|
PLearn 0.1
|
|
PLearn 0.1
|
Layer in an RBM formed with binomial units, with lateral connections. More...
#include <RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| RBMLateralBinomialLayer (real the_learning_rate=0.) | |
| Default constructor. | |
| virtual void | reset () |
| resets activations, sample and expectation fields | |
| virtual void | clearStats () |
| resets the statistics and counts | |
| virtual void | forget () |
| forgets everything | |
| virtual void | generateSample () |
| generate a sample, and update the sample field | |
| virtual void | generateSamples () |
| Inherited. | |
| virtual void | computeExpectation () |
| Compute expectation. | |
| virtual void | computeExpectations () |
| Compute mini-batch expectations. | |
| virtual void | fprop (const Vec &input, Vec &output) const |
| forward propagation | |
| virtual void | fprop (const Mat &inputs, Mat &outputs) |
| Batch forward propagation. | |
| virtual void | fprop (const Vec &input, const Vec &rbm_bias, Vec &output) const |
| forward propagation with provided bias | |
| virtual void | bpropUpdate (const Vec &input, const Vec &output, Vec &input_gradient, const Vec &output_gradient, bool accumulate=false) |
| back-propagates the output gradient to the input | |
| virtual void | bpropUpdate (const Vec &input, const Vec &rbm_bias, const Vec &output, Vec &input_gradient, Vec &rbm_bias_gradient, const Vec &output_gradient) |
| back-propagates the output gradient to the input and the bias | |
| virtual void | bpropUpdate (const Mat &inputs, const Mat &outputs, Mat &input_gradients, const Mat &output_gradients, bool accumulate=false) |
| Back-propagate the output gradient to the input, and update parameters. | |
| virtual real | fpropNLL (const Vec &target) |
| Computes the negative log-likelihood of target given the internal activations of the layer. | |
| virtual void | fpropNLL (const Mat &targets, const Mat &costs_column) |
| virtual void | bpropNLL (const Vec &target, real nll, Vec &bias_gradient) |
| Computes the gradient of the negative log-likelihood of target with respect to the layer's bias, given the internal activations. | |
| virtual void | bpropNLL (const Mat &targets, const Mat &costs_column, Mat &bias_gradients) |
| virtual void | accumulatePosStats (const Vec &pos_values) |
| Accumulates positive phase statistics. | |
| virtual void | accumulatePosStats (const Mat &ps_values) |
| virtual void | accumulateNegStats (const Vec &neg_values) |
| Accumulates negative phase statistics. | |
| virtual void | accumulateNegStats (const Mat &neg_values) |
| virtual void | update () |
| Update bias and lateral connections parameters according to accumulated statistics. | |
| virtual void | update (const Vec &grad) |
| Updates ONLY the bias parameters according to the given gradient. | |
| virtual void | update (const Vec &pos_values, const Vec &neg_values) |
| Update bias and lateral connections parameters according to one pair of vectors. | |
| virtual void | update (const Mat &pos_values, const Mat &neg_values) |
| Update bias and lateral connections parameters according to one pair of matrices. | |
| virtual void | updateCDandGibbs (const Mat &pos_values, const Mat &cd_neg_values, const Mat &gibbs_neg_values, real background_gibbs_update_ratio) |
| virtual void | updateGibbs (const Mat &pos_values, const Mat &gibbs_neg_values) |
| virtual real | energy (const Vec &unit_values) const |
| compute -bias' unit_values | |
| virtual real | freeEnergyContribution (const Vec &unit_activations) const |
| This function is not implemented for this class (returns an error) | |
| virtual int | getConfigurationCount () |
| Returns a number of different configurations the layer can be in. | |
| virtual void | getConfiguration (int conf_index, Vec &output) |
| Computes the conf_index configuration of the layer. | |
| virtual string | classname () const |
| virtual OptionList & | getOptionList () const |
| virtual OptionMap & | getOptionMap () const |
| virtual RemoteMethodMap & | getRemoteMethodMap () const |
| virtual RBMLateralBinomialLayer * | deepCopy (CopiesMap &copies) const |
| virtual void | build () |
| Post-constructor. | |
| virtual void | makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy (CopiesMap &copies) |
| Transforms a shallow copy into a deep copy. | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static string | _classname_ () |
| static OptionList & | _getOptionList_ () |
| static RemoteMethodMap & | _getRemoteMethodMap_ () |
| static Object * | _new_instance_for_typemap_ () |
| static bool | _isa_ (const Object *o) |
| static void | _static_initialize_ () |
| static const PPath & | declaringFile () |
Public Attributes | |
| int | n_lateral_connections_passes |
| Number of passes through the lateral connections. | |
| real | dampening_factor |
| Dampening factor ( expectation_t = (1-df) * currrent mean field + df * expectation_{t-1}) | |
| real | mean_field_precision_threshold |
| Mean-field precision threshold that, once reached, stops the mean-field expectation approximation computation. | |
| int | topographic_length |
| Length of the topographic map. | |
| int | topographic_width |
| Width of the topographic map. | |
| int | topographic_patch_vradius |
| Vertical radius of the topographic local weight patches. | |
| int | topographic_patch_hradius |
| Horizontal radius of the topographic local weight patches. | |
| real | topographic_lateral_weights_init_value |
| Initial value for the topographic_lateral_weights. | |
| bool | do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights |
| Indication that the topographic_lateral_weights should be fixed at their initial value. | |
| Mat | lateral_weights |
| Lateral connections. | |
| TVec< Vec > | topographic_lateral_weights |
| Local topographic lateral connections. | |
| Mat | lateral_weights_pos_stats |
| Accumulates positive contribution to the gradient of lateral weights. | |
| Mat | lateral_weights_neg_stats |
| Accumulates negative contribution to the gradient of lateral weights. | |
| bool | use_parametric_mean_field |
| Indication that a parametric predictor of the mean-field approximation of the hidden layer conditional distribution. | |
| Mat | mean_field_output_weights |
| Output weights of the mean field predictor. | |
| Vec | mean_field_output_bias |
| Output bias of the mean field predictor. | |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static StaticInitializer | _static_initializer_ |
Protected Member Functions | |
| void | externalSymetricProductAcc (const Mat &mat, const Vec &v1, const Vec &v2) |
| Computes mat[i][j] += 0.5 * (v1[i] * v2[j] + v1[j] * v2[i]) | |
| void | productTopoLateralWeights (const Vec &result, const Vec &input) const |
| void | productTopoLateralWeightsGradients (const Vec &input, const Vec &input_gradient, const Vec &result_gradient, const TVec< Vec > &weights_gradient) |
| void | updateTopoLateralWeightsCD (const Vec &pos_values, const Vec &neg_values) |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static void | declareOptions (OptionList &ol) |
| Declares the class options. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| Vec | dampening_expectation |
| Mat | dampening_expectations |
| Vec | mean_field_input |
| Vec | pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output |
| TVec< Vec > | temp_output |
| TVec< Mat > | temp_outputs |
| Vec | current_temp_output |
| Vec | previous_temp_output |
| Mat | current_temp_outputs |
| Mat | previous_temp_outputs |
| Vec | bias_plus_input |
| Mat | bias_plus_inputs |
| Vec | temp_input_gradient |
| Vec | temp_mean_field_gradient |
| Vec | temp_mean_field_gradient2 |
| Mat | lateral_weights_gradient |
| Mat | lateral_weights_inc |
| TVec< Vec > | topographic_lateral_weights_gradient |
Private Types | |
| typedef RBMLayer | inherited |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | build_ () |
| This does the actual building. | |
Layer in an RBM formed with binomial units, with lateral connections.
Definition at line 52 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
typedef RBMLayer PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::inherited [private] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 54 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
| PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::RBMLateralBinomialLayer | ( | real | the_learning_rate = 0. | ) |
Default constructor.
Definition at line 53 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
:
inherited( the_learning_rate ),
n_lateral_connections_passes( 1 ),
dampening_factor( 0. ),
mean_field_precision_threshold( 0. ),
topographic_length( -1 ),
topographic_width( -1 ),
topographic_patch_vradius( 5 ),
topographic_patch_hradius( 5 ),
topographic_lateral_weights_init_value( 0. ),
do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights( false ),
use_parametric_mean_field( false )
{
}
| string PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::_classname_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 51 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
| OptionList & PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::_getOptionList_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 51 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::_getRemoteMethodMap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 51 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 51 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
| Object * PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::_new_instance_for_typemap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 51 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
| StaticInitializer RBMLateralBinomialLayer::_static_initializer_ & PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::_static_initialize_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 51 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::accumulateNegStats | ( | const Mat & | neg_values | ) | [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1565 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::accumulateNegStats(), lateral_weights_neg_stats, and PLearn::transposeProductAcc().
{
inherited::accumulateNegStats( neg_values);
transposeProductAcc(lateral_weights_neg_stats, neg_values, neg_values);
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::accumulateNegStats | ( | const Vec & | neg_values | ) | [virtual] |
Accumulates negative phase statistics.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1559 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::accumulateNegStats(), PLearn::externalProductAcc(), and lateral_weights_neg_stats.
{
inherited::accumulateNegStats( neg_values);
externalProductAcc(lateral_weights_neg_stats, neg_values, neg_values);
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::accumulatePosStats | ( | const Mat & | ps_values | ) | [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1553 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::accumulatePosStats(), lateral_weights_pos_stats, and PLearn::transposeProductAcc().
{
inherited::accumulatePosStats( pos_values);
transposeProductAcc(lateral_weights_pos_stats, pos_values, pos_values);
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::accumulatePosStats | ( | const Vec & | pos_values | ) | [virtual] |
Accumulates positive phase statistics.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1547 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::accumulatePosStats(), PLearn::externalProductAcc(), and lateral_weights_pos_stats.
{
inherited::accumulatePosStats( pos_values);
externalProductAcc(lateral_weights_pos_stats, pos_values, pos_values);
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::bpropNLL | ( | const Vec & | target, |
| real | nll, | ||
| Vec & | bias_gradient | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Computes the gradient of the negative log-likelihood of target with respect to the layer's bias, given the internal activations.
Will also update the lateral weight connections according to their gradient. Assumes computeExpectation(s) or fpropNLL was called before.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1322 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::clear(), PLearn::TVec< T >::clear(), computeExpectation(), current_temp_output, d, dampening_factor, PLearn::TMat< T >::data(), do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectation, externalSymetricProductAcc(), i, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::input_size, lateral_weights, lateral_weights_gradient, lateral_weights_inc, PLearn::RBMLayer::learning_rate, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::TMat< T >::mod(), PLearn::RBMLayer::momentum, PLearn::multiplyScaledAdd(), n_lateral_connections_passes, PLASSERT, PLERROR, productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(), PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, PLearn::substract(), temp_mean_field_gradient, temp_mean_field_gradient2, temp_output, topographic_lateral_weights, topographic_lateral_weights_gradient, PLearn::transposeProductAcc(), and use_parametric_mean_field.
{
computeExpectation();
PLASSERT( target.size() == input_size );
bias_gradient.resize( size );
bias_gradient.clear();
if( use_parametric_mean_field )
{
PLERROR("RBMLateralBinomialLayer::bpropNLL: use_parametric_mean_field=true "
"not implemented yet.");
}
else
{
// bias_gradient = expectation - target
substract(expectation, target, temp_mean_field_gradient);
current_temp_output = expectation;
lateral_weights_gradient.clear();
real output_i;
for( int t=n_lateral_connections_passes-1 ; t>=0 ; t-- )
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
output_i = current_temp_output[i];
// Contribution from the mean field approximation
temp_mean_field_gradient2[i] = (1-dampening_factor)*
output_i * (1-output_i) * temp_mean_field_gradient[i];
// Contribution from the dampening
temp_mean_field_gradient[i] *= dampening_factor;
}
// Input gradient contribution
bias_gradient += temp_mean_field_gradient2;
// Lateral weights gradient contribution
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0)
{
externalSymetricProductAcc( lateral_weights_gradient,
temp_mean_field_gradient2,
temp_output[t] );
transposeProductAcc(temp_mean_field_gradient, lateral_weights,
temp_mean_field_gradient2);
}
else
{
productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(
temp_output[t],
temp_mean_field_gradient,
temp_mean_field_gradient2,
topographic_lateral_weights_gradient);
}
current_temp_output = temp_output[t];
}
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
output_i = current_temp_output[i];
temp_mean_field_gradient[i] *= output_i * (1-output_i);
}
bias_gradient += temp_mean_field_gradient;
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0)
{
// Update lateral connections
if( momentum == 0. )
{
multiplyScaledAdd( lateral_weights_gradient, 1.0, -learning_rate,
lateral_weights);
}
else
{
multiplyScaledAdd( lateral_weights_gradient, momentum, -learning_rate,
lateral_weights_inc);
lateral_weights += lateral_weights_inc;
}
}
else
{
if( !do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights )
{
if( momentum == 0. )
for( int i=0; i<topographic_lateral_weights.length(); i++ )
multiplyScaledAdd( topographic_lateral_weights_gradient[i], 1.0,
-learning_rate,
topographic_lateral_weights[i]);
else
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer:bpropNLL - Not implemented for "
"topographic weights");
}
}
// Set diagonal to 0
if( lateral_weights.length() != 0 )
{
real *d = lateral_weights.data();
for (int i=0; i<lateral_weights.length(); i++,d+=lateral_weights.mod()+1)
*d = 0;
}
}
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::bpropNLL | ( | const Mat & | targets, |
| const Mat & | costs_column, | ||
| Mat & | bias_gradients | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1431 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::batch_size, PLearn::TMat< T >::clear(), computeExpectations(), current_temp_output, d, dampening_factor, PLearn::TMat< T >::data(), do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectations, externalSymetricProductAcc(), i, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::input_size, j, lateral_weights, lateral_weights_gradient, PLearn::RBMLayer::learning_rate, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::TMat< T >::mod(), PLearn::RBMLayer::momentum, PLearn::multiplyScaledAdd(), n_lateral_connections_passes, PLASSERT, PLERROR, productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(), PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, PLearn::substract(), temp_mean_field_gradient, temp_mean_field_gradient2, temp_outputs, topographic_lateral_weights, topographic_lateral_weights_gradient, PLearn::transposeProductAcc(), use_parametric_mean_field, and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
{
computeExpectations();
PLASSERT( targets.width() == input_size );
PLASSERT( targets.length() == batch_size );
PLASSERT( costs_column.width() == 1 );
PLASSERT( costs_column.length() == batch_size );
bias_gradients.resize( batch_size, size );
bias_gradients.clear();
// TODO Can we do this more efficiently? (using BLAS)
if( use_parametric_mean_field )
{
PLERROR("RBMLateralBinomialLayer::bpropNLL: use_parametric_mean_field=true "
"not implemented yet.");
}
else
{
// We use the average gradient over the mini-batch.
lateral_weights_gradient.clear();
real output_i;
for (int j = 0; j < batch_size; j++)
{
// top_gradient = expectations(j) - targets(j)
substract(expectations(j), targets(j), temp_mean_field_gradient);
current_temp_output = expectations(j);
for( int t=n_lateral_connections_passes-1 ; t>=0 ; t-- )
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
output_i = current_temp_output[i];
// Contribution from the mean field approximation
temp_mean_field_gradient2[i] = (1-dampening_factor)*
output_i * (1-output_i) * temp_mean_field_gradient[i];
// Contribution from the dampening
temp_mean_field_gradient[i] *= dampening_factor;
}
// Input gradient contribution
bias_gradients(j) += temp_mean_field_gradient2;
// Lateral weights gradient contribution
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0)
{
externalSymetricProductAcc( lateral_weights_gradient,
temp_mean_field_gradient2,
temp_outputs[t](j) );
transposeProductAcc(temp_mean_field_gradient, lateral_weights,
temp_mean_field_gradient2);
}
else
{
productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(
temp_outputs[t](j),
temp_mean_field_gradient,
temp_mean_field_gradient2,
topographic_lateral_weights_gradient);
}
current_temp_output = temp_outputs[t](j);
}
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
output_i = current_temp_output[i];
temp_mean_field_gradient[i] *= output_i * (1-output_i);
}
bias_gradients(j) += temp_mean_field_gradient;
}
// Update lateral connections
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0 )
{
if( momentum == 0. )
multiplyScaledAdd( lateral_weights_gradient, 1.0, -learning_rate,
lateral_weights);
else
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer:bpropUpdate - Not implemented for "
"momentum with mini-batches");
}
else
{
if( !do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights )
{
if( momentum == 0. )
for( int i=0; i<topographic_lateral_weights.length(); i++ )
multiplyScaledAdd( topographic_lateral_weights_gradient[i], 1.0,
-learning_rate,
topographic_lateral_weights[i]);
else
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer:bpropNLL - Not implemented for "
"topographic weights");
}
}
// Set diagonal to 0
if( lateral_weights.length() != 0 )
{
real *d = lateral_weights.data();
for (int i=0; i<lateral_weights.length(); i++,d+=lateral_weights.mod()+1)
*d = 0;
}
}
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::bpropUpdate | ( | const Vec & | input, |
| const Vec & | output, | ||
| Vec & | input_gradient, | ||
| const Vec & | output_gradient, | ||
| bool | accumulate = false |
||
| ) | [virtual] |
back-propagates the output gradient to the input
Implements PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 844 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::bias, PLearn::RBMLayer::bias_inc, PLearn::clear(), PLearn::TMat< T >::clear(), PLearn::TVec< T >::clear(), current_temp_output, d, dampening_factor, PLearn::TMat< T >::data(), do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights, PLearn::externalProductScaleAcc(), externalSymetricProductAcc(), i, lateral_weights, lateral_weights_gradient, lateral_weights_inc, PLearn::RBMLayer::learning_rate, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), mean_field_input, mean_field_output_bias, mean_field_output_weights, PLearn::TMat< T >::mod(), PLearn::RBMLayer::momentum, PLearn::multiplyScaledAdd(), n_lateral_connections_passes, PLASSERT, PLASSERT_MSG, PLERROR, productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(), PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), temp_input_gradient, temp_mean_field_gradient, temp_mean_field_gradient2, temp_output, topographic_lateral_weights, topographic_lateral_weights_gradient, PLearn::transposeProductAcc(), and use_parametric_mean_field.
{
PLASSERT( input.size() == size );
PLASSERT( output.size() == size );
PLASSERT( output_gradient.size() == size );
if( accumulate )
PLASSERT_MSG( input_gradient.size() == size,
"Cannot resize input_gradient AND accumulate into it" );
else
{
input_gradient.resize( size );
input_gradient.clear();
}
//if( momentum != 0. )
// bias_inc.resize( size );
if( use_parametric_mean_field )
{
real mean_field_i;
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
mean_field_i = output[i];
temp_mean_field_gradient[i] = output_gradient[i] * mean_field_i * (1 - mean_field_i);
}
transposeProductAcc( input_gradient, mean_field_output_weights, temp_mean_field_gradient );
externalProductScaleAcc( mean_field_output_weights, temp_mean_field_gradient,
mean_field_input, -learning_rate );
multiplyScaledAdd( temp_mean_field_gradient, 1.0, -learning_rate, mean_field_output_bias);
real input_mean_field_i;
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
input_mean_field_i = mean_field_input[i];
input_gradient[i] = input_gradient[i] * input_mean_field_i * (1 - input_mean_field_i);
}
}
else
{
temp_input_gradient.clear();
temp_mean_field_gradient << output_gradient;
current_temp_output = output;
lateral_weights_gradient.clear();
for( int i=0; i<topographic_lateral_weights_gradient.length(); i++)
topographic_lateral_weights_gradient[i].clear();
real output_i;
for( int t=n_lateral_connections_passes-1 ; t>=0 ; t-- )
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
output_i = current_temp_output[i];
// Contribution from the mean field approximation
temp_mean_field_gradient2[i] = (1-dampening_factor)*
output_i * (1-output_i) * temp_mean_field_gradient[i];
// Contribution from the dampening
temp_mean_field_gradient[i] *= dampening_factor;
}
// Input gradient contribution
temp_input_gradient += temp_mean_field_gradient2;
// Lateral weights gradient contribution
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0)
{
externalSymetricProductAcc( lateral_weights_gradient,
temp_mean_field_gradient2,
temp_output[t] );
transposeProductAcc(temp_mean_field_gradient, lateral_weights,
temp_mean_field_gradient2);
}
else
{
productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(
temp_output[t],
temp_mean_field_gradient,
temp_mean_field_gradient2,
topographic_lateral_weights_gradient);
}
current_temp_output = temp_output[t];
}
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
output_i = current_temp_output[i];
temp_mean_field_gradient[i] *= output_i * (1-output_i);
}
temp_input_gradient += temp_mean_field_gradient;
input_gradient += temp_input_gradient;
// Update bias
real in_grad_i;
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
in_grad_i = temp_input_gradient[i];
if( momentum == 0. )
{
// update the bias: bias -= learning_rate * input_gradient
bias[i] -= learning_rate * in_grad_i;
}
else
{
// The update rule becomes:
// bias_inc = momentum * bias_inc - learning_rate * input_gradient
// bias += bias_inc
bias_inc[i] = momentum * bias_inc[i] - learning_rate * in_grad_i;
bias[i] += bias_inc[i];
}
}
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0)
{
if( momentum == 0. )
{
multiplyScaledAdd( lateral_weights_gradient, 1.0, -learning_rate,
lateral_weights);
}
else
{
multiplyScaledAdd( lateral_weights_gradient, momentum, -learning_rate,
lateral_weights_inc);
lateral_weights += lateral_weights_inc;
}
}
else
{
if( !do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights )
{
if( momentum == 0. )
for( int i=0; i<topographic_lateral_weights.length(); i++ )
multiplyScaledAdd( topographic_lateral_weights_gradient[i], 1.0,
-learning_rate,
topographic_lateral_weights[i]);
else
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer:bpropUpdate - Not implemented for "
"topographic weights");
}
}
// Set diagonal to 0
if( lateral_weights.length() != 0 )
{
real *d = lateral_weights.data();
for (int i=0; i<lateral_weights.length(); i++,d+=lateral_weights.mod()+1)
*d = 0;
}
}
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::bpropUpdate | ( | const Vec & | input, |
| const Vec & | rbm_bias, | ||
| const Vec & | output, | ||
| Vec & | input_gradient, | ||
| Vec & | rbm_bias_gradient, | ||
| const Vec & | output_gradient | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
back-propagates the output gradient to the input and the bias
TODO: add "accumulate" here.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1159 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::clear(), PLearn::TVec< T >::clear(), current_temp_output, d, dampening_factor, PLearn::TMat< T >::data(), do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights, externalSymetricProductAcc(), i, lateral_weights, lateral_weights_gradient, lateral_weights_inc, PLearn::RBMLayer::learning_rate, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::TMat< T >::mod(), PLearn::RBMLayer::momentum, PLearn::multiplyScaledAdd(), n_lateral_connections_passes, PLASSERT, PLERROR, productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(), PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, temp_input_gradient, temp_mean_field_gradient, temp_mean_field_gradient2, temp_output, topographic_lateral_weights, topographic_lateral_weights_gradient, PLearn::transposeProductAcc(), and use_parametric_mean_field.
{
PLASSERT( input.size() == size );
PLASSERT( rbm_bias.size() == size );
PLASSERT( output.size() == size );
PLASSERT( output_gradient.size() == size );
input_gradient.resize( size );
rbm_bias_gradient.resize( size );
if( use_parametric_mean_field )
{
PLERROR("RBMLateralBinomialLayer::bpropUpdate: use_parametric_mean_field=true "
"not implemented yet for bias input.");
}
else
{
temp_input_gradient.clear();
temp_mean_field_gradient << output_gradient;
current_temp_output = output;
lateral_weights_gradient.clear();
real output_i;
for( int t=n_lateral_connections_passes-1 ; t>=0 ; t-- )
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
output_i = current_temp_output[i];
// Contribution from the mean field approximation
temp_mean_field_gradient2[i] = (1-dampening_factor)*
output_i * (1-output_i) * temp_mean_field_gradient[i];
// Contribution from the dampening
temp_mean_field_gradient[i] *= dampening_factor;
}
// Input gradient contribution
temp_input_gradient += temp_mean_field_gradient2;
// Lateral weights gradient contribution
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0)
{
externalSymetricProductAcc( lateral_weights_gradient,
temp_mean_field_gradient2,
temp_output[t] );
transposeProductAcc(temp_mean_field_gradient, lateral_weights,
temp_mean_field_gradient2);
}
else
{
productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(
temp_output[t],
temp_mean_field_gradient,
temp_mean_field_gradient2,
topographic_lateral_weights_gradient);
}
current_temp_output = temp_output[t];
}
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
output_i = current_temp_output[i];
temp_mean_field_gradient[i] *= output_i * (1-output_i);
}
temp_input_gradient += temp_mean_field_gradient;
input_gradient << temp_input_gradient;
rbm_bias_gradient << temp_input_gradient;
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0)
{
if( momentum == 0. )
{
multiplyScaledAdd( lateral_weights_gradient, 1.0, -learning_rate,
lateral_weights);
}
else
{
multiplyScaledAdd( lateral_weights_gradient, momentum, -learning_rate,
lateral_weights_inc);
lateral_weights += lateral_weights_inc;
}
}
else
{
if( !do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights )
{
if( momentum == 0. )
for( int i=0; i<topographic_lateral_weights.length(); i++ )
multiplyScaledAdd( topographic_lateral_weights_gradient[i], 1.0,
-learning_rate,
topographic_lateral_weights[i]);
else
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer:bpropUpdate - Not implemented for "
"topographic weights");
}
}
// Set diagonal to 0
if( lateral_weights.length() != 0 )
{
real *d = lateral_weights.data();
for (int i=0; i<lateral_weights.length(); i++,d+=lateral_weights.mod()+1)
*d = 0;
}
}
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::bpropUpdate | ( | const Mat & | inputs, |
| const Mat & | outputs, | ||
| Mat & | input_gradients, | ||
| const Mat & | output_gradients, | ||
| bool | accumulate = false |
||
| ) | [virtual] |
Back-propagate the output gradient to the input, and update parameters.
Implements PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1006 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::bias, PLearn::TMat< T >::clear(), PLearn::TVec< T >::clear(), current_temp_output, d, dampening_factor, PLearn::TMat< T >::data(), do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights, externalSymetricProductAcc(), i, j, lateral_weights, lateral_weights_gradient, PLearn::RBMLayer::learning_rate, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::TMat< T >::mod(), PLearn::RBMLayer::momentum, PLearn::multiplyScaledAdd(), n_lateral_connections_passes, PLASSERT, PLASSERT_MSG, PLERROR, productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(), PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, temp_input_gradient, temp_mean_field_gradient, temp_mean_field_gradient2, temp_outputs, topographic_lateral_weights, topographic_lateral_weights_gradient, PLearn::transposeProductAcc(), use_parametric_mean_field, and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
{
PLASSERT( inputs.width() == size );
PLASSERT( outputs.width() == size );
PLASSERT( output_gradients.width() == size );
int mbatch_size = inputs.length();
PLASSERT( outputs.length() == mbatch_size );
PLASSERT( output_gradients.length() == mbatch_size );
if( accumulate )
{
PLASSERT_MSG( input_gradients.width() == size &&
input_gradients.length() == mbatch_size,
"Cannot resize input_gradients and accumulate into it" );
}
else
{
input_gradients.resize(mbatch_size, size);
input_gradients.clear();
}
//if( momentum != 0. )
// bias_inc.resize( size );
// TODO Can we do this more efficiently? (using BLAS)
// We use the average gradient over the mini-batch.
real avg_lr = learning_rate / inputs.length();
if( use_parametric_mean_field )
{
PLERROR("RBMLateralBinomialLayer::bpropUpdate: use_parametric_mean_field=true "
"not implemented yet for batch mode.");
}
else
{
lateral_weights_gradient.clear();
real output_i;
for (int j = 0; j < mbatch_size; j++)
{
temp_input_gradient.clear();
temp_mean_field_gradient << output_gradients(j);
current_temp_output = outputs(j);
for( int t=n_lateral_connections_passes-1 ; t>=0 ; t-- )
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
output_i = current_temp_output[i];
// Contribution from the mean field approximation
temp_mean_field_gradient2[i] = (1-dampening_factor)*
output_i * (1-output_i) * temp_mean_field_gradient[i];
// Contribution from the dampening
temp_mean_field_gradient[i] *= dampening_factor;
}
// Input gradient contribution
temp_input_gradient += temp_mean_field_gradient2;
// Lateral weights gradient contribution
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0)
{
externalSymetricProductAcc( lateral_weights_gradient,
temp_mean_field_gradient2,
temp_outputs[t](j) );
transposeProductAcc(temp_mean_field_gradient, lateral_weights,
temp_mean_field_gradient2);
}
else
{
productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(
temp_outputs[t](j),
temp_mean_field_gradient,
temp_mean_field_gradient2,
topographic_lateral_weights_gradient);
}
current_temp_output = temp_outputs[t](j);
}
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
output_i = current_temp_output[i];
temp_mean_field_gradient[i] *= output_i * (1-output_i);
}
temp_input_gradient += temp_mean_field_gradient;
input_gradients(j) += temp_input_gradient;
// Update bias
real in_grad_i;
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
in_grad_i = temp_input_gradient[i];
if( momentum == 0. )
{
// update the bias: bias -= learning_rate * input_gradient
bias[i] -= avg_lr * in_grad_i;
}
else
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer:bpropUpdate - Not implemented for "
"momentum with mini-batches");
}
}
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0)
{
if( momentum == 0. )
multiplyScaledAdd( lateral_weights_gradient, 1.0, -learning_rate,
lateral_weights);
else
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer:bpropUpdate - Not implemented for "
"momentum with mini-batches");
}
else
{
if( !do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights )
{
if( momentum == 0. )
for( int i=0; i<topographic_lateral_weights.length(); i++ )
multiplyScaledAdd( topographic_lateral_weights_gradient[i], 1.0,
-learning_rate,
topographic_lateral_weights[i]);
else
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer:bpropUpdate - Not implemented for "
"topographic weights");
}
}
// Set diagonal to 0
if( lateral_weights.length() != 0 )
{
real *d = lateral_weights.data();
for (int i=0; i<lateral_weights.length(); i++,d+=lateral_weights.mod()+1)
*d = 0;
}
}
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::build | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Post-constructor.
The normal implementation should call simply inherited::build(), then this class's build_(). This method should be callable again at later times, after modifying some option fields to change the "architecture" of the object.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1892 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::build(), and build_().
{
inherited::build();
build_();
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::build_ | ( | ) | [private] |
This does the actual building.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1816 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::bias_inc, dampening_expectation, dampening_factor, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), i, lateral_weights, lateral_weights_gradient, lateral_weights_inc, lateral_weights_neg_stats, lateral_weights_pos_stats, mean_field_input, mean_field_output_bias, mean_field_output_weights, PLearn::RBMLayer::momentum, n_lateral_connections_passes, PLERROR, pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output, PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, temp_input_gradient, temp_mean_field_gradient, temp_mean_field_gradient2, topographic_lateral_weights, topographic_lateral_weights_gradient, topographic_length, topographic_patch_hradius, topographic_patch_vradius, topographic_width, and use_parametric_mean_field.
Referenced by build().
{
if( n_lateral_connections_passes == 0 &&
!fast_exact_is_equal(dampening_factor, 0) )
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer::build_(): when not using the lateral\n"
"connections, dampening_factor should be 0.");
if( dampening_factor < 0 || dampening_factor > 1)
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer::build_(): dampening_factor should be\n"
"in [0,1].");
if( n_lateral_connections_passes < 0 )
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer::build_(): n_lateral_connections_passes\n"
" should be >= 0.");
if( use_parametric_mean_field && topographic_length > 0 && topographic_width > 0 )
PLERROR("RBMLateralBinomialLayer::build_(): can't use parametric mean field "
"and topographic lateral connections.");
if( use_parametric_mean_field )
{
mean_field_output_weights.resize(size,size);
mean_field_output_bias.resize(size);
mean_field_input.resize(size);
pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output.resize(size);
}
if( topographic_length <= 0 || topographic_width <= 0)
{
lateral_weights.resize(size,size);
lateral_weights_gradient.resize(size,size);
lateral_weights_pos_stats.resize(size,size);
lateral_weights_neg_stats.resize(size,size);
if( momentum != 0. )
{
bias_inc.resize( size );
lateral_weights_inc.resize(size,size);
}
}
else
{
if( size != topographic_length * topographic_width )
PLERROR( "In RBMLateralBinomialLayer::build_(): size != "
"topographic_length * topographic_width.\n" );
if( topographic_length-1 <= 2*topographic_patch_vradius )
PLERROR( "In RBMLateralBinomialLayer::build_(): "
"topographic_patch_vradius is too large.\n" );
if( topographic_width-1 <= 2*topographic_patch_hradius )
PLERROR( "In RBMLateralBinomialLayer::build_(): "
"topographic_patch_hradius is too large.\n" );
topographic_lateral_weights.resize(size);
topographic_lateral_weights_gradient.resize(size);
for( int i=0; i<size; i++ )
{
topographic_lateral_weights[i].resize(
( 2 * topographic_patch_hradius + 1 ) *
( 2 * topographic_patch_vradius + 1 ) - 1 );
topographic_lateral_weights_gradient[i].resize(
( 2 * topographic_patch_hradius + 1 ) *
( 2 * topographic_patch_vradius + 1 ) - 1 );
}
// Should probably have separate lateral_weights_*_stats
}
// Resizing temporary variables
dampening_expectation.resize(size);
temp_input_gradient.resize(size);
temp_mean_field_gradient.resize(size);
temp_mean_field_gradient2.resize(size);
}

| string PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::classname | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 51 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::clearStats | ( | ) | [virtual] |
resets the statistics and counts
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 74 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::clear(), PLearn::RBMLayer::clearStats(), lateral_weights_neg_stats, and lateral_weights_pos_stats.
{
inherited::clearStats();
lateral_weights_pos_stats.clear();
lateral_weights_neg_stats.clear();
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::computeExpectation | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Compute expectation.
Implements PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 150 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::activation, current_temp_output, dampening_expectation, dampening_factor, PLearn::dist(), PLearn::RBMLayer::expectation, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectation_is_up_to_date, PLearn::externalProductScaleAcc(), PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), PLearn::fastsigmoid(), i, PLearn::TVec< T >::last(), lateral_weights, PLearn::RBMLayer::learning_rate, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), mean_field_input, mean_field_output_bias, mean_field_output_weights, mean_field_precision_threshold, PLearn::multiplyScaledAdd(), n_lateral_connections_passes, pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output, previous_temp_output, PLearn::product(), productTopoLateralWeights(), PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::sigmoid(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, temp_mean_field_gradient, temp_output, topographic_lateral_weights, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::use_fast_approximations, and use_parametric_mean_field.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), and fpropNLL().
{
if( expectation_is_up_to_date )
return;
if( use_parametric_mean_field )
{
if (use_fast_approximations)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
mean_field_input[i] = fastsigmoid( activation[i] );
else
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
mean_field_input[i] = sigmoid( activation[i] );
product(pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output, mean_field_output_weights, mean_field_input);
pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output += mean_field_output_bias;
if (use_fast_approximations)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
expectation[i] = fastsigmoid( pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output[i] );
else
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
expectation[i] = sigmoid( pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output[i] );
// Update mean-field predictor, using KL-divergence gradient:
// dKL/dp_i = -activation[i] - \sum_{j \neq i} p_j + V_i h
// where - V_i is the ith row of mean_field_output_weights
// - h is sigmoid(activation)
real mean_field_i;
product(temp_mean_field_gradient, lateral_weights, expectation);
temp_mean_field_gradient += activation;
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
mean_field_i = expectation[i];
temp_mean_field_gradient[i] = (pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output[i]
- temp_mean_field_gradient[i])
* mean_field_i * (1 - mean_field_i);
}
externalProductScaleAcc( mean_field_output_weights, temp_mean_field_gradient,
mean_field_input, -learning_rate );
multiplyScaledAdd( temp_mean_field_gradient, 1.0, -learning_rate, mean_field_output_bias);
}
else
{
if( temp_output.length() != n_lateral_connections_passes+1 )
{
temp_output.resize(n_lateral_connections_passes+1);
for( int i=0 ; i<n_lateral_connections_passes+1 ; i++ )
temp_output[i].resize(size);
}
current_temp_output = temp_output[0];
temp_output.last() = expectation;
if (use_fast_approximations)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] = fastsigmoid( activation[i] );
else
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] = sigmoid( activation[i] );
for( int t=0; t<n_lateral_connections_passes; t++ )
{
previous_temp_output = current_temp_output;
current_temp_output = temp_output[t+1];
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0 )
product(dampening_expectation, lateral_weights, previous_temp_output);
else
productTopoLateralWeights( dampening_expectation, previous_temp_output );
dampening_expectation += activation;
if (use_fast_approximations)
{
if( fast_exact_is_equal( dampening_factor, 0) )
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] = fastsigmoid( dampening_expectation[i] );
}
else
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] =
(1-dampening_factor) * fastsigmoid( dampening_expectation[i] )
+ dampening_factor * previous_temp_output[i];
}
}
else
{
if( fast_exact_is_equal( dampening_factor, 0) )
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] = sigmoid( dampening_expectation[i] );
}
else
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] =
(1-dampening_factor) * sigmoid( dampening_expectation[i] )
+ dampening_factor * previous_temp_output[i];
}
}
if( !fast_exact_is_equal(mean_field_precision_threshold, 0.) &&
dist(current_temp_output, previous_temp_output,2)/size < mean_field_precision_threshold )
{
expectation << current_temp_output;
break;
}
//cout << sqrt(max(square(current_temp_output-previous_temp_output))) << " ";
//cout << dist(current_temp_output, previous_temp_output,2)/current_temp_output.length() << " ";
}
//cout << endl;
//expectation << current_temp_output;
}
expectation_is_up_to_date = true;
}
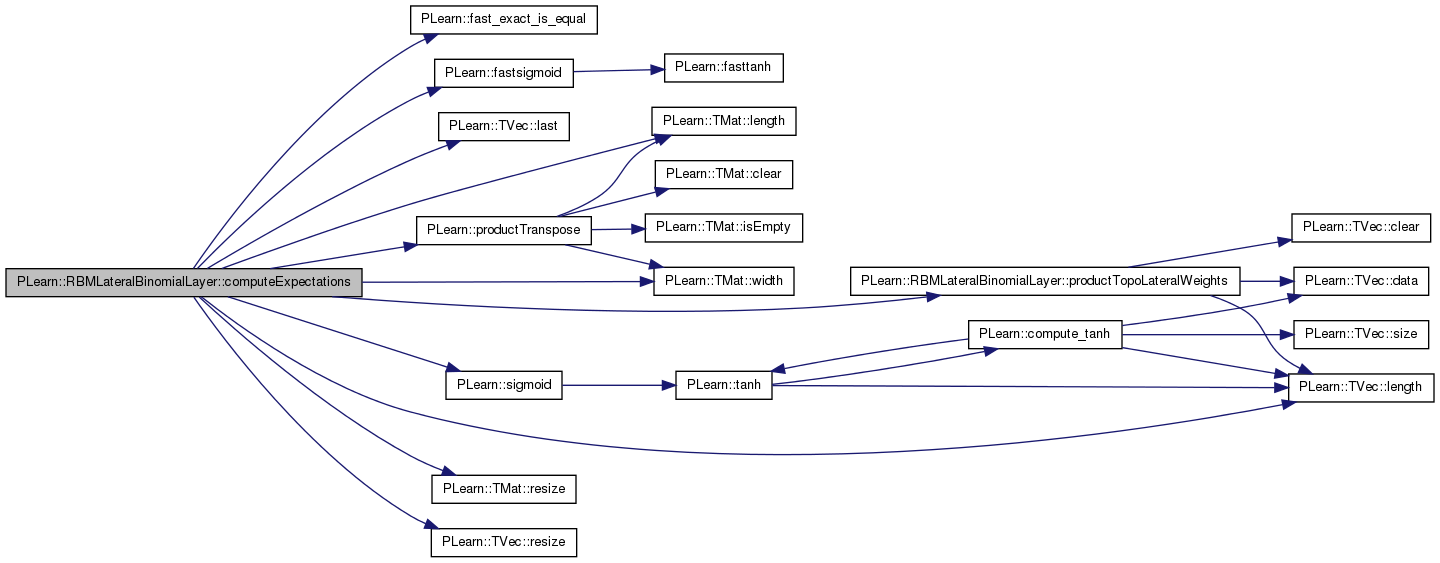
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::computeExpectations | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Compute mini-batch expectations.
Implements PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 270 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::activations, b, PLearn::RBMLayer::batch_size, current_temp_outputs, dampening_expectations, dampening_factor, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectations, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectations_are_up_to_date, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), PLearn::fastsigmoid(), i, PLearn::TVec< T >::last(), lateral_weights, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), n_lateral_connections_passes, PLASSERT, PLERROR, previous_temp_outputs, productTopoLateralWeights(), PLearn::productTranspose(), PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::sigmoid(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, temp_outputs, topographic_lateral_weights, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::use_fast_approximations, use_parametric_mean_field, and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
Referenced by bpropNLL(), and fpropNLL().
{
if( expectations_are_up_to_date )
return;
PLASSERT( expectations.width() == size
&& expectations.length() == batch_size );
if( use_parametric_mean_field )
{
PLERROR("RBMLateralBinomialLayer::computeExpectations(): use_parametric_mean_field=true "
"not implemented yet.");
}
else
{
dampening_expectations.resize( batch_size, size );
if( temp_outputs.length() != n_lateral_connections_passes+1 )
{
temp_outputs.resize(n_lateral_connections_passes+1);
for( int i=0 ; i<n_lateral_connections_passes+1 ; i++ )
temp_outputs[i].resize( batch_size, size);
}
current_temp_outputs = temp_outputs[0];
temp_outputs.last() = expectations;
if (use_fast_approximations)
for (int k = 0; k < batch_size; k++)
for (int i = 0 ; i < size ; i++)
current_temp_outputs(k, i) = fastsigmoid(activations(k, i));
else
for (int k = 0; k < batch_size; k++)
for (int i = 0 ; i < size ; i++)
current_temp_outputs(k, i) = sigmoid(activations(k, i));
for( int t=0; t<n_lateral_connections_passes; t++ )
{
previous_temp_outputs = current_temp_outputs;
current_temp_outputs = temp_outputs[t+1];
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0 )
productTranspose(dampening_expectations, previous_temp_outputs,
lateral_weights);
else
for( int b = 0; b<dampening_expectations.length(); b++)
productTopoLateralWeights( dampening_expectations(b),
previous_temp_outputs(b) );
dampening_expectations += activations;
if (use_fast_approximations)
{
if( fast_exact_is_equal( dampening_factor, 0) )
{
for(int k = 0; k < batch_size; k++)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_outputs(k, i) =
fastsigmoid( dampening_expectations(k, i) );
}
else
{
for(int k = 0; k < batch_size; k++)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_outputs(k, i) = (1-dampening_factor)
* fastsigmoid( dampening_expectations(k, i) )
+ dampening_factor * previous_temp_outputs(k, i);
}
}
else
{
if( fast_exact_is_equal( dampening_factor, 0) )
{
for(int k = 0; k < batch_size; k++)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_outputs(k, i) =
sigmoid( dampening_expectations(k, i) );
}
else
{
for(int k = 0; k < batch_size; k++)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_outputs(k, i) = (1-dampening_factor)
* sigmoid( dampening_expectations(k, i) )
+ dampening_factor * previous_temp_outputs(k, i);
}
}
}
//expectations << current_temp_outputs;
}
expectations_are_up_to_date = true;
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::declareOptions | ( | OptionList & | ol | ) | [static, protected] |
Declares the class options.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1734 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::OptionBase::buildoption, dampening_factor, PLearn::declareOption(), PLearn::RBMLayer::declareOptions(), do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights, lateral_weights, PLearn::OptionBase::learntoption, mean_field_output_bias, mean_field_output_weights, mean_field_precision_threshold, n_lateral_connections_passes, topographic_lateral_weights, topographic_lateral_weights_init_value, topographic_length, topographic_patch_hradius, topographic_patch_vradius, topographic_width, and use_parametric_mean_field.
{
declareOption(ol, "n_lateral_connections_passes",
&RBMLateralBinomialLayer::n_lateral_connections_passes,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Number of passes through the lateral connections.\n");
declareOption(ol, "dampening_factor",
&RBMLateralBinomialLayer::dampening_factor,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Dampening factor ( expectation_t = (1-df) * currrent mean field"
" + df * expectation_{t-1}).\n");
declareOption(ol, "mean_field_precision_threshold",
&RBMLateralBinomialLayer::mean_field_precision_threshold,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Mean-field precision threshold that, once reached, stops the mean-field\n"
"expectation approximation computation. Used only in computeExpectation().\n"
"Precision is computed as:\n"
" dist(last_mean_field, current_mean_field) / size\n");
declareOption(ol, "topographic_length",
&RBMLateralBinomialLayer::topographic_length,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Length of the topographic map.\n");
declareOption(ol, "topographic_width",
&RBMLateralBinomialLayer::topographic_width,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Width of the topographic map.\n");
declareOption(ol, "topographic_patch_vradius",
&RBMLateralBinomialLayer::topographic_patch_vradius,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Vertical radius of the topographic local weight patches.\n");
declareOption(ol, "topographic_patch_hradius",
&RBMLateralBinomialLayer::topographic_patch_hradius,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Horizontal radius of the topographic local weight patches.\n");
declareOption(ol, "topographic_lateral_weights_init_value",
&RBMLateralBinomialLayer::topographic_lateral_weights_init_value,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Initial value for the topographic_lateral_weights.\n");
declareOption(ol, "do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights",
&RBMLateralBinomialLayer::do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Indication that the topographic_lateral_weights should\n"
"be fixed at their initial value.\n");
declareOption(ol, "lateral_weights",
&RBMLateralBinomialLayer::lateral_weights,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"Lateral connections.\n");
declareOption(ol, "topographic_lateral_weights",
&RBMLateralBinomialLayer::topographic_lateral_weights,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"Local topographic lateral connections.\n");
declareOption(ol, "use_parametric_mean_field",
&RBMLateralBinomialLayer::use_parametric_mean_field,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Indication that a parametric predictor of the mean-field\n"
"approximation of the hidden layer conditional distribution.\n");
declareOption(ol, "mean_field_output_weights",
&RBMLateralBinomialLayer::mean_field_output_weights,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"Output weights of the mean field predictor.\n");
declareOption(ol, "mean_field_output_bias",
&RBMLateralBinomialLayer::mean_field_output_bias,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"Output bias of the mean field predictor.\n");
// Now call the parent class' declareOptions
inherited::declareOptions(ol);
}
| static const PPath& PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::declaringFile | ( | ) | [inline, static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 236 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
:
//##### Not Options #####################################################
| RBMLateralBinomialLayer * PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::deepCopy | ( | CopiesMap & | copies | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 51 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
compute -bias' unit_values
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1928 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::bias, dampening_expectation, PLearn::dot(), lateral_weights, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::product(), productTopoLateralWeights(), and topographic_lateral_weights.
{
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0 )
product(dampening_expectation, lateral_weights, unit_values);
else
productTopoLateralWeights( dampening_expectation, unit_values );
return -dot(unit_values, bias) - 0.5 * dot(unit_values, dampening_expectation);
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::externalSymetricProductAcc | ( | const Mat & | mat, |
| const Vec & | v1, | ||
| const Vec & | v2 | ||
| ) | [protected] |
Computes mat[i][j] += 0.5 * (v1[i] * v2[j] + v1[j] * v2[i])
Definition at line 625 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::data(), PLearn::TVec< T >::data(), i, PLearn::TMat< T >::isCompact(), j, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLERROR, w, and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
Referenced by bpropNLL(), and bpropUpdate().
{
#ifdef BOUNDCHECK
if (v1.length()!=mat.length() || mat.width()!=v2.length()
|| v1.length() != v2.length())
PLERROR("externalSymetricProductAcc(Mat,Vec,Vec), incompatible "
"arguments sizes");
#endif
real* v_1=v1.data();
real* v_2=v2.data();
real* mp = mat.data();
int l = mat.length();
int w = mat.width();
if(mat.isCompact())
{
real* pv11 = v_1;
real* pv21 = v_2;
for(int i=0; i<l; i++)
{
real* pv22 = v_2;
real* pv12 = v_1;
real val1 = *pv11++;
real val2 = *pv21++;
for(int j=0; j<w; j++)
//*mp++ += 0.5 * (val1 * *pv22++ + val2 * *pv12++) ;
*mp++ += (val1 * *pv22++ + val2 * *pv12++) ;
}
}
else
{
cerr << "!";
for (int i=0;i<l;i++)
{
real* mi = mat[i];
real v1i = v_1[i];
real v2i = v_2[i];
for (int j=0;j<w;j++)
//mi[j] += 0.5 * ( v1i * v_2[j] + v2i * v_1[j]);
mi[j] += ( v1i * v_2[j] + v2i * v_1[j]);
}
}
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::forget | ( | ) | [virtual] |
forgets everything
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 81 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::clear(), d, PLearn::TMat< T >::data(), PLearn::RBMLayer::forget(), i, lateral_weights, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), mean_field_output_bias, mean_field_output_weights, PLearn::TMat< T >::mod(), topographic_lateral_weights, and topographic_lateral_weights_init_value.
{
inherited::forget();
//real bu;
//for( int i=0; i<lateral_weights.length(); i++)
// for( int j=0; j<lateral_weights.width(); j++)
// {
// bu = random_gen->bounded_uniform(-1.0/size,1.0/size);
// lateral_weights(i,j) = bu;
// lateral_weights(j,i) = bu;
// }
lateral_weights.clear();
// Set diagonal to 0
if( lateral_weights.length() != 0 )
{
real *d = lateral_weights.data();
for (int i=0; i<lateral_weights.length(); i++,d+=lateral_weights.mod()+1)
*d = 0;
}
for( int i=0; i<topographic_lateral_weights.length(); i++ )
//topographic_lateral_weights[i].clear();
topographic_lateral_weights[i].fill( topographic_lateral_weights_init_value );
mean_field_output_weights.clear();
for( int i=0; i<mean_field_output_weights.length(); i++ )
mean_field_output_weights(i,i) = 1;
for( int i=0; i<mean_field_output_bias.length(); i++ )
mean_field_output_bias[i] = -0.5;
}
Batch forward propagation.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 453 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References b, PLearn::RBMLayer::batch_size, PLearn::RBMLayer::bias, bias_plus_inputs, current_temp_outputs, dampening_expectations, dampening_factor, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), PLearn::fastsigmoid(), i, PLearn::TVec< T >::last(), lateral_weights, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), n_lateral_connections_passes, PLASSERT, PLERROR, previous_temp_outputs, productTopoLateralWeights(), PLearn::productTranspose(), PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), PLearn::sigmoid(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, temp_outputs, topographic_lateral_weights, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::use_fast_approximations, use_parametric_mean_field, and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
{
int mbatch_size = inputs.length();
PLASSERT( inputs.width() == size );
outputs.resize( mbatch_size, size );
dampening_expectations.resize( mbatch_size, size );
if( use_parametric_mean_field )
{
PLERROR("RBMLateralBinomialLayer::fprop: use_parametric_mean_field = true "
"not implemented yet for batch mode.");
}
else
{
if(bias_plus_inputs.length() != inputs.length() ||
bias_plus_inputs.width() != inputs.width())
bias_plus_inputs.resize(inputs.length(), inputs.width());
bias_plus_inputs << inputs;
bias_plus_inputs += bias;
if( temp_outputs.length() != n_lateral_connections_passes+1 )
{
temp_outputs.resize(n_lateral_connections_passes+1);
for( int i=0 ; i<n_lateral_connections_passes+1 ; i++ )
temp_outputs[i].resize(mbatch_size,size);
}
temp_outputs.last() = outputs;
current_temp_outputs = temp_outputs[0];
if (use_fast_approximations)
for( int k = 0; k < mbatch_size; k++ )
for( int i = 0; i < size; i++ )
current_temp_outputs(k,i) = fastsigmoid( bias_plus_inputs(k,i) );
else
for( int k = 0; k < mbatch_size; k++ )
for( int i = 0; i < size; i++ )
current_temp_outputs(k,i) = sigmoid( bias_plus_inputs(k,i) );
for( int t=0; t<n_lateral_connections_passes; t++ )
{
previous_temp_outputs = current_temp_outputs;
current_temp_outputs = temp_outputs[t+1];
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0 )
productTranspose(dampening_expectations, previous_temp_outputs,
lateral_weights);
else
for( int b = 0; b<dampening_expectations.length(); b++)
productTopoLateralWeights( dampening_expectations(b),
previous_temp_outputs(b) );
dampening_expectations += bias_plus_inputs;
if (use_fast_approximations)
{
if( fast_exact_is_equal( dampening_factor, 0) )
{
for(int k = 0; k < batch_size; k++)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_outputs(k, i) =
fastsigmoid( dampening_expectations(k, i) );
}
else
{
for(int k = 0; k < batch_size; k++)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_outputs(k, i) = (1-dampening_factor)
* fastsigmoid( dampening_expectations(k, i) )
+ dampening_factor * previous_temp_outputs(k, i);
}
}
else
{
if( fast_exact_is_equal( dampening_factor, 0) )
{
for(int k = 0; k < batch_size; k++)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_outputs(k, i) =
sigmoid( dampening_expectations(k, i) );
}
else
{
for(int k = 0; k < batch_size; k++)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_outputs(k, i) = (1-dampening_factor)
* sigmoid( dampening_expectations(k, i) )
+ dampening_factor * previous_temp_outputs(k, i);
}
}
}
}
}
forward propagation
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 364 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::add(), PLearn::RBMLayer::bias, bias_plus_input, current_temp_output, dampening_expectation, dampening_factor, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), PLearn::fastsigmoid(), i, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::input_size, PLearn::TVec< T >::last(), lateral_weights, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), mean_field_input, mean_field_output_bias, mean_field_output_weights, n_lateral_connections_passes, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::output_size, PLASSERT, pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output, previous_temp_output, PLearn::product(), productTopoLateralWeights(), PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::sigmoid(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), temp_output, topographic_lateral_weights, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::use_fast_approximations, and use_parametric_mean_field.
{
PLASSERT( input.size() == input_size );
output.resize( output_size );
add(bias, input, bias_plus_input);
if( use_parametric_mean_field )
{
if (use_fast_approximations)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
mean_field_input[i] = fastsigmoid( bias_plus_input[i] );
else
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
mean_field_input[i] = sigmoid( bias_plus_input[i] );
product(pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output, mean_field_output_weights, mean_field_input);
pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output += mean_field_output_bias;
if (use_fast_approximations)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
output[i] = fastsigmoid( pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output[i] );
else
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
output[i] = sigmoid( pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output[i] );
}
else
{
if( temp_output.length() != n_lateral_connections_passes+1 )
{
temp_output.resize(n_lateral_connections_passes+1);
for( int i=0 ; i<n_lateral_connections_passes+1 ; i++ )
temp_output[i].resize(size);
}
temp_output.last() = output;
current_temp_output = temp_output[0];
if (use_fast_approximations)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] = fastsigmoid( bias_plus_input[i] );
else
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] = sigmoid( bias_plus_input[i] );
for( int t=0; t<n_lateral_connections_passes; t++ )
{
previous_temp_output = current_temp_output;
current_temp_output = temp_output[t+1];
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0 )
product(dampening_expectation, lateral_weights, previous_temp_output);
else
productTopoLateralWeights( dampening_expectation, previous_temp_output );
dampening_expectation += bias_plus_input;
if (use_fast_approximations)
{
if( fast_exact_is_equal( dampening_factor, 0) )
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] = fastsigmoid( dampening_expectation[i] );
}
else
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] =
(1-dampening_factor) * fastsigmoid( dampening_expectation[i] )
+ dampening_factor * previous_temp_output[i];
}
}
else
{
if( fast_exact_is_equal( dampening_factor, 0) )
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] = sigmoid( dampening_expectation[i] );
}
else
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] =
(1-dampening_factor) * sigmoid( dampening_expectation[i] )
+ dampening_factor * previous_temp_output[i];
}
}
}
}
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::fprop | ( | const Vec & | input, |
| const Vec & | rbm_bias, | ||
| Vec & | output | ||
| ) | const [virtual] |
forward propagation with provided bias
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 546 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::add(), bias_plus_input, current_temp_output, dampening_expectation, dampening_factor, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), PLearn::fastsigmoid(), i, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::input_size, PLearn::TVec< T >::last(), lateral_weights, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), n_lateral_connections_passes, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::output_size, PLASSERT, PLERROR, previous_temp_output, PLearn::product(), productTopoLateralWeights(), PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::sigmoid(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, temp_output, topographic_lateral_weights, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::use_fast_approximations, and use_parametric_mean_field.
{
PLASSERT( input.size() == input_size );
PLASSERT( rbm_bias.size() == input_size );
output.resize( output_size );
add(rbm_bias, input, bias_plus_input);
if( use_parametric_mean_field )
{
PLERROR("RBMLateralBinomialLayer::fprop: use_parametric_mean_field = true "
"not implemented yet for rbm_bias input.");
}
else
{
if( temp_output.length() != n_lateral_connections_passes+1 )
{
temp_output.resize(n_lateral_connections_passes+1);
for( int i=0 ; i<n_lateral_connections_passes+1 ; i++ )
temp_output[i].resize(size);
}
temp_output.last() = output;
current_temp_output = temp_output[0];
if (use_fast_approximations)
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] = fastsigmoid( bias_plus_input[i] );
else
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] = sigmoid( bias_plus_input[i] );
for( int t=0; t<n_lateral_connections_passes; t++ )
{
previous_temp_output = current_temp_output;
current_temp_output = temp_output[t+1];
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0 )
product(dampening_expectation, lateral_weights, previous_temp_output);
else
productTopoLateralWeights( dampening_expectation, previous_temp_output );
dampening_expectation += bias_plus_input;
if (use_fast_approximations)
{
if( fast_exact_is_equal( dampening_factor, 0) )
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] = fastsigmoid( dampening_expectation[i] );
}
else
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] =
(1-dampening_factor) * fastsigmoid( dampening_expectation[i] )
+ dampening_factor * previous_temp_output[i];
}
}
else
{
if( fast_exact_is_equal( dampening_factor, 0) )
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] = sigmoid( dampening_expectation[i] );
}
else
{
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
current_temp_output[i] =
(1-dampening_factor) * sigmoid( dampening_expectation[i] )
+ dampening_factor * previous_temp_output[i];
}
}
}
}
}
Computes the negative log-likelihood of target given the internal activations of the layer.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1276 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References computeExpectation(), PLearn::RBMLayer::expectation, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), i, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::input_size, PLASSERT, PLearn::safeflog(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), and PLearn::RBMLayer::size.
{
PLASSERT( target.size() == input_size );
computeExpectation();
real ret = 0;
real target_i, expectation_i;
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
{
target_i = target[i];
expectation_i = expectation[i];
// TODO: implement more numerically stable version
if(!fast_exact_is_equal(target_i,0.0))
ret -= target_i*safeflog(expectation_i) ;
if(!fast_exact_is_equal(target_i,1.0))
ret -= (1-target_i)*safeflog(1-expectation_i);
}
return ret;
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::fpropNLL | ( | const Mat & | targets, |
| const Mat & | costs_column | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1296 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::batch_size, computeExpectations(), PLearn::RBMLayer::expectation, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectations, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), i, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::input_size, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLASSERT, PLearn::safeflog(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
{
computeExpectations();
PLASSERT( targets.width() == input_size );
PLASSERT( targets.length() == batch_size );
PLASSERT( costs_column.width() == 1 );
PLASSERT( costs_column.length() == batch_size );
for (int k=0;k<batch_size;k++) // loop over minibatch
{
real nll = 0;
real* expectation = expectations[k];
real* target = targets[k];
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ ) // loop over outputs
{
// TODO: implement more numerically stable version
if(!fast_exact_is_equal(target[i],0.0))
nll -= target[i]*safeflog(expectation[i]) ;
if(!fast_exact_is_equal(target[i],1.0))
nll -= (1-target[i])*safeflog(1-expectation[i]);
}
costs_column(k,0) = nll;
}
}
| real PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::freeEnergyContribution | ( | const Vec & | unit_activations | ) | const [virtual] |
This function is not implemented for this class (returns an error)
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1937 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLERROR.
{
PLERROR(
"In RBMLateralBinomialLayer::freeEnergyContribution(): not implemented.");
return -1;
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::generateSample | ( | ) | [virtual] |
generate a sample, and update the sample field
Implements PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 116 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::expectation, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectation_is_up_to_date, i, PLASSERT_MSG, PLCHECK_MSG, PLearn::RBMLayer::random_gen, PLearn::RBMLayer::sample, and PLearn::RBMLayer::size.
{
PLASSERT_MSG(random_gen,
"random_gen should be initialized before generating samples");
PLCHECK_MSG(expectation_is_up_to_date, "Expectation should be computed "
"before calling generateSample()");
for( int i=0 ; i<size ; i++ )
sample[i] = random_gen->binomial_sample( expectation[i] );
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::generateSamples | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Inherited.
Implements PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 131 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::batch_size, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectations, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectations_are_up_to_date, i, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLASSERT, PLASSERT_MSG, PLCHECK_MSG, PLearn::RBMLayer::random_gen, PLearn::RBMLayer::samples, PLearn::RBMLayer::size, and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
{
PLASSERT_MSG(random_gen,
"random_gen should be initialized before generating samples");
PLCHECK_MSG(expectations_are_up_to_date, "Expectations should be computed "
"before calling generateSamples()");
PLASSERT( samples.width() == size && samples.length() == batch_size );
for (int k = 0; k < batch_size; k++) {
for (int i=0 ; i<size ; i++)
samples(k, i) = random_gen->binomial_sample( expectations(k, i) );
}
}

Computes the conf_index configuration of the layer.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1950 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References getConfigurationCount(), i, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLASSERT, and PLearn::RBMLayer::size.
{
PLASSERT( output.length() == size );
PLASSERT( conf_index >= 0 && conf_index < getConfigurationCount() );
for ( int i = 0; i < size; ++i ) {
output[i] = conf_index & 1;
conf_index >>= 1;
}
}
| int PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::getConfigurationCount | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Returns a number of different configurations the layer can be in.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1945 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::INFINITE_CONFIGURATIONS, and PLearn::RBMLayer::size.
Referenced by getConfiguration().
{
return size < 31 ? 1<<size : INFINITE_CONFIGURATIONS;
}

| OptionList & PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::getOptionList | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 51 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
| OptionMap & PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::getOptionMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 51 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::getRemoteMethodMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 51 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy | ( | CopiesMap & | copies | ) | [virtual] |
Transforms a shallow copy into a deep copy.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1899 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References bias_plus_input, bias_plus_inputs, current_temp_output, current_temp_outputs, dampening_expectation, dampening_expectations, PLearn::deepCopyField(), lateral_weights, lateral_weights_gradient, lateral_weights_inc, lateral_weights_neg_stats, lateral_weights_pos_stats, PLearn::RBMLayer::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), mean_field_input, mean_field_output_bias, mean_field_output_weights, pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output, previous_temp_output, previous_temp_outputs, temp_input_gradient, temp_mean_field_gradient, temp_mean_field_gradient2, temp_output, temp_outputs, topographic_lateral_weights, and topographic_lateral_weights_gradient.
{
inherited::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(copies);
deepCopyField(lateral_weights,copies);
deepCopyField(topographic_lateral_weights,copies);
deepCopyField(lateral_weights_pos_stats,copies);
deepCopyField(lateral_weights_neg_stats,copies);
deepCopyField(dampening_expectation,copies);
deepCopyField(dampening_expectations,copies);
deepCopyField(mean_field_input,copies);
deepCopyField(pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output,copies);
deepCopyField(temp_output,copies);
deepCopyField(temp_outputs,copies);
deepCopyField(current_temp_output,copies);
deepCopyField(previous_temp_output,copies);
deepCopyField(current_temp_outputs,copies);
deepCopyField(previous_temp_outputs,copies);
deepCopyField(bias_plus_input,copies);
deepCopyField(bias_plus_inputs,copies);
deepCopyField(temp_input_gradient,copies);
deepCopyField(temp_mean_field_gradient,copies);
deepCopyField(temp_mean_field_gradient2,copies);
deepCopyField(lateral_weights_gradient,copies);
deepCopyField(lateral_weights_inc,copies);
deepCopyField(topographic_lateral_weights_gradient,copies);
deepCopyField(mean_field_output_weights,copies);
deepCopyField(mean_field_output_bias,copies);
}

| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::productTopoLateralWeights | ( | const Vec & | result, |
| const Vec & | input | ||
| ) | const [protected] |
Definition at line 670 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::TVec< T >::clear(), PLearn::TVec< T >::data(), i, j, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), topographic_lateral_weights, topographic_length, topographic_patch_hradius, topographic_patch_vradius, and topographic_width.
Referenced by computeExpectation(), computeExpectations(), energy(), and fprop().
{
// Could be made faster, in terms of memory access
result.clear();
int connected_neuron;
int wi;
real* current_weights;
int neuron_v, neuron_h;
int vmin, vmax, hmin, hmax;
for( int i=0; i<topographic_lateral_weights.length(); i++ )
{
neuron_v = i/topographic_width;
neuron_h = i%topographic_width;
wi = 0;
current_weights = topographic_lateral_weights[i].data();
vmin = neuron_v < topographic_patch_vradius ?
- neuron_v : - topographic_patch_vradius;
vmax = topographic_length - neuron_v - 1 < topographic_patch_vradius ?
topographic_length - neuron_v - 1: topographic_patch_vradius;
hmin = neuron_h < topographic_patch_hradius ?
- neuron_h : - topographic_patch_hradius;
hmax = topographic_width - neuron_h - 1 < topographic_patch_hradius ?
topographic_width - neuron_h - 1: topographic_patch_hradius;
for( int j = -1 * topographic_patch_vradius;
j <= topographic_patch_vradius ; j++ )
{
for( int k = -1 * topographic_patch_hradius;
k <= topographic_patch_hradius; k++ )
{
connected_neuron = (i+j*topographic_width)+k;
if( connected_neuron != i )
{
if( j >= vmin && j <= vmax &&
k >= hmin && k <= hmax )
result[i] += input[connected_neuron]
* current_weights[wi];
wi++;
}
}
}
}
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::productTopoLateralWeightsGradients | ( | const Vec & | input, |
| const Vec & | input_gradient, | ||
| const Vec & | result_gradient, | ||
| const TVec< Vec > & | weights_gradient | ||
| ) | [protected] |
Definition at line 717 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::TVec< T >::data(), i, j, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), topographic_lateral_weights, topographic_length, topographic_patch_hradius, topographic_patch_vradius, and topographic_width.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), and bpropUpdate().
{
// Could be made faster, in terms of memory access
int connected_neuron;
int wi;
real* current_weights;
real* current_weights_gradient;
int neuron_v, neuron_h;
int vmin, vmax, hmin, hmax;
real result_gradient_i;
real input_i;
for( int i=0; i<topographic_lateral_weights.length(); i++ )
{
neuron_v = i/topographic_width;
neuron_h = i%topographic_width;
wi = 0;
current_weights = topographic_lateral_weights[i].data();
current_weights_gradient = weights_gradient[i].data();
vmin = neuron_v < topographic_patch_vradius ?
- neuron_v : - topographic_patch_vradius;
vmax = topographic_length - neuron_v - 1 < topographic_patch_vradius ?
topographic_length - neuron_v - 1: topographic_patch_vradius;
hmin = neuron_h < topographic_patch_hradius ?
- neuron_h : - topographic_patch_hradius;
hmax = topographic_width - neuron_h - 1 < topographic_patch_hradius ?
topographic_width - neuron_h - 1: topographic_patch_hradius;
result_gradient_i = result_gradient[i];
input_i = input[i];
for( int j = -1 * topographic_patch_vradius;
j <= topographic_patch_vradius ; j++ )
{
for( int k = -1 * topographic_patch_hradius;
k <= topographic_patch_hradius; k++ )
{
connected_neuron = (i+j*topographic_width)+k;
if( connected_neuron != i )
{
if( j >= vmin && j <= vmax &&
k >= hmin && k <= hmax )
{
input_gradient[connected_neuron] +=
result_gradient_i * current_weights[wi];
current_weights_gradient[wi] +=
//0.5 * ( result_gradient_i * input[connected_neuron] +
( result_gradient_i * input[connected_neuron] +
input_i * result_gradient[connected_neuron] );
}
wi++;
}
}
}
}
}


| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::reset | ( | ) | [virtual] |
resets activations, sample and expectation fields
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 68 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::clear(), lateral_weights_inc, and PLearn::RBMLayer::reset().
{
inherited::reset();
lateral_weights_inc.clear();
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::update | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Update bias and lateral connections parameters according to accumulated statistics.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1572 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References d, PLearn::TMat< T >::data(), i, lateral_weights, lateral_weights_inc, lateral_weights_neg_stats, lateral_weights_pos_stats, PLearn::RBMLayer::learning_rate, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::TMat< T >::mod(), PLearn::RBMLayer::momentum, PLearn::multiplyScaledAdd(), PLearn::RBMLayer::neg_count, PLERROR, PLearn::RBMLayer::pos_count, topographic_lateral_weights, and PLearn::RBMLayer::update().
{
//real pos_factor = 0.5 * learning_rate / pos_count;
//real neg_factor = - 0.5 * learning_rate / neg_count;
real pos_factor = learning_rate / pos_count;
real neg_factor = - learning_rate / neg_count;
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() != 0 )
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer:update - Not implemented for "
"topographic weights");
// Update lateral connections
if( momentum == 0. )
{
multiplyScaledAdd( lateral_weights_pos_stats, neg_factor, pos_factor,
lateral_weights_neg_stats);
lateral_weights += lateral_weights_neg_stats;
}
else
{
multiplyScaledAdd( lateral_weights_pos_stats, neg_factor, pos_factor,
lateral_weights_neg_stats);
multiplyScaledAdd( lateral_weights_neg_stats, momentum, 1.0,
lateral_weights_inc);
lateral_weights += lateral_weights_inc;
}
// Set diagonal to 0
if( lateral_weights.length() != 0 )
{
real *d = lateral_weights.data();
for (int i=0; i<lateral_weights.length(); i++,d+=lateral_weights.mod()+1)
*d = 0;
}
// Call to update() must be at the end, since update() calls clearStats()!
inherited::update();
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::update | ( | const Vec & | grad | ) | [virtual] |
Updates ONLY the bias parameters according to the given gradient.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1611 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLWARNING, and PLearn::RBMLayer::update().
{
inherited::update( grad );
PLWARNING("RBMLateralBinomialLayer::update( grad ): does not update the\n"
"lateral connections.");
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::update | ( | const Vec & | pos_values, |
| const Vec & | neg_values | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Update bias and lateral connections parameters according to one pair of vectors.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1618 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References d, PLearn::TMat< T >::data(), PLearn::externalProductScaleAcc(), i, lateral_weights, lateral_weights_inc, PLearn::RBMLayer::learning_rate, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::TMat< T >::mod(), PLearn::RBMLayer::momentum, PLERROR, topographic_lateral_weights, PLearn::RBMLayer::update(), and updateTopoLateralWeightsCD().
{
// Update lateral connections
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0 )
{
if( momentum == 0. )
{
externalProductScaleAcc(lateral_weights, pos_values, pos_values,
//0.5 * learning_rate);
learning_rate);
externalProductScaleAcc(lateral_weights, neg_values, neg_values,
//- 0.5 * learning_rate);
-learning_rate);
}
else
{
lateral_weights_inc *= momentum;
externalProductScaleAcc(lateral_weights_inc, pos_values, pos_values,
//0.5 * learning_rate);
learning_rate);
externalProductScaleAcc(lateral_weights_inc, neg_values, neg_values,
//- 0.5 * learning_rate);
- learning_rate);
lateral_weights += lateral_weights_inc;
}
// Set diagonal to 0
if( lateral_weights.length() != 0 )
{
real *d = lateral_weights.data();
for (int i=0; i<lateral_weights.length(); i++,d+=lateral_weights.mod()+1)
*d = 0;
}
}
else
{
if( momentum == 0. )
updateTopoLateralWeightsCD(pos_values, neg_values);
else
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer:bpropNLL - Not implemented for "
"topographic weights");
}
inherited::update( pos_values, neg_values );
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::update | ( | const Mat & | pos_values, |
| const Mat & | neg_values | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Update bias and lateral connections parameters according to one pair of matrices.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1664 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References b, d, PLearn::TMat< T >::data(), i, lateral_weights, lateral_weights_inc, PLearn::RBMLayer::learning_rate, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::TMat< T >::mod(), PLearn::RBMLayer::momentum, n, PLASSERT, PLERROR, topographic_lateral_weights, PLearn::transposeProductScaleAcc(), PLearn::RBMLayer::update(), and updateTopoLateralWeightsCD().
{
int n = pos_values.length();
PLASSERT( neg_values.length() == n );
// We take the average gradient over the mini-batch.
//real avg_lr = 0.5 * learning_rate / n;
real avg_lr = learning_rate / n;
// Update lateral connections
if( topographic_lateral_weights.length() == 0 )
{
if( momentum == 0. )
{
transposeProductScaleAcc(lateral_weights, pos_values, pos_values,
avg_lr, 1);
transposeProductScaleAcc(lateral_weights, neg_values, neg_values,
-avg_lr, 1);
}
else
{
lateral_weights_inc *= momentum;
transposeProductScaleAcc(lateral_weights_inc, pos_values, pos_values,
avg_lr, 1);
transposeProductScaleAcc(lateral_weights_inc, neg_values, neg_values,
-avg_lr, 1);
lateral_weights += lateral_weights_inc;
}
// Set diagonal to 0
if( lateral_weights.length() != 0 )
{
real *d = lateral_weights.data();
for (int i=0; i<lateral_weights.length(); i++,d+=lateral_weights.mod()+1)
*d = 0;
}
}
else
{
if( momentum == 0. )
{
for(int b=0; b<pos_values.length(); b++)
updateTopoLateralWeightsCD(pos_values(b), neg_values(b));
}
else
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer:bpropNLL - Not implemented for "
"topographic weights");
}
inherited::update( pos_values, neg_values );
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::updateCDandGibbs | ( | const Mat & | pos_values, |
| const Mat & | cd_neg_values, | ||
| const Mat & | gibbs_neg_values, | ||
| real | background_gibbs_update_ratio | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1717 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLERROR, and PLearn::RBMLayer::updateCDandGibbs().
{
inherited::updateCDandGibbs( pos_values, cd_neg_values,
gibbs_neg_values, background_gibbs_update_ratio );
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer::updateCDandGibbs(): not implemented yet.");
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::updateGibbs | ( | const Mat & | pos_values, |
| const Mat & | gibbs_neg_values | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 1727 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLERROR, and PLearn::RBMLayer::updateGibbs().
{
inherited::updateGibbs( pos_values, gibbs_neg_values );
PLERROR("In RBMLateralBinomialLayer::updateCDandGibbs(): not implemented yet.");
}
| void PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::updateTopoLateralWeightsCD | ( | const Vec & | pos_values, |
| const Vec & | neg_values | ||
| ) | [protected] |
Definition at line 780 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::TVec< T >::data(), do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights, i, j, PLearn::RBMLayer::learning_rate, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), topographic_lateral_weights, topographic_length, topographic_patch_hradius, topographic_patch_vradius, and topographic_width.
Referenced by update().
{
if( !do_not_learn_topographic_lateral_weights )
{
// Could be made faster, in terms of memory access
int connected_neuron;
int wi;
int neuron_v, neuron_h;
int vmin, vmax, hmin, hmax;
real* current_weights;
real pos_values_i;
real neg_values_i;
for( int i=0; i<topographic_lateral_weights.length(); i++ )
{
neuron_v = i/topographic_width;
neuron_h = i%topographic_width;
wi = 0;
vmin = neuron_v < topographic_patch_vradius ?
- neuron_v : - topographic_patch_vradius;
vmax = topographic_length - neuron_v - 1 < topographic_patch_vradius ?
topographic_length - neuron_v - 1: topographic_patch_vradius;
hmin = neuron_h < topographic_patch_hradius ?
- neuron_h : - topographic_patch_hradius;
hmax = topographic_width - neuron_h - 1 < topographic_patch_hradius ?
topographic_width - neuron_h - 1: topographic_patch_hradius;
current_weights = topographic_lateral_weights[i].data();
pos_values_i = pos_values[i];
neg_values_i = neg_values[i];
for( int j = - topographic_patch_vradius;
j <= topographic_patch_vradius ; j++ )
{
for( int k = -topographic_patch_hradius;
k <= topographic_patch_hradius; k++ )
{
connected_neuron = (i+j*topographic_width)+k;
if( connected_neuron != i )
{
if( j >= vmin && j <= vmax &&
k >= hmin && k <= hmax )
{
current_weights[wi] +=
//learning_rate * 0.5 * (
learning_rate * (
pos_values_i * pos_values[connected_neuron] -
neg_values_i * neg_values[connected_neuron] );
}
wi++;
}
}
}
}
}
}

Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 236 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Vec PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::bias_plus_input [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 259 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by fprop(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Mat PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::bias_plus_inputs [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 260 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by fprop(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Vec PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::current_temp_output [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 256 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), bpropUpdate(), computeExpectation(), fprop(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Mat PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::current_temp_outputs [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 257 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by computeExpectations(), fprop(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Vec PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::dampening_expectation [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 247 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by build_(), computeExpectation(), energy(), fprop(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Mat PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::dampening_expectations [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 248 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by computeExpectations(), fprop(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Dampening factor ( expectation_t = (1-df) * currrent mean field + df * expectation_{t-1})
Definition at line 64 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), computeExpectations(), declareOptions(), and fprop().
Indication that the topographic_lateral_weights should be fixed at their initial value.
Definition at line 89 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), bpropUpdate(), declareOptions(), and updateTopoLateralWeightsCD().
Lateral connections.
Definition at line 92 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), computeExpectations(), declareOptions(), energy(), forget(), fprop(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), and update().
Definition at line 266 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), bpropUpdate(), build_(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Definition at line 267 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), bpropUpdate(), build_(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), reset(), and update().
Accumulates negative contribution to the gradient of lateral weights.
Definition at line 101 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by accumulateNegStats(), build_(), clearStats(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), and update().
Accumulates positive contribution to the gradient of lateral weights.
Definition at line 98 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by accumulatePosStats(), build_(), clearStats(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), and update().
Vec PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::mean_field_input [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 250 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), fprop(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Output bias of the mean field predictor.
Definition at line 111 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), declareOptions(), forget(), fprop(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Output weights of the mean field predictor.
Definition at line 108 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), declareOptions(), forget(), fprop(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Mean-field precision threshold that, once reached, stops the mean-field expectation approximation computation.
Used only in computeExpectation(). Precision is computed as: dist(last_mean_field, current_mean_field) / size
Definition at line 70 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by computeExpectation(), and declareOptions().
Number of passes through the lateral connections.
Definition at line 60 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), computeExpectations(), declareOptions(), and fprop().
Vec PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::pre_sigmoid_mean_field_output [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 251 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by build_(), computeExpectation(), fprop(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Vec PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::previous_temp_output [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 256 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by computeExpectation(), fprop(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Mat PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::previous_temp_outputs [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 257 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by computeExpectations(), fprop(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Definition at line 262 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropUpdate(), build_(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Definition at line 263 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Definition at line 264 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), bpropUpdate(), build_(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
TVec<Vec> PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::temp_output [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 253 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), bpropUpdate(), computeExpectation(), fprop(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
TVec<Mat> PLearn::RBMLateralBinomialLayer::temp_outputs [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 254 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), bpropUpdate(), computeExpectations(), fprop(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Local topographic lateral connections.
Definition at line 95 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), computeExpectations(), declareOptions(), energy(), forget(), fprop(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), productTopoLateralWeights(), productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(), update(), and updateTopoLateralWeightsCD().
Definition at line 269 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), bpropUpdate(), build_(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Initial value for the topographic_lateral_weights.
Definition at line 85 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), and forget().
Length of the topographic map.
Definition at line 73 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by build_(), declareOptions(), productTopoLateralWeights(), productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(), and updateTopoLateralWeightsCD().
Horizontal radius of the topographic local weight patches.
Definition at line 82 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by build_(), declareOptions(), productTopoLateralWeights(), productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(), and updateTopoLateralWeightsCD().
Vertical radius of the topographic local weight patches.
Definition at line 79 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by build_(), declareOptions(), productTopoLateralWeights(), productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(), and updateTopoLateralWeightsCD().
Width of the topographic map.
Definition at line 76 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by build_(), declareOptions(), productTopoLateralWeights(), productTopoLateralWeightsGradients(), and updateTopoLateralWeightsCD().
Indication that a parametric predictor of the mean-field approximation of the hidden layer conditional distribution.
Definition at line 105 of file RBMLateralBinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropNLL(), bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), computeExpectations(), declareOptions(), and fprop().
 1.7.4
1.7.4