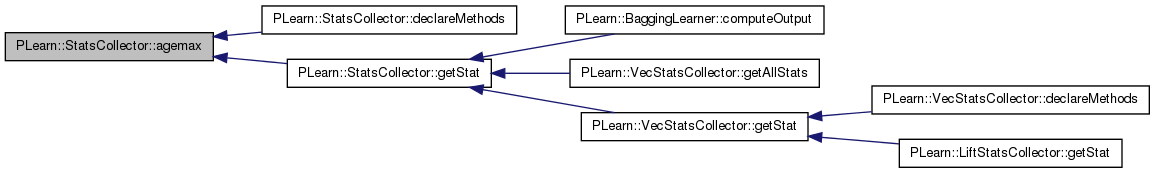
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::agemin | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 248 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareMethods(), and getStat().
{ return agemin_; }
| void PLearn::StatsCollector::build | ( | ) | [virtual] |
simply calls inherited::build() then build_()
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 504 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References PLearn::Object::build(), and build_().
Referenced by PLearn::ConditionalDensityNet::train().
{
inherited::build();
build_();
}

| void PLearn::StatsCollector::build_ | ( | ) | [private] |
This does the actual building.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 479 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References calculate_binary_integer(), count_ids, counts, maxnvalues, more_than_maxnvalues, PLASSERT, and storeCounts().
Referenced by build(), forget(), and StatsCollector().
{
PLASSERT( maxnvalues == -1 || maxnvalues >= 0 );
// make sure counts.size==0. If not, the object must have been loaded, and FLT_MAX is an existing key
// but rounded to some precision, and there would be 2 keys approx.= FLT_MAX
if(storeCounts() && counts.size()==0)
counts[FLT_MAX] = StatsCollectorCounts();
// If no values are kept, then we always see more than 0 values.
if (maxnvalues == 0)
more_than_maxnvalues = true;
// build count_ids
count_ids.clear();
for(map<real, StatsCollectorCounts>::iterator it= counts.begin();
it != counts.end(); ++it)
count_ids[it->second.id]= it->first;
//In case we reload an old version
calculate_binary_integer();
}

| void PLearn::StatsCollector::calculate_binary_integer | ( | ) | [private] |
used to calculate binary_ and integer_ if we reload an old version
Definition at line 1545 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References binary_, counts, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), integer_, maxnvalues, more_than_maxnvalues, nnonmissing(), nnonmissing_, PLCHECK, and PLWARNING.
Referenced by build_().
{
if(binary_==-1 && maxnvalues!=0 && nnonmissing_>0)
{
PLCHECK(integer_==-1);
binary_ = true;
integer_ = true;
for(map<real, StatsCollectorCounts>::iterator it = counts.begin();
it!=counts.end();it++)
{
if(it->second.n!=0)
{
if(!(fast_exact_is_equal(it->first,0)||
fast_exact_is_equal(it->first,1)))
binary_ = false;
if(!fast_exact_is_equal(int(round(it->first)),it->first)){
integer_ = false;
break;
}
}
}
if((binary_||integer_)&&more_than_maxnvalues)
PLWARNING("In StatsCollector::calculate_binary_integer() - "
"Reloading an old StatsCollector. While recalculating data for isbinary() and isinteger(), we found a possible error case. The StatsCollector have more value then maxnvalues(%d), but we are still thinking it is a binary or an integer. This can be false.",maxnvalues);
}
else if(maxnvalues==0 && nnonmissing()>0 && -1==binary_ && -1==integer_)
PLWARNING("In StatsCollector::calculate_binary_integer() - "
"Reloadind old StatsCollector with maxnvalues==0 and "
"nnonmissing()>0. This cause trouble as we can't recompute"
"the data for the function isbinary() and isinteger()"
);
}

returns a Mat with x,y coordinates for plotting the cdf only if normalized will the cdf go to 1, otherwise it will go to nsamples
Definition at line 982 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::column(), counts, i, max_, min_, and nnonmissing_.
Referenced by PLearn::interactiveDisplayCDF(), and PLearn::ConditionalDensityNet::train().
{
int l = 2*(int)counts.size();
Mat xy(l+1,2);
int i=0;
double currentcount = 0;
xy(i,0) = min_;
xy(i++,1) = 0;
map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator it = counts.begin();
map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator itend = counts.end();
for(; it!=itend; ++it)
{
real val = it->first;
if(val>max_)
val = max_;
currentcount += it->second.nbelow;
xy(i,0) = val;
xy(i++,1) = currentcount;
currentcount += it->second.n;
xy(i,0) = val;
xy(i++,1) = currentcount;
}
if(normalized)
xy.column(1) /= real(nnonmissing_);
return xy;
}
| string PLearn::StatsCollector::classname | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 151 of file StatsCollector.cc.
| void PLearn::StatsCollector::declareMethods | ( | RemoteMethodMap & | rmm | ) | [static, protected] |
Declare the methods that are remote-callable.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 339 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References PLearn::Object::_getRemoteMethodMap_(), agemax(), agemin(), PLearn::declareMethod(), first_obs(), getCount(), PLearn::RemoteMethodMap::inherited(), isbinary(), isinteger(), kurtosis(), last_obs(), max(), mean(), mean_over_kurtosis(), mean_over_skewness(), mean_over_skewness_ms(), min(), n(), nmissing(), nnonmissing(), range(), sharperatio(), skewness(), stddev(), stderror(), sum(), sumsquare(), sumsquarew(), and variance().
{
// Insert a backpointer to remote methods; note that this
// different than for declareOptions()
rmm.inherited(inherited::_getRemoteMethodMap_());
declareMethod(
rmm, "n", &StatsCollector::n,
(BodyDoc("Returns the total number of value seen\n"),
RetDoc ("n")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "nmissing", &StatsCollector::nmissing,
(BodyDoc("Return the total number of missing value seen\n"),
RetDoc ("nmissing")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "nnonmissing", &StatsCollector::nnonmissing,
(BodyDoc("Return the total number of non missing value seen\n"),
RetDoc ("nnonmissing")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "sumsquarew", &StatsCollector::sumsquarew,
(BodyDoc("Return sumsquarew of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("sumsquarew")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "sum", &StatsCollector::sum,
(BodyDoc("Return sum of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("sum")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "sumsquare", &StatsCollector::sumsquare,
(BodyDoc("Return sumsquare of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("sumsquare")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "min", &StatsCollector::min,
(BodyDoc("Return the minimum value seeup to date\n"),
RetDoc ("the minimum")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "max", &StatsCollector::max,
(BodyDoc("Return the maximum value see up to date\n"),
RetDoc ("the maximum")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "agemin", &StatsCollector::agemin,
(BodyDoc("Return the agemin value\n"),
RetDoc ("agemin")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "agemax", &StatsCollector::agemax,
(BodyDoc("Return the agemax value\n"),
RetDoc ("agemax")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "range", &StatsCollector::range,
(BodyDoc("Return min - max\n"),
RetDoc ("min - max")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "mean", &StatsCollector::mean,
(BodyDoc("Return mean of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("sum/nnonmissing")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "variance", &StatsCollector::variance,
(BodyDoc("Return the variance of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("variance")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "stddev", &StatsCollector::stddev,
(BodyDoc("Return stddev of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("stddev")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "skewness", &StatsCollector::skewness,
(BodyDoc("Return skewness of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("skewness")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "kurtosis", &StatsCollector::kurtosis,
(BodyDoc("Return kurtosis of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("kurtosis")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "stderror", &StatsCollector::stderror,
(BodyDoc("Return stderror of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("stderror")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "first_obs", &StatsCollector::first_obs,
(BodyDoc("Return first_obs of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("first_obs")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "last_obs", &StatsCollector::last_obs,
(BodyDoc("Return last_obs of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("last_obs")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "sharperatio", &StatsCollector::sharperatio,
(BodyDoc("Return sharperatio of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("sharperatio")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "mean_over_skewness", &StatsCollector::mean_over_skewness,
(BodyDoc("Return mean_over_skewness of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("mean_over_skewness")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "mean_over_skewness_ms", &StatsCollector::mean_over_skewness_ms,
(BodyDoc("Return mean_over_skewness_ms of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("mean_over_skewness_ms")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "mean_over_kurtosis", &StatsCollector::mean_over_kurtosis,
(BodyDoc("Return mean_over_kurtosis of the seen value\n"),
RetDoc ("mean_over_kurtosis")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "isbinary", &StatsCollector::isbinary,
(BodyDoc("Return true is all value seen are binary value\n"),
RetDoc ("binary_")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "isinteger", &StatsCollector::isinteger,
(BodyDoc("Return true is all value seen are integer value\n"),
RetDoc ("integer_")));
declareMethod(
rmm, "getCount", &StatsCollector::getCount,
(BodyDoc("return the value stored in a StatsCollectorCount: (n, nbellow, sum, sumsquare, id)\n"),
ArgDoc ("v", "The value of the counts to lookup.\n"),
RetDoc ("Vec(n, nbellow, sum, sumsquare, id)")));
}
| void PLearn::StatsCollector::declareOptions | ( | OptionList & | ol | ) | [static, protected] |
Declares this class' options.
DEPRECATED: don't sort ids -xsm ! fix 'id' attribute of all StatCollectorCounts so that increasing ids correspond to increasing real values ! *** NOT TESTED YET (Julien) void StatsCollector::sortIds() { PairRealSCCType* allreals= new PairRealSCCType[counts.size()]; unsigned int i=0; for(map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::iterator it = counts.begin();it!=counts.end();++it,i++) allreals[i]=make_pair(it->first,&(it->second)); qsort(allreals,counts.size(),sizeof(PairRealSCCType),sortIdComparator); for(i=0;i<counts.size();i++) allreals[i].second->id=i; delete allreals; }.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 202 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References agemax_, agemin_, binary_, PLearn::OptionBase::buildoption, count_ids, counts, PLearn::declareOption(), PLearn::Object::declareOptions(), epsilon, first_, integer_, last_, PLearn::OptionBase::learntoption, max_, maxnvalues, min_, more_than_maxnvalues, nmissing_, nnonmissing_, no_removal_warnings, PLearn::OptionBase::nosave, sum_, sumcube_, sumfourth_, sumsquare_, and sumsquarew_.
{
// buid options
declareOption(
ol, "epsilon", &StatsCollector::epsilon,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Small regularizing value to be added to the variance (V) estimator (and\n"
"indirectly, to standard deviation (STDDEV)). This permits dividing by\n"
"the standard deviation to perform a normalization, without fearing a\n"
"division by zero. Forwarded from the option of the same name in\n"
"VecStatsCollector if this StatsCollector belong in one.\n");
declareOption(
ol, "maxnvalues", &StatsCollector::maxnvalues,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Maximum number of different values to keep track of in counts.\n"
"If -1, we will keep track of all different values.\n"
"If 0, we will only keep track of global statistics.\n");
declareOption(
ol, "no_removal_warnings", &StatsCollector::no_removal_warnings,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"If the remove_observation mecanism is used and the removed\n"
"value is equal to one of last_, min_ or max_, the default\n"
"behavior is to warn the user.\n"
"\n"
"If one want to disable this feature, he may set\n"
"no_removal_warnings to true.\n"
"\n"
"Default: false (0)." );
// learnt options
declareOption(
ol, "nmissing_", &StatsCollector::nmissing_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"number of missing values");
declareOption(
ol, "nnonmissing_", &StatsCollector::nnonmissing_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"number of non missing value ");
declareOption(
ol, "sumsquarew_", &StatsCollector::sumsquarew_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"sum of square of all weights");
declareOption(
ol, "sum_", &StatsCollector::sum_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"sum of all (values-first_observation)");
declareOption(
ol, "sumsquare_", &StatsCollector::sumsquare_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"sum of square of all (values-first_observation)");
declareOption(
ol, "sumcube_", &StatsCollector::sumcube_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"sum of cube of all (values-first_observation)");
declareOption(
ol, "sumfourth_", &StatsCollector::sumfourth_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"sum of fourth power of all (values-first_observation)");
declareOption(
ol, "min_", &StatsCollector::min_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"the min");
declareOption(
ol, "max_", &StatsCollector::max_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"the max");
declareOption(
ol, "agmemin_", &StatsCollector::agemin_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"How many observations ago the min was observed");
declareOption(
ol, "agemax_", &StatsCollector::agemax_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"How many observations ago the max was observed");
declareOption(
ol, "first_", &StatsCollector::first_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"first encountered observation");
declareOption(
ol, "last_", &StatsCollector::last_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"last encountered observation");
declareOption(
ol, "binary_", &StatsCollector::binary_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"1(true) if all seen value are binary. 0(false) otherwise"
"In the case where we would have reloaded and old version"
"we will calculate the result from the data in counts"
"If maxnvalues==0, we are in trouble as we can't recalculate it"
"So binary_==-1 and integer_==-1, but "
"if we do new update, it will contain the result of only the "
" new value if they change it for 0.");
declareOption(
ol, "integer_", &StatsCollector::integer_,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"as binary_, execpt for integer");
declareOption(
ol, "counts", &StatsCollector::counts,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"Will contain up to 'maxnvalues' values and associated counts, as\n"
"well as a last element which maps FLT_MAX, so that we do not miss\n"
"anything (remains empty if maxnvalues == 0).");
declareOption(
ol, "count_ids", &StatsCollector::count_ids,
OptionBase::learntoption | OptionBase::nosave,
"Maps an id to a count value.");
declareOption(
ol, "more_than_maxnvalues", &StatsCollector::more_than_maxnvalues,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"Set to 1 when more than 'maxnvalues' are seen. This is to warn the user when computing\n"
"statistics that may be inaccurate when not all values are kept (e.g., LIFT).");
// Now call the parent class' declareOptions
inherited::declareOptions(ol);
}
| static const PPath& PLearn::StatsCollector::declaringFile | ( | ) | [inline, static] |
| StatsCollector * PLearn::StatsCollector::deepCopy | ( | CopiesMap & | copies | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 151 of file StatsCollector.cc.
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::dmode | ( | ) | const |
discrete distribution mode
Definition at line 1344 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References dmodes(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), and MISSING_VALUE.
Referenced by getStat().
{
Vec ret = dmodes();
if(ret.length() == 0)
return MISSING_VALUE;
return ret[0];
}

| Vec PLearn::StatsCollector::dmodes | ( | ) | const |
Definition at line 1352 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References counts, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), and PLearn::TVec< T >::push_back().
Referenced by dmode().
{
Vec cargmax(0);
real cmax = -1;
map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator it = counts.begin();
map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator itend = counts.end();
for(; it!=itend; ++it)
{
if(it->second.n > cmax)
cmax = it->second.n;
}
it = counts.begin();
for(; it!=itend; ++it)
{
if(fast_exact_is_equal(it->second.n, cmax))
cargmax.push_back(it->first);
}
return cargmax;
}
| void PLearn::StatsCollector::finalize | ( | ) | [inline] |
finishes whatever computation are needed after all updates have been made
Definition at line 310 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by PLearn::RepeatSplitter::build_().
{}

| real PLearn::StatsCollector::first_obs | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 264 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareMethods(), getStat(), and newwrite().
{ return first_; }
| void PLearn::StatsCollector::forget | ( | ) |
clears all statistics, allowing to restart collecting them
Definition at line 513 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References agemax_, agemin_, approximate_counts, binary_, build_(), counts, first_, integer_, last_, max_, maxnvalues, min_, MISSING_VALUE, more_than_maxnvalues, nmissing_, nnonmissing_, sorted, sum_, sumcube_, sumfourth_, sumsquare_, and sumsquarew_.
Referenced by PLearn::StackedLearner::computeOutput(), PLearn::NatGradSMPNNet::pvGradUpdate(), and PLearn::ConditionalDensityNet::train().
{
nmissing_ = 0.;
nnonmissing_ = 0.;
sumsquarew_ = 0.;
sum_ = 0.;
sumsquare_ = 0.;
sumcube_ = 0.;
sumfourth_ = 0.;
min_ = MISSING_VALUE;
max_ = MISSING_VALUE;
agemin_ = MISSING_VALUE;
agemax_ = MISSING_VALUE;
first_ = last_ = MISSING_VALUE;
binary_ = -1;
integer_ = -1;
more_than_maxnvalues = (maxnvalues == 0);
approximate_counts.clear();
sorted = false;
counts.clear();
build_();
}
| RealMapping PLearn::StatsCollector::getAllValuesMapping | ( | TVec< double > * | fcount = 0 | ) | const |
Definition at line 875 of file StatsCollector.cc.
{
return getAllValuesMapping(0,fcount);
}
| RealMapping PLearn::StatsCollector::getAllValuesMapping | ( | TVec< bool > * | to_be_included, |
| TVec< double > * | fcount = 0, |
||
| bool | ignore_other = false, |
||
| real | tolerance = 0 |
||
| ) | const |
Same as getAllValuesMapping, except we can specify a bool vector, that indicates whether the k-th range should be included or not.
The boolean 'ignore_other' indicates whether a value not appearing in the mapping should be mapped to itself (false), or to -1 (true). We can also give a 'tolerance': in this case, each mapping will be expanded by '-epsilon' below and '+epsilon' above, with epsilon = tolerance * mean(difference between two consecutive values). If two consecutive mappings have a non-empty intersection after the expansion, they will be merged.
Definition at line 880 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References PLearn::RealMapping::addMapping(), PLearn::TVec< T >::append(), counts, epsilon, i, j, PLearn::RealMapping::keep_other_as_is, mean(), nmissing_, nnonmissing_, PLearn::RealMapping::other_mapsto, PLERROR, PLWARNING, PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), and update().
{
RealMapping mapping;
if (ignore_other) {
mapping.keep_other_as_is = false;
mapping.other_mapsto = -1;
}
int i = 0;
int k = 0;
if(fcount)
{
(*fcount) = TVec<double>();
fcount->resize(0,int(counts.size())+2);
fcount->append(nmissing_);
fcount->append(0);
}
double count=0;
real epsilon = 0;
if (tolerance > 0) {
// Compute the expansion coefficient 'epsilon'.
StatsCollector values_diff;
for (map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator it = counts.begin();
size_t(i) < counts.size() - 2; i++) {
real val1 = it->first;
it++;
real val2 = it->first;
values_diff.update(val2 - val1);
}
// Mean of the difference between two consecutive values.
real mean = values_diff.mean();
epsilon = tolerance * mean;
if (epsilon < 0) {
PLERROR("In StatsCollector::getAllValuesMapping - epsilon < 0, there must be something wrong");
}
}
i = 0;
for(map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator it = counts.begin() ;
size_t(i) < counts.size() - 1; ++it)
{
real low_val = it->first - epsilon;
real up_val = it->first + epsilon;
map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator itup = it;
itup++;
int j = i + 1;
bool to_include = true;
if (to_be_included) {
to_include = (*to_be_included)[i];
}
real count_in_range = it->second.n;
if (tolerance > 0) {
for (; itup != counts.end(); itup++) {
if (itup->first - epsilon <= up_val) {
// The next mapping needs to be merged with the current one.
if (fcount) {
PLWARNING("In StatsCollector::getAllValuesMapping - You are using fcount and some ranges are merged. "
"This case has not been tested yet. Please remove this warning if it works fine.");
}
up_val = itup->first + epsilon;
count_in_range += itup->second.n;
if (to_be_included) {
// As long as one of the merged mappings needs to be included,
// we include the result of the merge.
to_include = to_include || (*to_be_included)[j];
}
j++;
} else {
// No merging.
break;
}
}
}
// Because the last one won't be merged (even if all are merged, the one
// with FLT_MAX won't).
itup--;
it = itup;
i = j - 1;
if (to_include) {
mapping.addMapping(RealRange('[',low_val,up_val,']'),k);
k++;
if(fcount)
{
count += count_in_range;
fcount->append(count_in_range);
}
}
i++;
}
if(fcount)
(*fcount)[1] = nnonmissing_ - count;
return mapping;
}
| map< real, StatsCollectorCounts > * PLearn::StatsCollector::getApproximateCounts | ( | ) |
Same as getCounts(), except that the map that is returned has been transformed so that no two keys are equal, where equality is defined as the result of the PLearn function 'is_equal'.
This means some keys may be merged when they are found to be almost equal.
Definition at line 716 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References approximate_counts, counts, PLearn::is_equal(), PLearn::StatsCollectorCounts::n, PLearn::StatsCollectorCounts::nbelow, PLearn::StatsCollectorCounts::sum, and PLearn::StatsCollectorCounts::sumsquare.
Referenced by PLearn::GaussianizeVMatrix::append_col_to_gaussianize(), and PLearn::BasisSelectionRegressor::appendCandidateFunctionsOfSingleField().
{
if (!approximate_counts.empty())
return &approximate_counts;
map<real, StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator it_begin, it_current, it;
it_begin = counts.begin();
while (it_begin != counts.end()) {
real val_begin = it_begin->first;
it_current = it_begin;
it_current++;
while (it_current != counts.end() &&
is_equal(val_begin, it_current->first)) it_current++;
// Merge keys between 'begin' and 'current'.
StatsCollectorCounts sc = it_begin->second;
it = it_begin;
for (it++; it != it_current; it++) {
sc.n += it->second.n;
sc.nbelow += it->second.nbelow;
sc.sum += it->second.sum;
sc.sumsquare += it->second.sumsquare;
}
approximate_counts[val_begin] = sc;
it_begin = it_current;
}
return &approximate_counts;
}


| RealMapping PLearn::StatsCollector::getBinMapping | ( | double | discrete_mincount, |
| double | continuous_mincount, | ||
| real | tolerance = .1, |
||
| TVec< double > * | fcount = 0 |
||
| ) | const |
DEPRECATED: DO NOT SORT IDs -xsm ! fix 'id' attribute of all StatCollectorCounts so that increasing ids correspond to increasing real values ! *** NOT TESTED YET void sortIds();.
returns a mapping that maps values to a bin number (from 0 to mapping.length()-1) The mapping will leave missing values as MISSING_VALUE And values outside the [min, max] range will be mapped to -1 Tolerance is used to test wheter we join the two last bins or not. If last be is short of more then tolerance*100% of continuous_mincount elements, we join it with the previous bin.
Definition at line 746 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References PLearn::RealMapping::addMapping(), PLearn::TVec< T >::append(), PLearn::TVec< T >::back(), counts, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), PLearn::RealMapping::lastMapping(), m, max_, min_, nmissing_, nnonmissing_, PLERROR, PLWARNING, PLearn::TVec< T >::pop_back(), PLearn::RealMapping::removeMapping(), PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::RealMapping::setMappingForOther(), and PLearn::RealMapping::size().
{
real mapto=0.;
RealMapping mapping;
mapping.setMappingForOther(-1);
map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator it = counts.begin();
int nleft = int(counts.size())-1; // loop on all but last
if(fcount)
{
(*fcount) = TVec<double>();
// ouch, assume discrete_mincount == continuous_mincount
fcount->resize(0, int(2.*nnonmissing_ / discrete_mincount));
fcount->append(nmissing_);
fcount->append(0);
}
double count = 0, count2 = 0;
real low = min_;
real high = min_;
bool low_has_been_appended = false;
// ProgressBar pb("Computing PseudoQ Mapping...",counts.size()-1);
while(nleft--)
{
high = it->first;
// pb(counts.size()-1-nleft);
count += it->second.nbelow;
count2 += it->second.nbelow;
// cerr << "it->first:"<<it->first<<" nbelow:"<<it->second.nbelow<<" n:"<<it->second.n<<endl;
if(count>=continuous_mincount)
{
// append continuous range
mapping.addMapping(
RealRange(low_has_been_appended?']':'[',low, high, '['),
mapto++);
if(fcount)
fcount->append(count);
low = high;
low_has_been_appended = false;
count = 0;
}
if(it->second.n >= discrete_mincount)
{
if(count>0) // then append the previous continuous range
{
mapping.addMapping(RealRange(low_has_been_appended?']':'[',low, high, '['), mapto++);
if(fcount)
fcount->append(count);
count = 0;
}
// append discrete point
mapping.addMapping(RealRange('[',high,high,']'), mapto++);
if(fcount)
fcount->append(it->second.n + count);
count2+=it->second.n;
count=0;
low = high;
low_has_been_appended = true;
}
else
{
count2+=it->second.n;
count += it->second.n;
}
++it;
}
if(it->first<=max_)
PLERROR("Bug in StatsCollector::getBinMapping expected last element of mapping to be FLT_MAX...");
if (mapping.size() == 0)
{
PLWARNING("StatsCollector::getBinMapping: no mapping were created; probably a bug");
mapping.addMapping(RealRange('[',min_,max_,']'), 0);
return mapping;
}
// make sure we include max_
pair<RealRange, real> m = mapping.lastMapping();
// cnt is the number of elements that would be in the last bin
double cnt = nnonmissing_ - count2 + count;
// If the bin we're about to add is short of less then tolerance*100% of continuous_mincount elements,
// OR if the last we added is a discrete point AND the max is not already in the last range, we append it
if(m.first.high<max_)
{
if( ((real)cnt/(real)continuous_mincount)>(1.-tolerance) ||
(fast_exact_is_equal(m.first.low, m.first.high)))
{
// don't join last bin with last-but-one bin
mapping.addMapping(RealRange(m.first.rightbracket=='[' ? '[' : ']',m.first.high,max_,']'),
mapto++);
if(fcount)
fcount->append(cnt);
}
else
{
// otherwise, we can join it with the previous
mapping.removeMapping(m.first);
mapping.addMapping(RealRange(m.first.leftbracket, m.first.low, max_, ']'),
m.second);
if(fcount)
{
double v = fcount->back();
fcount->pop_back();
fcount->append(v+cnt);
}
}
}
else if(fast_exact_is_equal(m.first.high, max_)) // make sure we have a closing bracket on the max_
{
mapping.removeMapping(m.first);
mapping.addMapping(RealRange(m.first.leftbracket, m.first.low, max_, ']'),
m.second);
}
return mapping;
}
Definition at line 387 of file StatsCollector.h.
References PLearn::TVec< T >::append(), c, PLearn::StatsCollectorCounts::id, PLearn::StatsCollectorCounts::n, PLearn::StatsCollectorCounts::nbelow, PLearn::StatsCollectorCounts::sum, and PLearn::StatsCollectorCounts::sumsquare.
Referenced by declareMethods().
{
Vec v(0,5);
StatsCollectorCounts c = counts[value];
v.append(c.n);
v.append(c.nbelow);
v.append(c.sum);
v.append(c.sumsquare);
v.append(c.id);
return v;
}


| map<real, StatsCollectorCounts>* PLearn::StatsCollector::getCounts | ( | ) | [inline] |
Return the mapping from encountered real values to StatsCollectorCounts.
Definition at line 314 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by PLearn::RepeatSplitter::build_().
{return &counts;}

| int PLearn::StatsCollector::getMaxNValues | ( | ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 322 of file StatsCollector.h.
{return maxnvalues;}
| OptionList & PLearn::StatsCollector::getOptionList | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 151 of file StatsCollector.cc.
| OptionMap & PLearn::StatsCollector::getOptionMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 151 of file StatsCollector.cc.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::StatsCollector::getRemoteMethodMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 151 of file StatsCollector.cc.
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::getStat | ( | const string & | statname | ) | const |
Compute a given statistic.
Returns the index in the vector returned by getAllStats of the stat with the given name.
Currently understood statnames are listed in the class help.
Currently available names are E (mean) V (variance) STDDEV MIN MAX STDERROR SHARPERATIO DMODE Will call PLERROR statname is invalid
Definition at line 1127 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References agemax(), agemin(), dmode(), first_obs(), in, iqr(), kurtosis(), last_obs(), lift(), max(), mean(), mean_lift(), mean_over_kurtosis(), mean_over_skewness(), mean_over_skewness_ms(), min(), n(), nips_lift(), nmissing(), nnonmissing(), PLearn::openString(), PLearn::PStream::plearn_ascii, PLERROR, prbp(), prr(), pseudo_quantile(), range(), sharperatio(), skewness(), PLearn::PStream::smartReadUntilNext(), stddev(), stderror(), sum(), sumsquare(), variance(), zpr1t(), zpr2t(), and zstat().
Referenced by PLearn::BaggingLearner::computeOutput(), PLearn::VecStatsCollector::getAllStats(), and PLearn::VecStatsCollector::getStat().
{
typedef real (StatsCollector::*STATFUN)() const;
static bool init = false;
static map<string,STATFUN> statistics;
if (!init) {
//the two if(!init) is volontary not to acquire a lock at each fct call
#pragma omp critical
if(!init){
init = true;
statistics["E"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::mean);
statistics["V"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::variance);
statistics["STDDEV"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::stddev);
statistics["STDERROR"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::stderror);
statistics["SKEW"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::skewness);
statistics["KURT"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::kurtosis);
statistics["MIN"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::min);
statistics["MAX"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::max);
statistics["AGEMIN"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::agemin);
statistics["AGEMAX"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::agemax);
statistics["RANGE"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::range);
statistics["SUM"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::sum);
statistics["SUMSQ"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::sumsquare);
statistics["FIRST"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::first_obs);
statistics["LAST"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::last_obs);
statistics["N"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::n);
statistics["NMISSING"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::nmissing);
statistics["NNONMISSING"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::nnonmissing);
statistics["SHARPERATIO"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::sharperatio);
statistics["EoverSKEW"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::mean_over_skewness);
statistics["EoverSKEWms"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::mean_over_skewness_ms);
statistics["EoverKURT"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::mean_over_kurtosis);
statistics["ZSTAT"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::zstat);
statistics["PZ1t"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::zpr1t);
statistics["PZ2t"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::zpr2t);
statistics["IQR"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::iqr);
statistics["PRR"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::prr);
statistics["NIPS_LIFT"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::nips_lift);
statistics["MEAN_LIFT"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::mean_lift);
statistics["PRBP"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::prbp);
statistics["DMODE"] = STATFUN(&StatsCollector::dmode);
}
}
// Special case :: interpret the PSEUDOQ(xx) and LIFT(xxx) forms
if (statname.substr(0,7) == "PSEUDOQ") {
PStream in = openString(statname, PStream::plearn_ascii);
string dummy;
in.smartReadUntilNext("(", dummy);
string quantile_str;
in.smartReadUntilNext(")", quantile_str);
real q = toreal(quantile_str);
return pseudo_quantile(q);
} else if (statname.substr(0, 5) == "LIFT(") {
PStream in = openString(statname, PStream::plearn_ascii);
string dummy;
in.smartReadUntilNext("(", dummy);
string fraction_str;
in.smartReadUntilNext(")", fraction_str);
real fraction = toreal(fraction_str);
int dummy_int;
return -100 * lift(int(round(fraction * nnonmissing())), dummy_int);
}
map<string,STATFUN>::iterator fun = statistics.find(statname);
if (fun == statistics.end())
PLERROR("In StatsCollector::getStat, invalid statname '%s'",
statname.c_str());
else
return (this->*(fun->second))();
return 0;
}
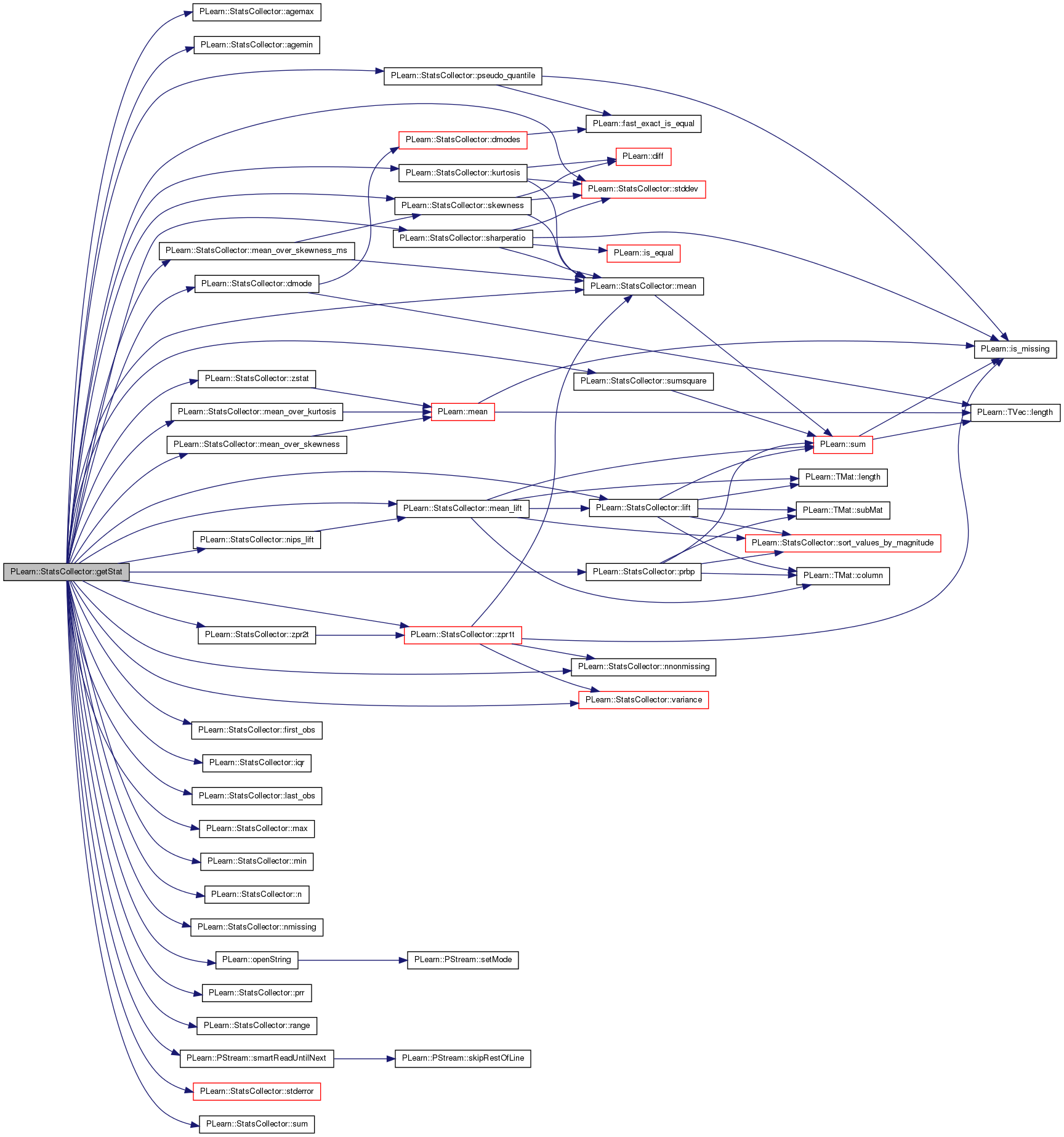

| real PLearn::StatsCollector::iqr | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 273 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by getStat().
{ return pseudo_quantile(0.75) - pseudo_quantile(0.25); }
| bool PLearn::StatsCollector::isbinary | ( | ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 379 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareMethods(), PLearn::GaussianizeVMatrix::setMetaDataDir(), and PLearn::vmatmain().
{return binary_;}

| bool PLearn::StatsCollector::isinteger | ( | ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 383 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareMethods(), PLearn::VMatrix::saveCMAT(), and PLearn::vmatmain().
{return integer_;}
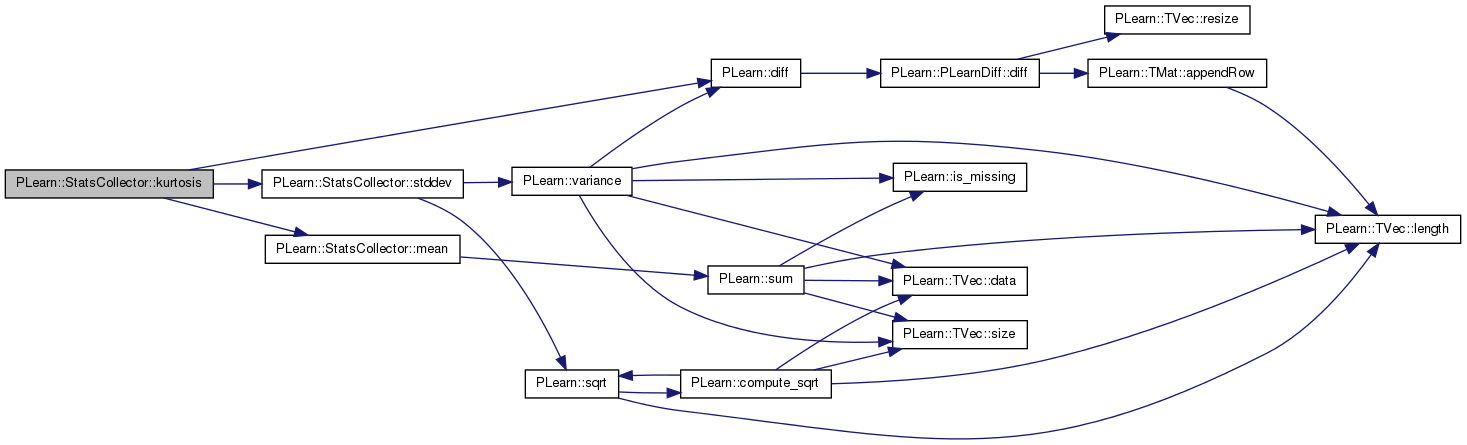
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::kurtosis | ( | ) | const |
Definition at line 1219 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References PLearn::diff(), first_, mean(), nnonmissing_, stddev(), sum_, sumcube_, sumfourth_, and sumsquare_.
Referenced by declareMethods(), and getStat().
{
// numerator
double diff = first_ - mean();
double numerator = sumfourth_/nnonmissing_ +
(4*sumcube_/nnonmissing_ +
(6*sumsquare_/nnonmissing_ + diff*(4*sum_/nnonmissing_+diff)) * diff)
* diff;
// denominator
double denominator = stddev();
denominator *= denominator;
denominator *= denominator;
return numerator / denominator - 3.0;
}
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::last_obs | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 265 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareMethods(), getStat(), and newwrite().
{ return last_; }
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::lift | ( | int | k, |
| int & | n_pos_in_k, | ||
| int | n_pos_in_k_minus_1 = -1, |
||
| real | pos_fraction = -1 |
||
| ) | const |
Return LIFT(k/n).
'n_pos_in_k' is filled with the number of positive examples in the first k examples. If provided, 'n_pos_in_k_minus_1' must be the number of positive examples in the first (k-1) examples. If provided, pos_fraction must be the average fraction of positive examples in the dataset (= n+ / n).
Definition at line 1269 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::column(), PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), more_than_maxnvalues, PLERROR, PLWARNING, sort_values_by_magnitude(), sorted, sorted_values, PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), and PLearn::sum().
Referenced by getStat(), and mean_lift().
{
if (more_than_maxnvalues)
PLWARNING("In StatsCollector::lift - You need to increase 'maxnvalues'"
" (or set it to -1) to get an accurate statistic");
if (k <= 0)
PLERROR("In StatsCollector::lift - It makes no sense to compute a lift with k <= 0");
if (!sorted)
sort_values_by_magnitude();
if (n_pos_in_k_minus_1 < 0)
// We are not given the number of positive examples in the first (k-1)
// examples, thus we need to compute it ourselves.
n_pos_in_k = int(round(PLearn::sum(sorted_values.subMat(0, 1, k, 1))));
else
n_pos_in_k = n_pos_in_k_minus_1 + int(sorted_values(k - 1, 1));
if (pos_fraction < 0)
// We are not given the fraction of positive examples.
pos_fraction = int(round(PLearn::sum(sorted_values.column(1)))) / real(sorted_values.length());
return real(n_pos_in_k) / (k * pos_fraction);
}
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::max | ( | ) | const [inline] |
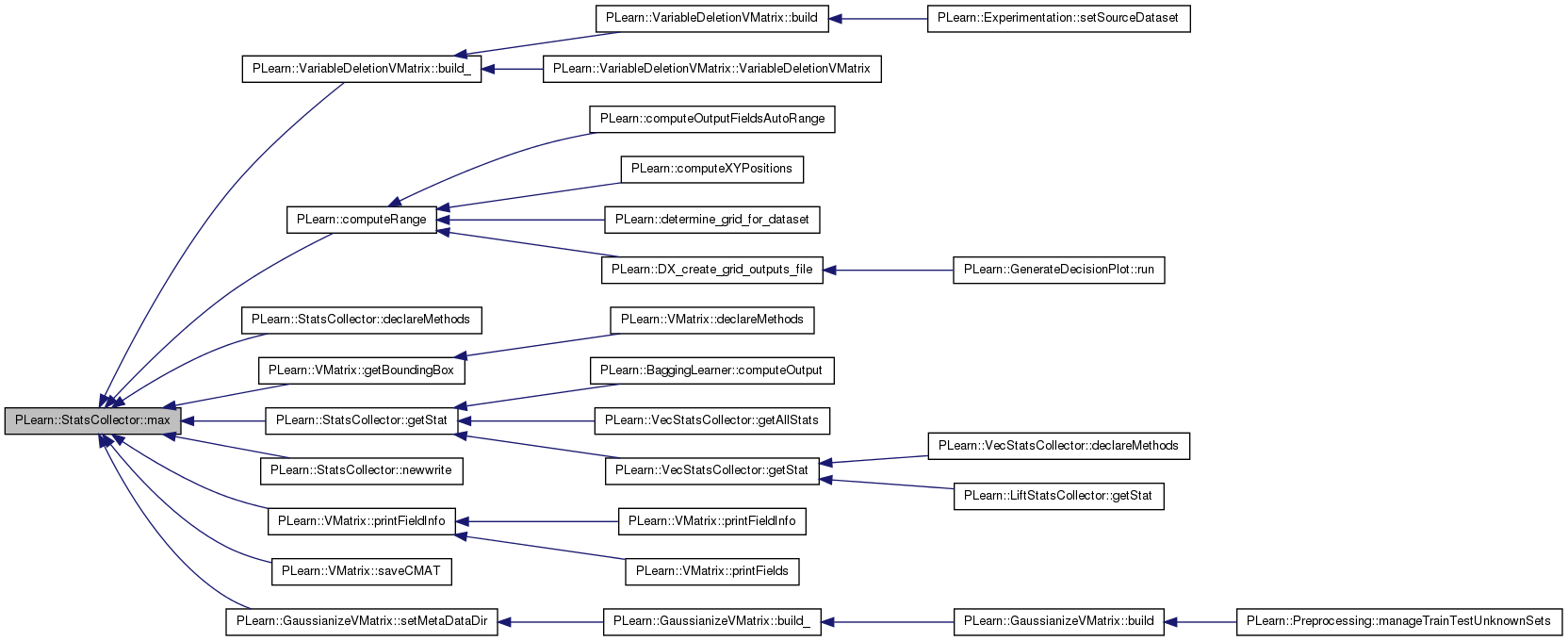
Definition at line 247 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by PLearn::VariableDeletionVMatrix::build_(), PLearn::computeRange(), declareMethods(), PLearn::VMatrix::getBoundingBox(), getStat(), newwrite(), PLearn::VMatrix::printFieldInfo(), PLearn::VMatrix::saveCMAT(), and PLearn::GaussianizeVMatrix::setMetaDataDir().
{ return max_; }
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::mean | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 251 of file StatsCollector.h.
References PLearn::sum().
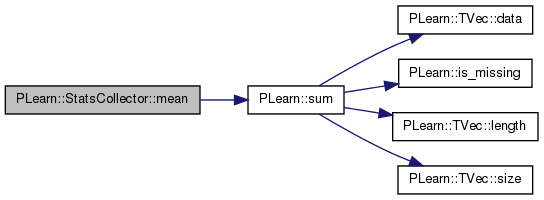
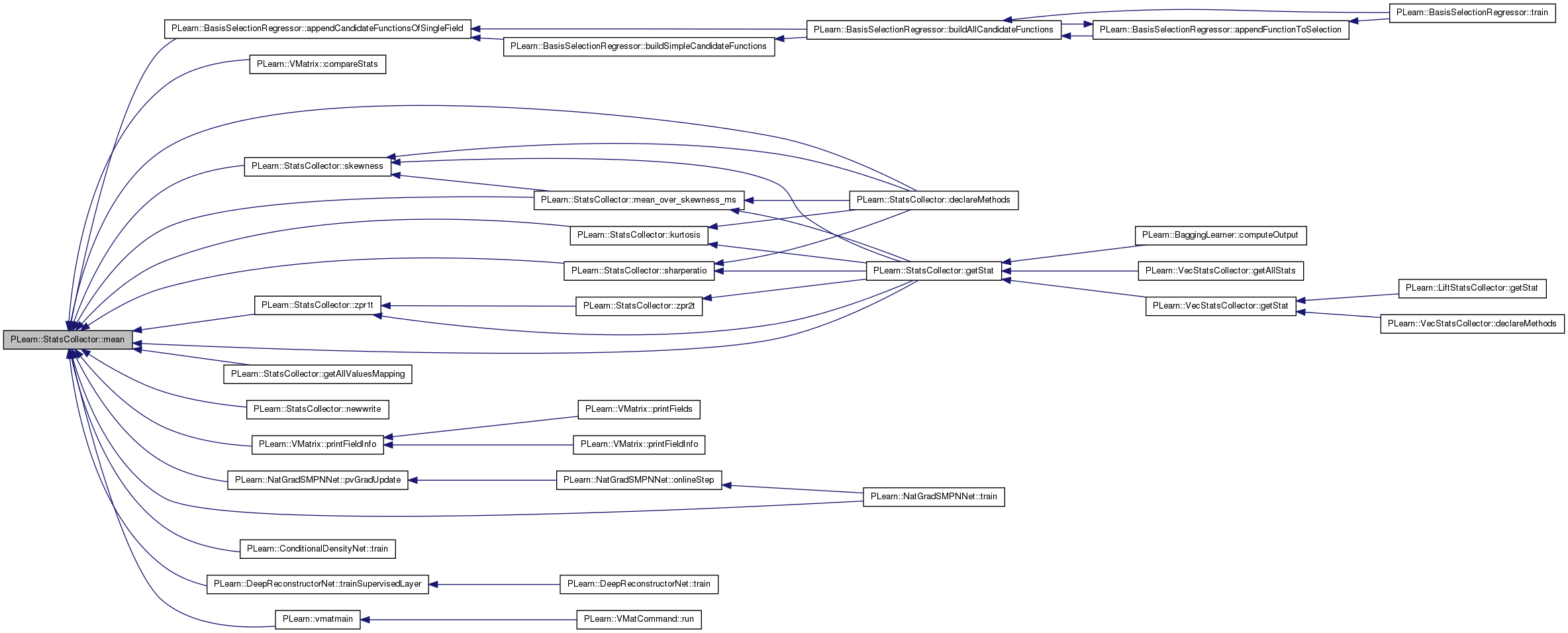
Referenced by PLearn::BasisSelectionRegressor::appendCandidateFunctionsOfSingleField(), PLearn::VMatrix::compareStats(), declareMethods(), getAllValuesMapping(), getStat(), kurtosis(), mean_over_skewness_ms(), newwrite(), PLearn::VMatrix::printFieldInfo(), PLearn::NatGradSMPNNet::pvGradUpdate(), sharperatio(), skewness(), PLearn::NatGradSMPNNet::train(), PLearn::ConditionalDensityNet::train(), PLearn::DeepReconstructorNet::trainSupervisedLayer(), PLearn::vmatmain(), and zpr1t().
{ return real(sum()/nnonmissing_); }
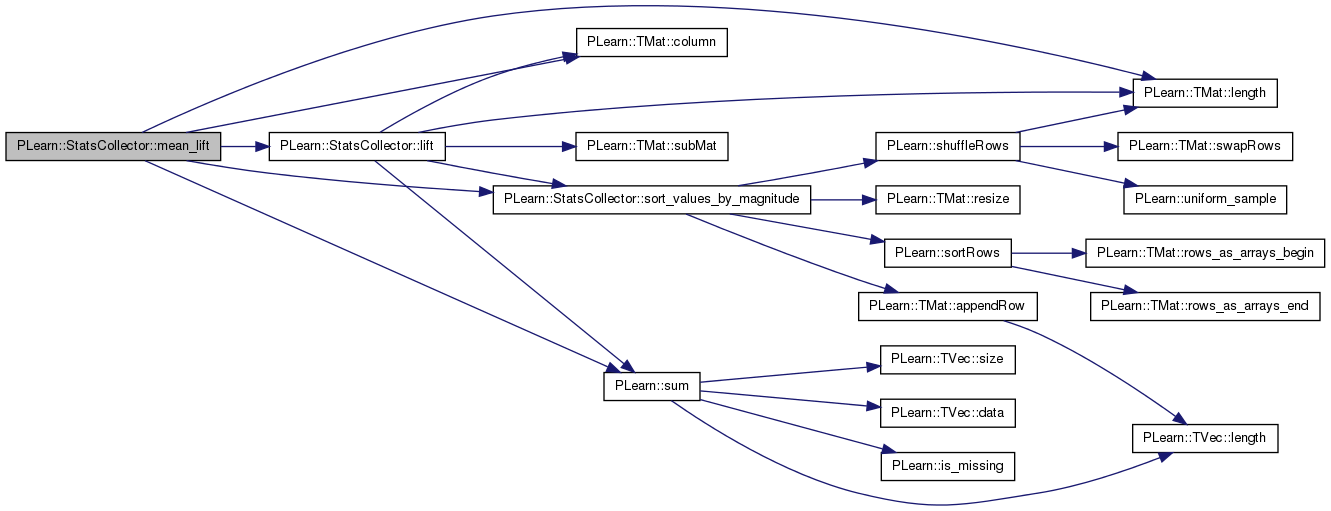
MEAN_LIFT statistic (see help).
If provided, 'pos_fraction' is filled with the fraction of positive examples seen in the updates so far.
Definition at line 1305 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::column(), PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), lift(), more_than_maxnvalues, PLWARNING, sort_values_by_magnitude(), sorted, sorted_values, and PLearn::sum().
Referenced by getStat(), and nips_lift().
{
if (more_than_maxnvalues)
PLWARNING("In StatsCollector::mean_lift - You need to increase "
"'maxnvalues' (or set it to -1) to get an accurate "
"statistic");
if (!sorted)
sort_values_by_magnitude();
real n_total = real(sorted_values.length());
real pos_f = int(round(PLearn::sum(sorted_values.column(1)))) / n_total;
if (pos_fraction)
*pos_fraction = pos_f;
int n_pos_in_k_minus_1 = -1;
real result = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < sorted_values.length(); k++)
result += lift(k + 1, n_pos_in_k_minus_1, n_pos_in_k_minus_1, pos_f);
result /= n_total;
return -result;
}
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::mean_over_kurtosis | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 269 of file StatsCollector.h.
References PLearn::mean().
Referenced by declareMethods(), and getStat().
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::mean_over_skewness | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 267 of file StatsCollector.h.
References PLearn::mean().
Referenced by declareMethods(), and getStat().
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::mean_over_skewness_ms | ( | ) | const |
Special version for model selection.
Definition at line 1256 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References m, mean(), and skewness().
Referenced by declareMethods(), and getStat().
{
real m = mean();
real s = skewness();
if (m > 0 && s > 0)
return m / s;
else
return - fabs(m / s);
}
| void PLearn::StatsCollector::merge | ( | const StatsCollector & | other | ) | [virtual] |
merge another StatsCollector into this one
Definition at line 1426 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References agemax_, agemin_, approximate_counts, count_ids, counts, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), first_, last_, max_, maxnvalues, min_, more_than_maxnvalues, n(), nmissing_, nnonmissing_, PLERROR, PLWARNING, sorted, storeCounts(), sum(), sum_, sumcube_, sumfourth_, sumsquare(), sumsquare_, and sumsquarew_.
{
if(storeCounts() && other.maxnvalues != -1)
PLERROR("Cannot merge stats collectors w/counts if 'other' stats col. has maxnvalues != -1");
if(fast_exact_is_equal(nnonmissing_,0)) // this was empty before merge
{
min_= other.min_;
max_= other.max_;
first_= other.first_;
last_= other.last_;
}
sum_+= other.sum() - first_*other.nnonmissing_;
double first2= first_*first_;
sumsquare_+= other.sumsquare() - 2.0*first_*other.sum() + first2*other.nnonmissing_;
double ofirst2= other.first_*other.first_;
double osum3= other.sumcube_ + 3.0*other.first_*other.sumsquare()
- 3.0*ofirst2*other.sum() + ofirst2*other.first_*other.nnonmissing_;
sumcube_+= osum3 - 3.0*first_*other.sumsquare()
+ 3.0*first2*other.sum() - first2*first_*other.nnonmissing_;
double osum4= other.sumfourth_ + 4.0*other.first_*osum3 - 6.0*ofirst2*other.sumsquare()
+ 4.0*other.first_*ofirst2*other.sum() - ofirst2*ofirst2*other.nnonmissing_;
sumfourth_+= osum4 - 4.0*first_*osum3 + 6.0*first2*other.sumsquare()
- 4.0*first_*first2*other.sum() + first2*first2*other.nnonmissing_;
nmissing_+= other.nmissing_;
nnonmissing_+= other.nnonmissing_;
sumsquarew_+= other.sumsquarew_;
// In merging first/last/ages, we assume that 'this' comes first, and
// 'other' comes last.
if (other.min_ < min_) {
min_ = other.min_;
agemin_ = other.agemin_;
}
else {
agemin_ += other.n();
}
if (other.max_ > max_) {
max_ = other.max_;
agemax_ = other.agemax_;
}
else {
agemax_ += other.n();
}
last_= other.last_; // assume this is first and other is last.
sorted = false;
if (storeCounts())//now merge counts
{
int nextid= 0;
set<real> already_merged;
map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::iterator it;
map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator ito;
map<int, real>::const_iterator iti;
while(nextid < int(other.counts.size()) && (maxnvalues == -1 || int(counts.size()) <= maxnvalues))
{// merge counts with smallest ids until maxnvalues reached
iti= other.count_ids.find(nextid);
if(iti == other.count_ids.end())
{
PLWARNING("Can't find count id %d", nextid);
break;
}
real val= iti->second;
ito= other.counts.find(val);
if(ito == other.counts.end())
{
PLWARNING("Can't find count id %d, val %f", nextid, val);
break;
}
int newid= int(counts.size());
it= counts.find(val);
if(it != counts.end())
it->second.merge(ito->second);
else
{
counts[val]= ito->second;
counts[val].id= newid;
count_ids[newid]= val;
}
++nextid;
already_merged.insert(val);
}
for(ito= other.counts.begin(); ito != other.counts.end(); ++ito)
{
real val= ito->first;
if(already_merged.count(val) == 0)//skip those merged earlier
{
it= counts.find(val);
if(it != counts.end())
it->second.merge(ito->second);
else if(maxnvalues == -1 || int(counts.size()) <= maxnvalues)
{
int id= int(counts.size());
counts[val]= ito->second;
counts[val].id= id;
count_ids[id]= val;
}
else
{
more_than_maxnvalues= true;
it= counts.lower_bound(val);
real weight= ito->second.n;
it->second.nbelow+= ito->second.nbelow + weight;
it->second.sum+= val*weight;//ito->second.sum;
it->second.sumsquare+= val*val*weight;//ito->second.sumsquare;
}
}
}
}
if (!approximate_counts.empty()) approximate_counts.clear();
}
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::min | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 246 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by PLearn::VariableDeletionVMatrix::build_(), PLearn::computeRange(), declareMethods(), PLearn::VMatrix::getBoundingBox(), getStat(), newwrite(), PLearn::VMatrix::printFieldInfo(), PLearn::VMatrix::saveCMAT(), and PLearn::GaussianizeVMatrix::setMetaDataDir().
{ return min_; }
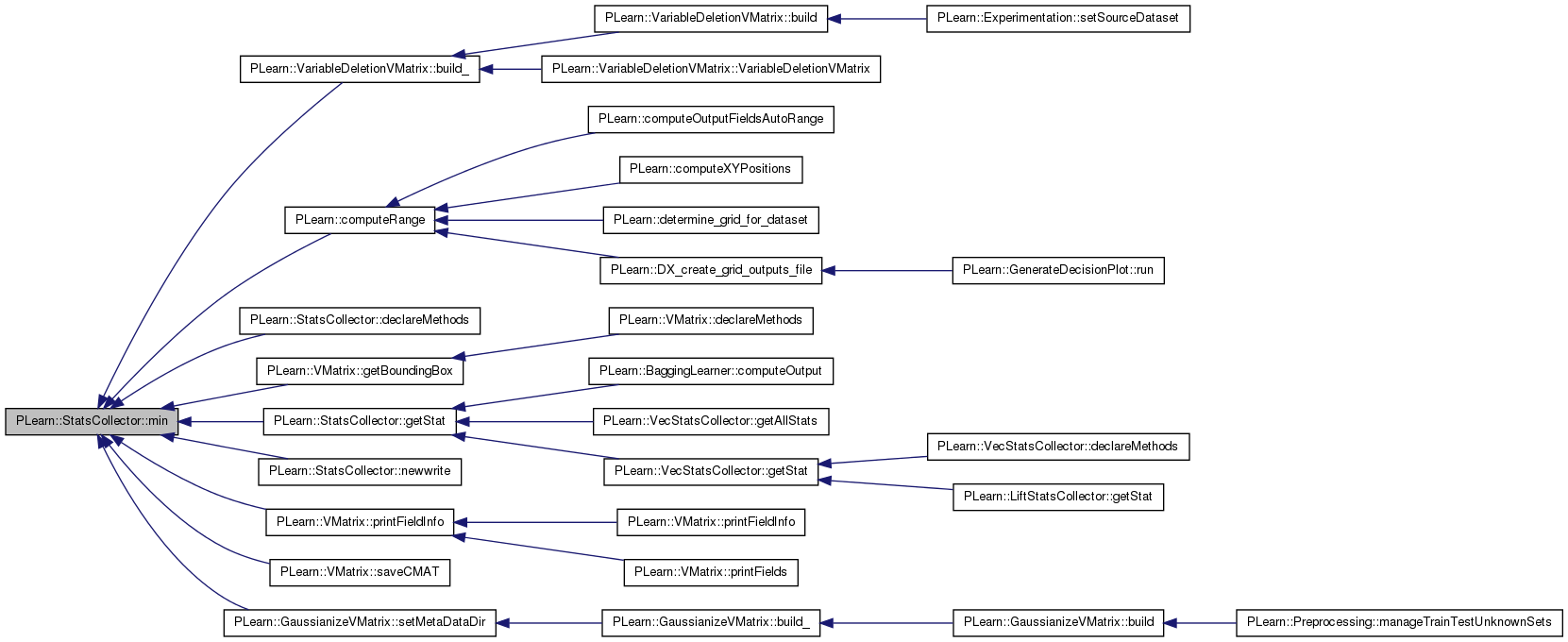
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::n | ( | ) | const [inline] |
number of samples seen with update (length of VMat for ex.)
Definition at line 235 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by PLearn::AnalyzeFieldStats::analyzeVariableStats(), PLearn::BasisSelectionRegressor::appendCandidateFunctionsOfSingleField(), PLearn::VMatrix::compareStats(), PLearn::AnalyzeFieldStats::createHeaderFile(), declareMethods(), PLearn::AnalyzeFieldStats::getHeaderRecord(), getStat(), merge(), newwrite(), PLearn::AnalyzeFieldStats::reviewGlobalStats(), and PLearn::vmatmain().
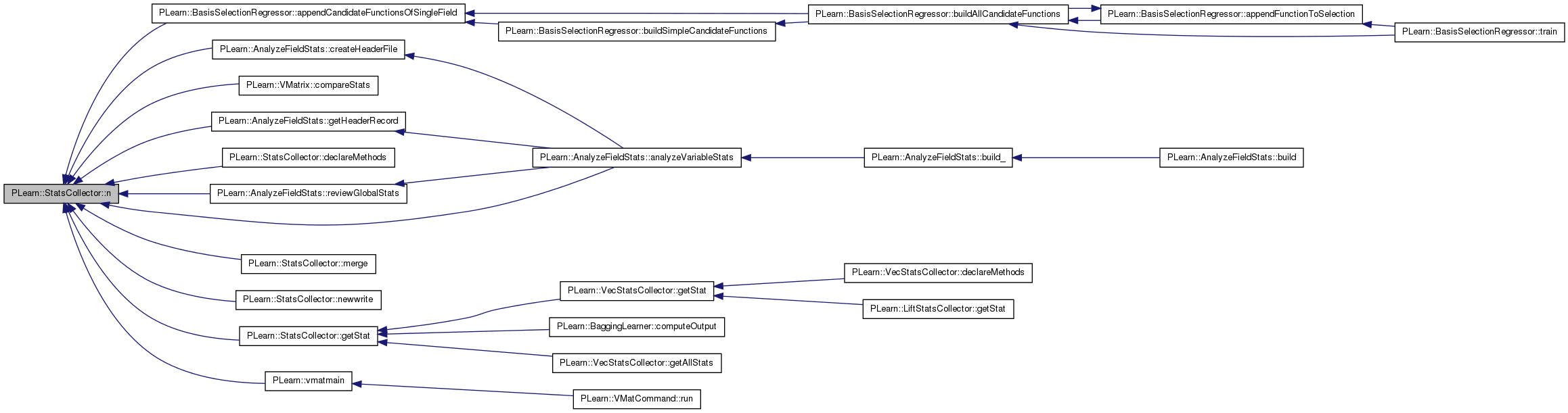
| void PLearn::StatsCollector::newwrite | ( | PStream & | out | ) | const [virtual] |
Overridden to have a fancy output for raw_ascii and pretty_ascii modes.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 1057 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References counts, PLearn::endl(), first_obs(), last_obs(), max(), mean(), min(), n(), PLearn::Object::newwrite(), nmissing(), nnonmissing(), PLearn::PStream::outmode, PLearn::PStream::pretty_ascii, PLearn::PStream::raw_ascii, stddev(), and stderror().
{
switch(out.outmode)
{
case PStream::raw_ascii:
case PStream::pretty_ascii:
{
map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator it = counts.begin();
map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator itend = counts.end();
for(; it!=itend; ++it)
{
out << "value: " << it->first
<< " #equal:" << it->second.n
<< " #less:" << it->second.nbelow
<< " avg_of_less:" << it->second.sum/it->second.nbelow
<< " % of non missing:"<< (real(it->second.n)/nnonmissing())
<< endl;
}
out << "\n# samples: " << n() << "\n";
out << "# missing: " << nmissing() << "\n";
out << "mean: " << mean() << "\n";
out << "stddev: " << stddev() << "\n";
out << "stderr: " << stderror() << "\n";
out << "min: " << min() << "\n";
out << "max: " << max() << "\n\n";
out << "first: " << first_obs() << "\n";
out << "last: " << last_obs() << "\n\n";
out << "counts size: " << (unsigned int) counts.size() << "\n";
break;
}
default:
inherited::newwrite(out);
}
}
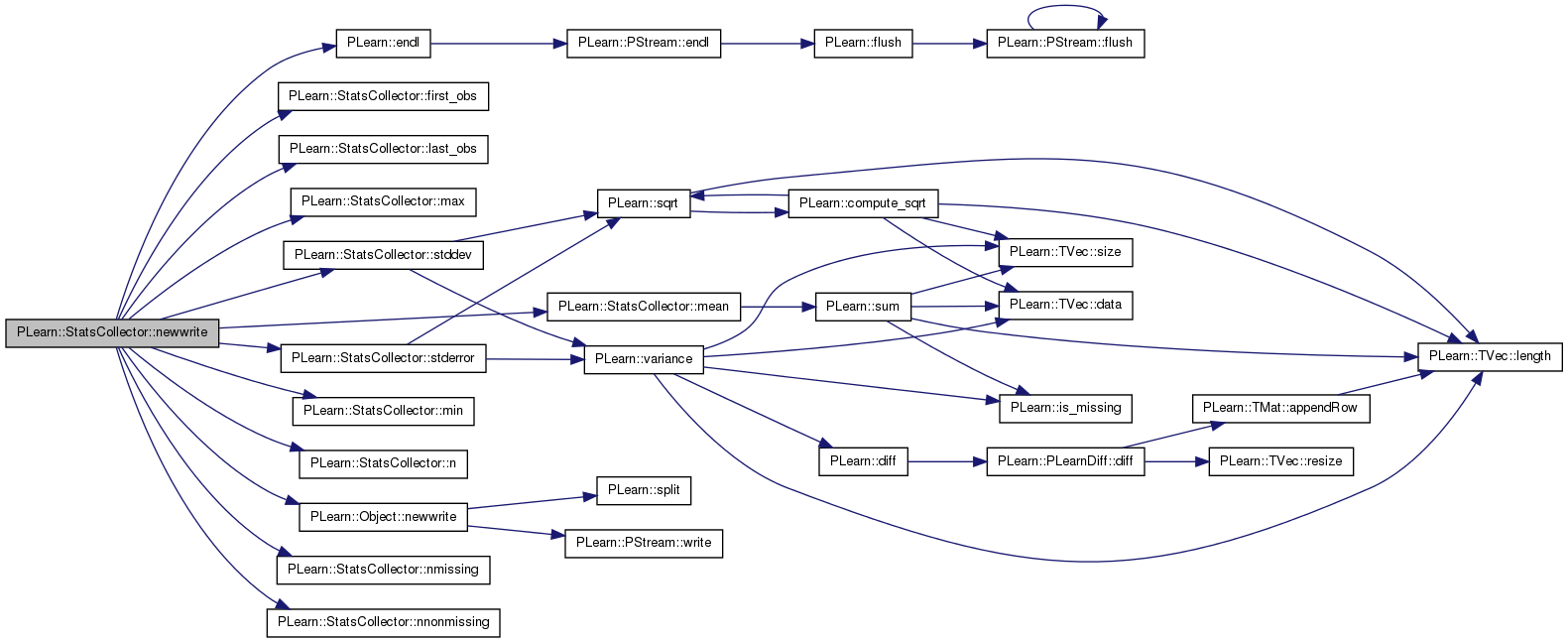
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::nips_lift | ( | ) | const |
NIPS_LIFT statistic (see help).
Definition at line 1293 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References mean_lift().
Referenced by getStat().
{
real pos_fraction;
real result = - mean_lift(&pos_fraction);
real max_performance = 0.5 * (1 / pos_fraction - 1) * (pos_fraction + 1) + 1;
result = (max_performance - result) / max_performance;
return result;
}
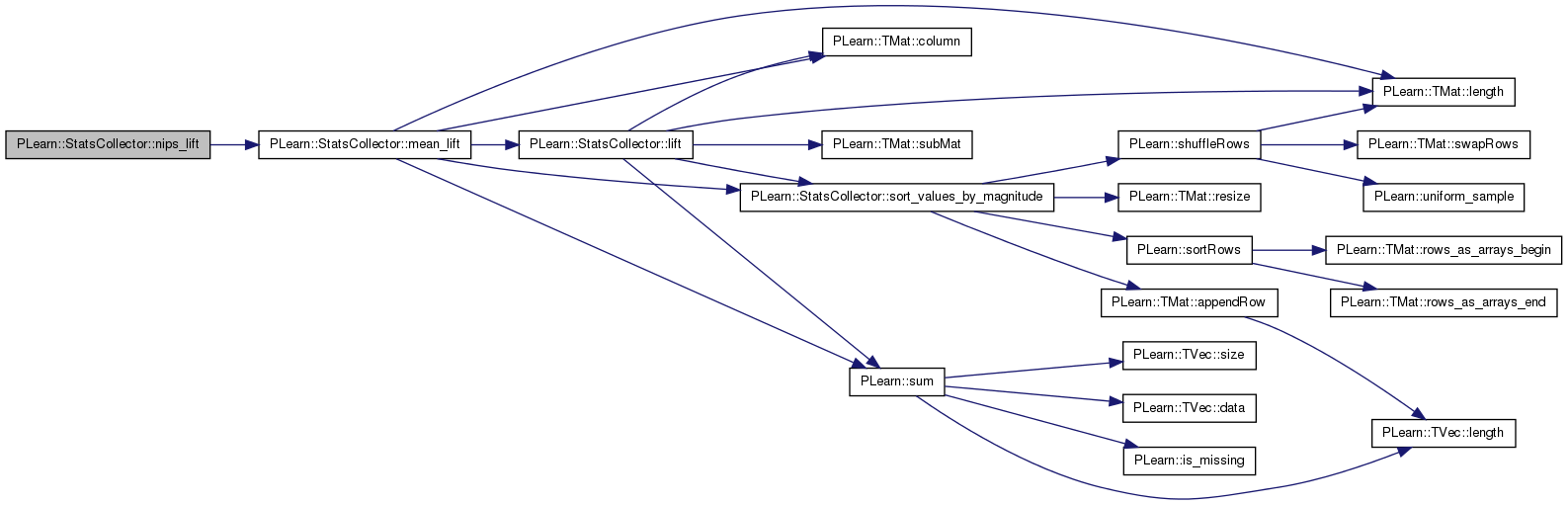
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::nmissing | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 236 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by PLearn::AnalyzeFieldStats::analyzeVariableStats(), PLearn::BasisSelectionRegressor::appendCandidateFunctionsOfSingleField(), PLearn::VMatrix::compareStats(), PLearn::AnalyzeFieldStats::createHeaderFile(), declareMethods(), PLearn::AnalyzeFieldStats::getHeaderRecord(), getStat(), newwrite(), PLearn::VMatrix::printFieldInfo(), PLearn::AnalyzeFieldStats::reviewGlobalStats(), PLearn::NormalizationLearner::train(), and PLearn::vmatmain().
{ return nmissing_; }
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::nnonmissing | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 237 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by PLearn::BasisSelectionRegressor::appendCandidateFunctionsOfSingleField(), PLearn::VariableDeletionVMatrix::build_(), calculate_binary_integer(), declareMethods(), getStat(), newwrite(), PLearn::VMatrix::printFieldInfo(), PLearn::NatGradSMPNNet::pvGradUpdate(), PLearn::vmatmain(), and zpr1t().
{ return nnonmissing_; }
| void PLearn::StatsCollector::oldwrite | ( | ostream & | out | ) | const [virtual] |
Definition at line 1093 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References counts, max_, maxnvalues, min_, nmissing_, nnonmissing_, sum_, sumsquare_, PLearn::Object::write(), PLearn::writeField(), PLearn::writeFieldName(), PLearn::writeFooter(), PLearn::writeHeader(), and PLearn::writeNewline().
{
writeHeader(out,"StatsCollector",0);
writeField(out, "nmissing_", nmissing_);
writeField(out, "nnonmissing_", nnonmissing_);
writeField(out, "sum_", sum_);
writeField(out, "sumsquare_", sumsquare_);
writeField(out, "min_", min_);
writeField(out, "max_", max_);
writeField(out, "maxnvalues", maxnvalues);
writeFieldName(out, "counts");
PLearn::write(out, (int)counts.size());
writeNewline(out);
map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator it = counts.begin();
map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator itend = counts.end();
for(; it!=itend; ++it)
{
PLearn::write(out, it->first);
PLearn::write(out, it->second.n);
PLearn::write(out, it->second.nbelow);
PLearn::write(out, it->second.sum);
PLearn::write(out, it->second.sumsquare);
writeNewline(out);
}
writeFooter(out,"StatsCollector");
}
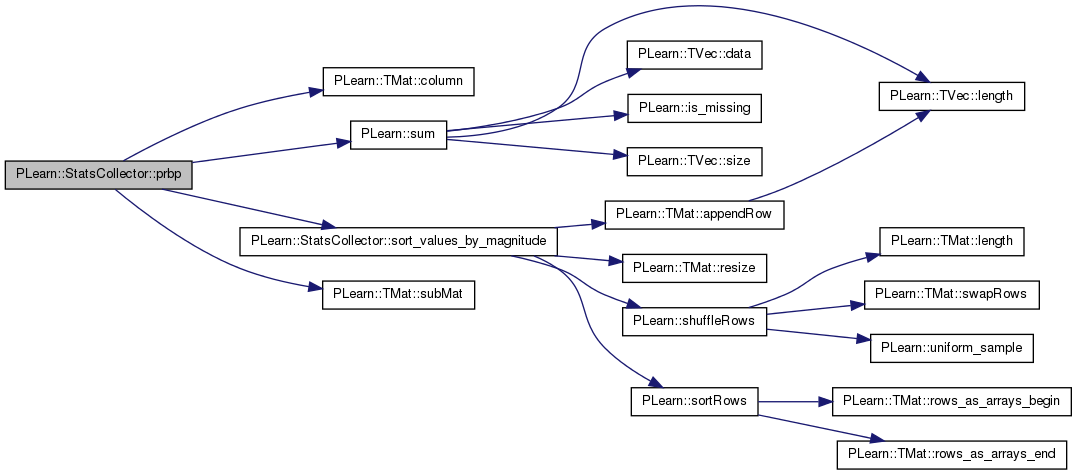
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::prbp | ( | ) | const |
PRBP statistic (see help).
Definition at line 1328 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::column(), more_than_maxnvalues, PLWARNING, sort_values_by_magnitude(), sorted, sorted_values, PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), and PLearn::sum().
Referenced by getStat().
{
if (more_than_maxnvalues)
PLWARNING("In StatsCollector::prbp - You need to increase 'maxnvalues'"
" (or set it to -1) to get an accurate statistic");
if (!sorted)
sort_values_by_magnitude();
int n_pos = int(round(PLearn::sum(sorted_values.column(1))));
int n_pos_at_prbp = int(round(PLearn::sum(sorted_values.subMat(0, 1, n_pos, 1))));
return - 100 * n_pos_at_prbp / real(n_pos);
}
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::prr | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 274 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by getStat().
{ return pseudo_quantile(0.99) - pseudo_quantile(0.01); }
Return the position of the pseudo-quantile Q.
This is derived from the bin-mapping, so maxnvalues must not be zero for this function to return something meaningful.
Definition at line 1013 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References counts, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), PLearn::is_missing(), MISSING_VALUE, nnonmissing_, and PLASSERT.
Referenced by getStat(), and PLearn::NatGradSMPNNet::train().
{
// Basic strategy is to iterate over the bins and stop when the fraction
// of total observations crosses q. Then we linearly interpolate between
// the previous bin and the current one.
map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator
it = counts.begin(), end = counts.end();
real previous_total = 0.0;
real current_total = MISSING_VALUE;
real previous_position = MISSING_VALUE;
if (fast_exact_is_equal(nnonmissing_, 0))
return MISSING_VALUE;
for ( ; it != end ; ++it ) {
current_total = previous_total + it->second.n + it->second.nbelow;
if (is_missing(current_total) ||
current_total / nnonmissing_ >= q)
break;
previous_total = current_total;
previous_position = it->first;
}
// Boudary case if we did not collect any count statistics
if (is_missing(current_total))
return MISSING_VALUE;
// If we stopped at the first bin, do not interpolate with previous bin
PLASSERT( it != end );
if (is_missing(previous_position))
return it->first;
// If we stopped at last bin, do not interpolate with current bin which
// should be equal to FLT_MAX
if (fast_exact_is_equal(it->first, FLT_MAX))
return previous_position;
// Otherwise, interpolate linearly between previous_position and
// current_position
real current_position = it->first;
real slope = (current_position - previous_position) /
(current_total - previous_total);
return slope * (q * nnonmissing_ - previous_total) + previous_position;
}
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::range | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 250 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareMethods(), PLearn::VMatrix::getBoundingBox(), and getStat().
update statistics as if an observation of value val was removed of the observation sequence.
Definition at line 637 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References agemax_, agemin_, counts, PLearn::endl(), PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), first_, PLearn::is_missing(), last_, max_, maxnvalues, min_, MISSING_VALUE, nmissing_, nnonmissing_, no_removal_warnings, PLearn::perr, PLASSERT, PLERROR, PLWARNING, sorted, PLearn::SQRT2_ABSOLUTE_TOLERANCE, PLearn::SQRT_ABSOLUTE_TOLERANCE, storeCounts(), sum_, sumcube_, sumfourth_, sumsquare_, and sumsquarew_.
{
if(is_missing(val))
{
nmissing_ -= weight;
PLASSERT( nmissing_ >= 0 );
}
else
{
sorted = false;
nnonmissing_ -= weight;
sumsquarew_ -= weight * weight;
PLASSERT( nnonmissing_ >= 0 );
PLASSERT( sumsquarew_ >= 0 );
if( !no_removal_warnings )
{
if(fast_exact_is_equal(val, first_))
PLWARNING( "Removed value is equal to the first value encountered.\n"
"StatsCollector::first() may not be valid anymore." );
if(fast_exact_is_equal(val, last_))
PLWARNING( "Removed value is equal to the last value encountered.\n"
"StatsCollector::last() may not be valid anymore." );
if(fast_exact_is_equal(val, min_))
PLWARNING( "Removed value is equal to the min value encountered.\n"
"StatsCollector::min() may not be valid anymore." );
if(fast_exact_is_equal(val, max_))
PLWARNING( "Removed value is equal to the max value encountered.\n"
"StatsCollector::max() may not be valid anymore." );
}
double sqval = (val-first_)*(val-first_);
sum_ -= (val-first_) * weight;
sumsquare_ -= sqval * weight;
sumcube_ -= sqval*(val-first_) * weight;
sumfourth_ -= sqval*sqval * weight;
if(fast_exact_is_equal(nnonmissing_, 0)) {
// We removed the last observation. It may be safer to reset
// everything so that numerical approximations do not lead to
// negative values for statistics that should always be
// positive. We don't call forget() since missing values' count
// would be lost...
min_ = max_ = agemin_ = agemax_ = first_ = last_ = MISSING_VALUE;
sum_ = sumsquare_ = sumcube_ = sumfourth_ = sumsquarew_ = 0.0;
}
// assertion is after previous check for nnonmissing_, since the last
// subtraction of sumsquare might have left sumsquare very slightly
// negative due to roundoff errors
if (-SQRT_ABSOLUTE_TOLERANCE < sumsquare_ && sumsquare_ < 0.0)
sumsquare_ = 0.0;
if (-SQRT2_ABSOLUTE_TOLERANCE < sumfourth_ && sumfourth_ < 0.0)
sumfourth_ = 0.0;
if ( sumsquare_ < 0.0 || sumfourth_ < 0.0 )
{
perr << "this = " << endl << *this << endl << endl;
PLERROR("Improper call to remove_observation "
"sumsquare_ = %g < 0.0 || sumfourth_ = %g < 0.0", sumsquare_, sumfourth_);
}
if(storeCounts())
{
if ( maxnvalues > 0 )
PLERROR("The remove observation mechanism is incompatible with "
"maxnvalues > 0.");
// Find the associated count and decrement. Note that I do not
// verify whether the count reaches 0.0. A null count does not have
// any impact on pseudo_quantile() while removing the element from
// the map could mess up with ids...
counts[val].n -= weight;
}
}
}
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::sharperatio | ( | ) | const |
Definition at line 1238 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References PLearn::is_equal(), PLearn::is_missing(), m, mean(), MISSING_VALUE, and stddev().
Referenced by declareMethods(), and getStat().
{
// Be careful because due to numerical errors, it is possible to get data
// series with extremely small returns and standard deviations, where we
// would be expecting a SharpeRatio of "exactly" 0.0.
real m = mean();
real s = stddev();
if (is_missing(m) || is_missing(s))
return MISSING_VALUE;
else if (is_equal(m, 0.0) || is_equal(s, 0.0))
return 0.0;
else
return m/s;
}
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::skewness | ( | ) | const |
Definition at line 1203 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References PLearn::diff(), first_, mean(), nnonmissing_, stddev(), sum_, sumcube_, and sumsquare_.
Referenced by declareMethods(), getStat(), and mean_over_skewness_ms().
{
// numerator
double diff = first_ - mean();
double numerator = sumcube_/nnonmissing_ +
(3*sumsquare_/nnonmissing_ + diff*(3*(sum_/nnonmissing_) + diff))*diff;
// denominator
double denominator = stddev();
denominator *= denominator * denominator;
return numerator / denominator;
}

| void PLearn::StatsCollector::sort_values_by_magnitude | ( | ) | const [protected] |
Sort values stored in 'counts' by magnitude, so as to fill 'sorted_values'.
Definition at line 1378 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::appendRow(), counts, i, PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), PLearn::shuffleRows(), sorted, sorted_values, and PLearn::sortRows().
Referenced by lift(), mean_lift(), and prbp().
{
sorted_values.resize(0, 2);
Vec to_add(2);
real val;
for (map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::const_iterator it = counts.begin();
it != counts.end(); it++) {
val = it->first;
to_add[0] = fabs(val);
to_add[1] = val > 0 ? 1 : 0;
for (int i = 0; i < it->second.n; i++)
sorted_values.appendRow(to_add);
}
// The STL map may have somehow performed some kind of sort, which could
// lead to a very specific sort when some predictions are equal (instead of
// a random one). Thus we make sure everything is shuffled first.
shuffleRows(sorted_values);
sortRows(sorted_values, 0, false); // Sort by decreasing order of first column.
sorted = true;
}

| real PLearn::StatsCollector::stddev | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 260 of file StatsCollector.h.
References PLearn::sqrt(), and PLearn::variance().
Referenced by PLearn::BasisSelectionRegressor::appendCandidateFunctionsOfSingleField(), declareMethods(), getStat(), kurtosis(), newwrite(), PLearn::VMatrix::printFieldInfo(), PLearn::GaussianizeVMatrix::setMetaDataDir(), sharperatio(), skewness(), and PLearn::NormalizationLearner::train().
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::stderror | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 263 of file StatsCollector.h.
References PLearn::sqrt(), and PLearn::variance().
Referenced by PLearn::VMatrix::compareStats(), declareMethods(), getStat(), newwrite(), PLearn::NatGradSMPNNet::pvGradUpdate(), PLearn::NatGradSMPNNet::train(), PLearn::DeepReconstructorNet::trainSupervisedLayer(), and PLearn::vmatmain().
{ return sqrt(variance()/nnonmissing()); }
| bool PLearn::StatsCollector::storeCounts | ( | ) | [inline, protected] |
Return 'true' iff this StatsCollector needs to fill the 'counts' map, i.e.
iff maxnvalues is set to either -1 or a strictly positive value.
Definition at line 229 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by build_(), merge(), remove_observation(), and update().
{ return (maxnvalues == -1 || maxnvalues > 0); }
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::sum | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 239 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareMethods(), getStat(), merge(), PLearn::VMatrix::printFieldInfo(), and PLearn::StatsCommand::run().
{ return real(nnonmissing_ > 0
? sum_ + nnonmissing_*first_
: 0); }
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::sumsquare | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 242 of file StatsCollector.h.
References PLearn::sum().
Referenced by declareMethods(), getStat(), and merge().
{ return real(nnonmissing_ > 0
? sumsquare_+2*first_*sum() -
first_*first_*nnonmissing_
: 0); }
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::sumsquarew | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 238 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareMethods().
{ return sumsquarew_; }

update statistics with next value val of sequence
Definition at line 539 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References agemax_, agemin_, approximate_counts, binary_, count_ids, counts, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), first_, integer_, PLearn::is_missing(), last_, max_, maxnvalues, min_, more_than_maxnvalues, nmissing_, nnonmissing_, PLWARNING, sorted, storeCounts(), sum_, sumcube_, sumfourth_, sumsquare_, and sumsquarew_.
Referenced by PLearn::ScoreLayerVariable::build_(), PLearn::RepeatSplitter::build_(), getAllValuesMapping(), PLearn::printDistanceStatistics(), PLearn::NatGradSMPNNet::train(), and PLearn::ConditionalDensityNet::train().
{
if(is_missing(val))
nmissing_ += weight;
else
{
// Updating with an inf produces a warning for now -- many tests still
// rely on this behavior, although it should be deprecated
if (isinf(val))
PLWARNING("Updating a StatsCollector with an 'inf'; check for a division by zero");
//sum_ += val * weight;
//sumsquare_ += val*val * weight;
last_ = val;
if(fast_exact_is_equal(nnonmissing_,0)) { // first value encountered
min_ = max_ = first_ = last_ = val;
agemin_ = 0;
agemax_ = 0;
binary_ = true;
integer_ = true;
}
else if(val<min_) {
min_ = val;
agemin_ = 0;
++agemax_;
}
else if(val>max_) {
max_ = val;
agemax_ = 0;
++agemin_;
}
else {
++agemax_; // works even if they are missing
++agemin_;
}
nnonmissing_ += weight;
sumsquarew_ += weight * weight;
double sqval = (val-first_)*(val-first_);
sum_ += (val-first_) * weight;
sumsquare_ += sqval * weight;
sumcube_ += sqval*(val-first_) * weight;
sumfourth_ += sqval*sqval * weight;
if(!(fast_exact_is_equal(val,0) ||fast_exact_is_equal(val,1)))
binary_ = false;
if(!fast_exact_is_equal(val,int(round(val))))
integer_ = false;
if (storeCounts())
{
// Also remembering statistics inside values ranges.
sorted = false;
map<real,StatsCollectorCounts>::iterator it;
if(maxnvalues == -1 || int(counts.size())<=maxnvalues)
{
// Still remembering new unseen values
it = counts.find(val);
if(it==counts.end()) {
// Create a new entry.
// Note that doing this in a single operation is not recommended.
// Indeed, depending on the compiler, counts.size() may differ by 1
// because the [] operator may be called before or after. That's why
// we explicitly call counts.size() first.
int id = int(counts.size());
counts[val].id = id;
count_ids[id]= val;
}
counts[val].n += weight;
}
else // We've filled up counts already
{
it = counts.lower_bound(val);
// TODO Should we allow approximate match? Note that it could
// potentially be a bit dangerous... But also maybe necessary
// when reloading a saved StatsCollector.
if(fast_exact_is_equal(it->first, val)) // found the exact value
it->second.n += weight;
else // found the value just above val (possibly FLT_MAX)
{
more_than_maxnvalues = true;
it->second.nbelow += weight;
it->second.sum += val * weight;
it->second.sumsquare += val*val * weight;
}
}
// Erase the approximate counts if they existed previously (less
// efficient, but easier to code).
if (!approximate_counts.empty())
approximate_counts.clear();
}
}
}
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::variance | ( | ) | const [inline] |
The normalization for variance (nnonmissing_ - sumsquarew_/nnonmissing_) is defined so that the estimator is unbiased.
When all weights are equal to 1, it reduces to the traditional (n-1) coefficient. The estimator is unbiased under the assumption that the weights are fixed and the samples are i.i.d. according to a Gaussian distribution.
Definition at line 257 of file StatsCollector.h.
References PLearn::square().
Referenced by declareMethods(), getStat(), PLearn::vmatmain(), and zpr1t().
{ return real((sumsquare_ - square(sum_)/nnonmissing_)/
(nnonmissing_ - sumsquarew_/nnonmissing_))
+ epsilon; }

| real PLearn::StatsCollector::zpr1t | ( | ) | const |
one-tailed P(zstat())
Definition at line 1412 of file StatsCollector.cc.
References PLearn::is_missing(), m, mean(), MISSING_VALUE, nnonmissing(), PLearn::p_value(), and variance().
Referenced by getStat(), and zpr2t().
{
real m = mean(), v = variance();
if (is_missing(m) || is_missing(v))
return MISSING_VALUE;
else
return p_value(mean(), variance()/nnonmissing());
}
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::zpr2t | ( | ) | const |
| real PLearn::StatsCollector::zstat | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 270 of file StatsCollector.h.
References PLearn::mean().
Referenced by getStat().
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 140 of file StatsCollector.h.
how many observations ago the max was observed
Definition at line 186 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), forget(), merge(), remove_observation(), and update().
how many observations ago the min was observed
Definition at line 185 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), forget(), merge(), remove_observation(), and update().
map<real, StatsCollectorCounts> PLearn::StatsCollector::approximate_counts [protected] |
This map is only created when getApproximateCounts() is called.
Definition at line 199 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by forget(), getApproximateCounts(), merge(), and update().
true if all seen variable are 0 or 1, -1 in some case
Definition at line 190 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by calculate_binary_integer(), declareOptions(), forget(), and update().
Definition at line 194 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by build_(), declareOptions(), merge(), and update().
Definition at line 193 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by build_(), calculate_binary_integer(), cdf(), declareOptions(), dmodes(), forget(), getAllValuesMapping(), getApproximateCounts(), getBinMapping(), merge(), newwrite(), oldwrite(), PLearn::VMatrix::printFieldInfo(), pseudo_quantile(), remove_observation(), sort_values_by_magnitude(), and update().
Small regularizing value to be added to the variance (V) estimator (and indirectly, to standard deviation (STDDEV)).
This permits dividing by the standard deviation to perform a normalization, without fearing a division by zero. Forwarded from the option of the same name in VecStatsCollector if this StatsCollector belong in one.
Definition at line 140 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), and getAllValuesMapping().
first encountered nonmissing observation
Definition at line 187 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), forget(), kurtosis(), merge(), remove_observation(), skewness(), and update().
true if all seen variable are integer, -1 in some case
Definition at line 191 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by calculate_binary_integer(), declareOptions(), forget(), and update().
last encountered nonmissing observation
Definition at line 188 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), forget(), merge(), remove_observation(), and update().
the max
Definition at line 184 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by cdf(), declareOptions(), forget(), getBinMapping(), merge(), oldwrite(), remove_observation(), and update().
Maximum number of different values to keep track of in counts.
If -1, we will keep track of all different values. If 0, we will only keep track of global statistics.
Definition at line 160 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by build_(), calculate_binary_integer(), declareOptions(), forget(), merge(), oldwrite(), PLearn::VMatrix::printFieldInfo(), remove_observation(), PLearn::ConditionalDensityNet::train(), and update().
the min
Definition at line 183 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by cdf(), declareOptions(), forget(), getBinMapping(), merge(), oldwrite(), remove_observation(), and update().
Definition at line 189 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by build_(), calculate_binary_integer(), declareOptions(), forget(), lift(), mean_lift(), merge(), prbp(), and update().
(weighted) number of missing values
Definition at line 176 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), forget(), getAllValuesMapping(), getBinMapping(), merge(), oldwrite(), remove_observation(), and update().
(weighted) number of non missing value
Definition at line 177 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by calculate_binary_integer(), cdf(), declareOptions(), forget(), getAllValuesMapping(), getBinMapping(), kurtosis(), merge(), oldwrite(), pseudo_quantile(), remove_observation(), skewness(), and update().
If the remove_observation mecanism is used and the removed value is equal to one of first_, last_, min_ or max_, the default behavior is to warn the user.
If one want to disable this feature, he may set no_removal_warnings to true.
Default: false (0).
Definition at line 172 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), and remove_observation().
bool PLearn::StatsCollector::sorted [mutable, protected] |
Set to 1 when the values stored in 'counts' are sorted and stored in 'sorted_values'.
Definition at line 206 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by forget(), lift(), mean_lift(), merge(), prbp(), remove_observation(), sort_values_by_magnitude(), and update().
Mat PLearn::StatsCollector::sorted_values [mutable, protected] |
Used to store the sorted values (after taking their absolute value), with their target value (1 or 0) in the second column.
Definition at line 203 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by lift(), mean_lift(), prbp(), and sort_values_by_magnitude().
| double PLearn::StatsCollector::sum_ |
sum of all (values-first_)
Definition at line 179 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), forget(), kurtosis(), merge(), oldwrite(), remove_observation(), skewness(), and update().
sum of cube of all (values-first_)
Definition at line 181 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), forget(), kurtosis(), merge(), remove_observation(), skewness(), and update().
sum of fourth-power of all (values-first_)
Definition at line 182 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), forget(), kurtosis(), merge(), remove_observation(), and update().
sum of square of all (values-first_)
Definition at line 180 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), forget(), kurtosis(), merge(), oldwrite(), remove_observation(), skewness(), and update().
sum of square of all weights
Definition at line 178 of file StatsCollector.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), forget(), merge(), remove_observation(), and update().
 1.7.4
1.7.4