|
PLearn 0.1
|
|
PLearn 0.1
|
Multiple multinomial units, each of them seeing an area of nearby pixels. More...
#include <RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| RBMLocalMultinomialLayer (real the_learning_rate=0.) | |
| Default constructor. | |
| RBMLocalMultinomialLayer (int the_size, real the_learning_rate=0.) | |
| Constructor from the number of units in the multinomial. | |
| virtual void | generateSample () |
| generate a sample, and update the sample field | |
| virtual void | generateSamples () |
| batch version | |
| virtual void | computeExpectation () |
| compute the expectation | |
| virtual void | computeExpectations () |
| batch version | |
| virtual void | fprop (const Vec &input, Vec &output) const |
| forward propagation | |
| virtual void | fprop (const Vec &input, const Vec &rbm_bias, Vec &output) const |
| forward propagation with provided bias | |
| virtual void | bpropUpdate (const Vec &input, const Vec &output, Vec &input_gradient, const Vec &output_gradient, bool accumulate=false) |
| back-propagates the output gradient to the input | |
| virtual void | bpropUpdate (const Mat &inputs, const Mat &outputs, Mat &input_gradients, const Mat &output_gradients, bool accumulate=false) |
| Back-propagate the output gradient to the input, and update parameters. | |
| virtual void | bpropUpdate (const Vec &input, const Vec &rbm_bias, const Vec &output, Vec &input_gradient, Vec &rbm_bias_gradient, const Vec &output_gradient) |
| back-propagates the output gradient to the input and the bias | |
| virtual real | fpropNLL (const Vec &target) |
| Computes the negative log-likelihood of target given the internal activations of the layer. | |
| virtual void | fpropNLL (const Mat &targets, const Mat &costs_column) |
| virtual void | bpropNLL (const Vec &target, real nll, Vec &bias_gradient) |
| Computes the gradient of the negative log-likelihood of target with respect to the layer's bias, given the internal activations. | |
| virtual void | bpropNLL (const Mat &targets, const Mat &costs_column, Mat &bias_gradients) |
| virtual real | energy (const Vec &unit_values) const |
| virtual real | freeEnergyContribution (const Vec &unit_activations) const |
Computes 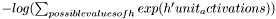 This quantity is used for computing the free energy of a sample x in the OTHER layer of an RBM, from which unit_activations was computed. This quantity is used for computing the free energy of a sample x in the OTHER layer of an RBM, from which unit_activations was computed. | |
| virtual int | getConfigurationCount () |
| Returns a number of different configurations the layer can be in. | |
| virtual void | getConfiguration (int conf_index, Vec &output) |
| Computes the conf_index configuration of the layer. | |
| virtual string | classname () const |
| virtual OptionList & | getOptionList () const |
| virtual OptionMap & | getOptionMap () const |
| virtual RemoteMethodMap & | getRemoteMethodMap () const |
| virtual RBMLocalMultinomialLayer * | deepCopy (CopiesMap &copies) const |
| virtual void | build () |
| Post-constructor. | |
| virtual void | makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy (CopiesMap &copies) |
| Transforms a shallow copy into a deep copy. | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static string | _classname_ () |
| static OptionList & | _getOptionList_ () |
| static RemoteMethodMap & | _getRemoteMethodMap_ () |
| static Object * | _new_instance_for_typemap_ () |
| static bool | _isa_ (const Object *o) |
| static void | _static_initialize_ () |
| static const PPath & | declaringFile () |
Public Attributes | |
| int | n_images |
| Number of images present at the same time in the input vector. | |
| int | images_length |
| Length of each of the images. | |
| int | images_width |
| Width of each of the images. | |
| int | area_length |
| Length of the areas to consider. | |
| int | area_width |
| Width of the areas to consider. | |
| int | images_size |
| int | area_size |
| int | n_areas |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static StaticInitializer | _static_initializer_ |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static void | declareOptions (OptionList &ol) |
| Declares the class options. | |
Private Types | |
| typedef RBMLayer | inherited |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | build_ () |
| This does the actual building. | |
Multiple multinomial units, each of them seeing an area of nearby pixels.
Definition at line 52 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.h.
typedef RBMLayer PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::inherited [private] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 54 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.h.
| PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer | ( | real | the_learning_rate = 0. | ) |
Default constructor.
Definition at line 140 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
:
inherited( the_learning_rate )
{
}
| PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer | ( | int | the_size, |
| real | the_learning_rate = 0. |
||
| ) |
Constructor from the number of units in the multinomial.
| string PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::_classname_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 138 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
| OptionList & PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::_getOptionList_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 138 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::_getRemoteMethodMap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 138 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 138 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
| Object * PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::_new_instance_for_typemap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 138 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
| StaticInitializer RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::_static_initializer_ & PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::_static_initialize_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 138 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::bpropNLL | ( | const Vec & | target, |
| real | nll, | ||
| Vec & | bias_gradient | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Computes the gradient of the negative log-likelihood of target with respect to the layer's bias, given the internal activations.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 695 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References computeExpectation(), PLearn::RBMLayer::expectation, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::input_size, PLASSERT, PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, and PLearn::substract().
{
computeExpectation();
PLASSERT( target.size() == input_size );
bias_gradient.resize( size );
// bias_gradient = expectation - target
substract(expectation, target, bias_gradient);
}
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::bpropNLL | ( | const Mat & | targets, |
| const Mat & | costs_column, | ||
| Mat & | bias_gradients | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 707 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::batch_size, computeExpectations(), PLearn::RBMLayer::expectations, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::input_size, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLASSERT, PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, PLearn::substract(), and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
{
computeExpectations();
PLASSERT( targets.width() == input_size );
PLASSERT( targets.length() == batch_size );
PLASSERT( costs_column.width() == 1 );
PLASSERT( costs_column.length() == batch_size );
bias_gradients.resize( batch_size, size );
// bias_gradients = expectations - targets
substract(expectations, targets, bias_gradients);
}
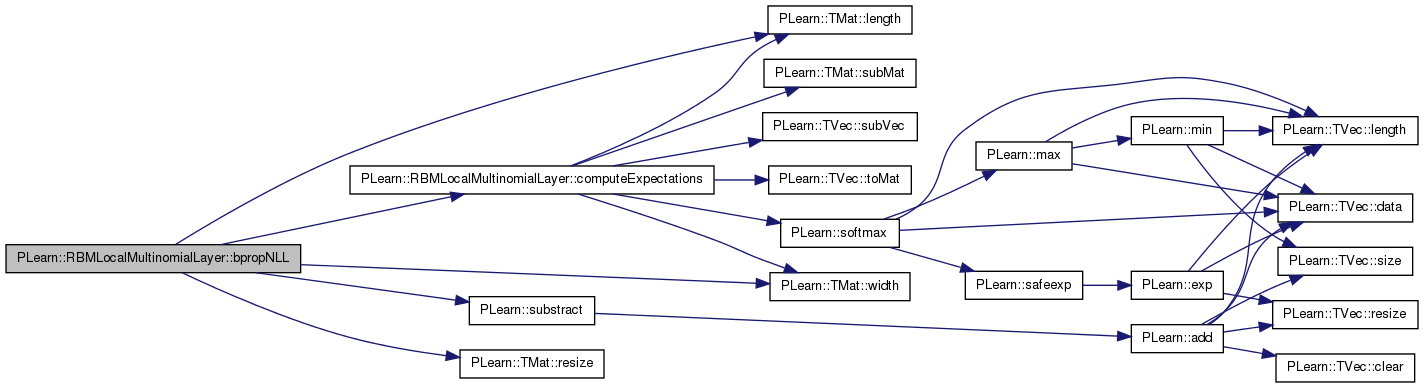
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::bpropUpdate | ( | const Mat & | inputs, |
| const Mat & | outputs, | ||
| Mat & | input_gradients, | ||
| const Mat & | output_gradients, | ||
| bool | accumulate = false |
||
| ) | [virtual] |
Back-propagate the output gradient to the input, and update parameters.
Implements PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 417 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References area_length, area_size, area_width, PLearn::TMat< T >::begin(), PLearn::RBMLayer::bias, PLearn::RBMLayer::bias_inc, PLearn::TMat< T >::clear(), PLearn::dot(), i, images_length, images_size, images_width, j, PLearn::RBMLayer::learning_rate, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::RBMLayer::momentum, n_images, PLASSERT, PLASSERT_MSG, PLCHECK_MSG, PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), PLearn::TVec< T >::subVec(), PLearn::TVec< T >::toMat(), and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
{
PLASSERT( inputs.width() == size );
PLASSERT( outputs.width() == size );
PLASSERT( output_gradients.width() == size );
int mbatch_size = inputs.length();
PLASSERT( outputs.length() == mbatch_size );
PLASSERT( output_gradients.length() == mbatch_size );
if( accumulate )
{
PLASSERT_MSG( input_gradients.width() == size &&
input_gradients.length() == inputs.length(),
"Cannot resize input_gradient and accumulate into it." );
}
else
{
input_gradients.resize(inputs.length(), size);
input_gradients.clear();
}
if( momentum != 0. )
bias_inc.resize( size );
// TODO see if we can have a speed-up by reorganizing the different steps
// input_gradients[k][i] =
// (output_gradients[k][i]-output_gradients[k].outputs[k]) outputs[k][i]
real mean_lr = learning_rate / mbatch_size;
for (int l=0; l<n_images; l++)
{
Mat bias_image = bias
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat bias_inc_image;
if (momentum != 0)
bias_inc_image = bias_inc
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
for( int k=0; k<mbatch_size; k++ )
{
Mat output_image = outputs(k)
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat input_grad_image = input_gradients(k)
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat output_grad_image = output_gradients(k)
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
for (int i=0; i<images_length; i+=area_length)
for (int j=0; j<images_width; j+=area_width)
{
Mat output_area = output_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat input_grad_area = input_grad_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat output_grad_area = output_grad_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat bias_area = bias_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat bias_inc_area;
if (momentum != 0)
bias_inc_area = bias_inc_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
real outga_dot_outa = dot(output_grad_area, output_area);
TMatElementIterator<real> pog = output_grad_area.begin();
TMatElementIterator<real> po = output_area.begin();
TMatElementIterator<real> pig = input_grad_area.begin();
TMatElementIterator<real> pb = bias_area.begin();
if (momentum == 0)
{
for (int i=0; i<area_size; i++, pog++, po++, pig++,
pb++)
{
real inga_i = (*pog - outga_dot_outa) * (*po);
*pig += inga_i;
// update the bias:
// bias -= learning_rate * input_grad
*pb -= mean_lr * (*pig);
}
}
else
PLCHECK_MSG(false,
"Momentum and mini-batch not implemented");
}
}
}
}
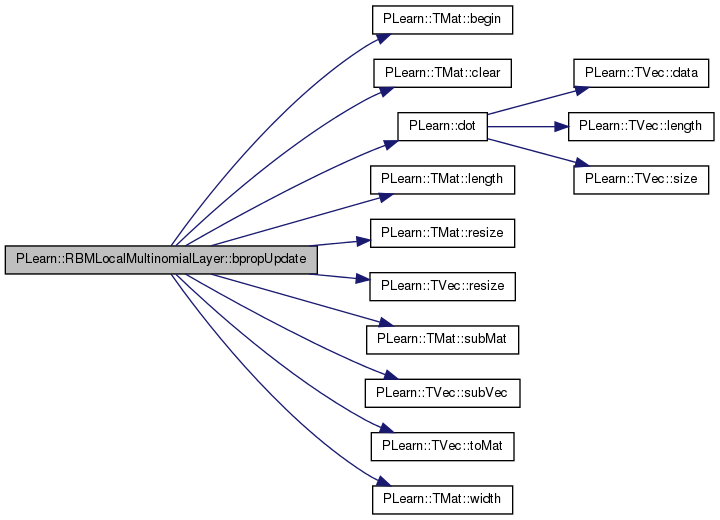
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::bpropUpdate | ( | const Vec & | input, |
| const Vec & | rbm_bias, | ||
| const Vec & | output, | ||
| Vec & | input_gradient, | ||
| Vec & | rbm_bias_gradient, | ||
| const Vec & | output_gradient | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
back-propagates the output gradient to the input and the bias
TODO: add "accumulate" here.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 520 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References area_length, area_size, area_width, PLearn::TMat< T >::begin(), PLearn::dot(), i, images_length, images_size, images_width, j, PLearn::RBMLayer::learning_rate, m, n_images, PLASSERT, PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), PLearn::TVec< T >::subVec(), and PLearn::TVec< T >::toMat().
{
PLASSERT( input.size() == size );
PLASSERT( rbm_bias.size() == size );
PLASSERT( output.size() == size );
PLASSERT( output_gradient.size() == size );
input_gradient.resize( size );
rbm_bias_gradient.resize( size );
for (int l=0; l<n_images; l++)
{
Mat output_image = output
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat input_grad_image = input_gradient
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat output_grad_image = output_gradient
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat rbm_bias_image = rbm_bias
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
for (int i=0; i<images_length; i+=area_length)
for (int j=0; j<images_width; j+=area_width)
{
Mat output_area = output_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat input_grad_area = input_grad_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat output_grad_area = output_grad_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat rbm_bias_area = rbm_bias_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
real outga_dot_outa = dot(output_grad_area, output_area);
TMatElementIterator<real> pog = output_grad_area.begin();
TMatElementIterator<real> po = output_area.begin();
TMatElementIterator<real> pig = input_grad_area.begin();
TMatElementIterator<real> prb = rbm_bias_area.begin();
for (int m=0; m<area_size; m++, pog++, po++, pig++, prb++)
{
real inga_m = (*pog - outga_dot_outa) * (*po);
*pig += inga_m;
// update the bias: bias -= learning_rate * input_grad
*prb -= learning_rate * (*pig);
}
}
}
rbm_bias_gradient << input_gradient;
}
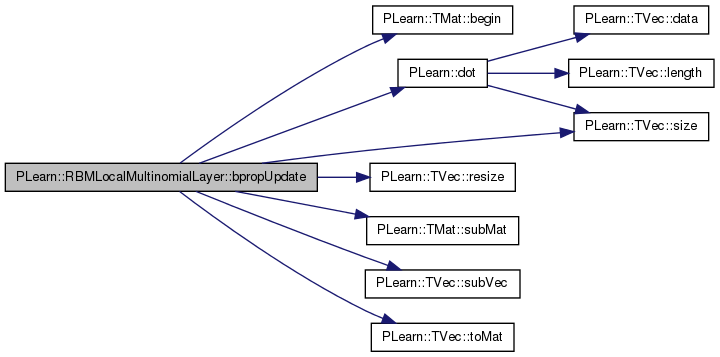
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::bpropUpdate | ( | const Vec & | input, |
| const Vec & | output, | ||
| Vec & | input_gradient, | ||
| const Vec & | output_gradient, | ||
| bool | accumulate = false |
||
| ) | [virtual] |
back-propagates the output gradient to the input
Implements PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 321 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References area_length, area_size, area_width, PLearn::TMat< T >::begin(), PLearn::RBMLayer::bias, PLearn::RBMLayer::bias_inc, PLearn::TVec< T >::clear(), PLearn::dot(), i, images_length, images_size, images_width, j, PLearn::RBMLayer::learning_rate, m, PLearn::RBMLayer::momentum, n_images, PLASSERT, PLASSERT_MSG, PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), PLearn::TVec< T >::subVec(), and PLearn::TVec< T >::toMat().
{
PLASSERT( input.size() == size );
PLASSERT( output.size() == size );
PLASSERT( output_gradient.size() == size );
if( accumulate )
{
PLASSERT_MSG( input_gradient.size() == size,
"Cannot resize input_gradient AND accumulate into it" );
}
else
{
input_gradient.resize( size );
input_gradient.clear();
}
if( momentum != 0. )
bias_inc.resize( size );
for (int l=0; l<n_images; l++)
{
Mat output_image = output
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat input_grad_image = input_gradient
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat output_grad_image = output_gradient
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat bias_image = bias
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat bias_inc_image;
if (momentum != 0)
bias_inc_image = bias_inc
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
for (int i=0; i<images_length; i+=area_length)
for (int j=0; j<images_width; j+=area_width)
{
Mat output_area = output_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat input_grad_area = input_grad_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat output_grad_area = output_grad_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat bias_area = bias_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat bias_inc_area;
if (momentum != 0)
bias_inc_area = bias_inc_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
real outga_dot_outa = dot(output_grad_area, output_area);
TMatElementIterator<real> pog = output_grad_area.begin();
TMatElementIterator<real> po = output_area.begin();
TMatElementIterator<real> pig = input_grad_area.begin();
TMatElementIterator<real> pb = bias_area.begin();
TMatElementIterator<real> pbi = bias_inc_area.begin();
/*
TMatElementIterator<real> pbi;
if (momentum != 0)
pbi = bias_inc_area.begin();
*/
for (int m=0; m<area_size; m++, pog++, po++, pig++, pb++)
{
real inga_m = (*pog - outga_dot_outa) * (*po);
*pig += inga_m;
if (momentum == 0)
{
// update the bias: bias -= learning_rate * input_grad
*pb -= learning_rate * (*pig);
}
else
{
// The update rule becomes:
// bias_inc = momentum * bias_inc
// - learning_rate * input_grad
*pbi = momentum * (*pbi) - learning_rate * (*pig);
*pb += *pbi;
pbi++;
}
}
}
}
}
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::build | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Post-constructor.
The normal implementation should call simply inherited::build(), then this class's build_(). This method should be callable again at later times, after modifying some option fields to change the "architecture" of the object.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 786 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::build(), and build_().
{
inherited::build();
build_();
}
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::build_ | ( | ) | [private] |
This does the actual building.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 773 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References area_length, area_size, area_width, images_length, images_size, images_width, n_areas, n_images, PLCHECK_MSG, and PLearn::RBMLayer::size.
Referenced by build().
{
PLCHECK_MSG(images_length % area_length == 0,
"\"images_length\" should be a multiple of \"area_length\"");
PLCHECK_MSG(images_width % area_width == 0,
"\"images_width\" should be a multiple of \"area_width\"");
images_size = images_length * images_width;
area_size = area_length * area_width;
size = images_size * n_images;
n_areas = size / area_size;
}

| string PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::classname | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 138 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::computeExpectation | ( | ) | [virtual] |
compute the expectation
Implements PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 209 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::activation, area_length, area_width, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectation, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectation_is_up_to_date, i, images_length, images_size, images_width, j, n_images, PLearn::softmax(), PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), PLearn::TVec< T >::subVec(), and PLearn::TVec< T >::toMat().
Referenced by bpropNLL(), and fpropNLL().
{
if( expectation_is_up_to_date )
return;
for (int l=0; l<n_images; l++)
{
Mat activation_image = activation
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat expectation_image = expectation
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
for (int i=0; i<images_length; i+=area_length)
for (int j=0; j<images_width; j+=area_width)
softmax(
activation_image.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width),
expectation_image.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width)
);
}
expectation_is_up_to_date = true;
}
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::computeExpectations | ( | ) | [virtual] |
batch version
Implements PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 233 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::activations, area_length, area_width, PLearn::RBMLayer::batch_size, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectations, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectations_are_up_to_date, i, images_length, images_size, images_width, j, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), n_images, PLASSERT, PLearn::RBMLayer::size, PLearn::softmax(), PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), PLearn::TVec< T >::subVec(), PLearn::TVec< T >::toMat(), and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
Referenced by bpropNLL(), and fpropNLL().
{
if( expectations_are_up_to_date )
return;
PLASSERT( expectations.width() == size
&& expectations.length() == batch_size );
for (int k = 0; k < batch_size; k++)
for (int l=0; l<n_images; l++)
{
Mat activation_image = activations(k)
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat expectation_image = expectations(k)
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
for (int i=0; i<images_length; i+=area_length)
for (int j=0; j<images_width; j+=area_width)
softmax(
activation_image.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width),
expectation_image.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width)
);
}
expectations_are_up_to_date = true;
}
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::declareOptions | ( | OptionList & | ol | ) | [static, protected] |
Declares the class options.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 722 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References area_length, area_size, area_width, PLearn::OptionBase::buildoption, PLearn::declareOption(), PLearn::RBMLayer::declareOptions(), images_length, images_size, images_width, PLearn::OptionBase::learntoption, n_images, PLearn::redeclareOption(), and PLearn::RBMLayer::size.
{
declareOption(ol, "n_images", &RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::n_images,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Number of images in the layer.");
declareOption(ol, "images_length",
&RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::images_length,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Length of the images.");
declareOption(ol, "images_width",
&RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::images_width,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Width of the images.");
declareOption(ol, "images_size",
&RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::images_size,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"images_width × images_length.");
declareOption(ol, "area_length",
&RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::area_length,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Length of the areas over which the multinomial is set.");
declareOption(ol, "area_width",
&RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::area_width,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Width of the areas over which the multinomial is set.");
declareOption(ol, "area_size",
&RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::area_size,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"area_width × area_length.");
/*
declareOption(ol, "size", &RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::size,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Number of units.");
*/
// Now call the parent class' declareOptions
inherited::declareOptions(ol);
redeclareOption(ol, "size",
&RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::size,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"n_images × images_width × images_length.");
}
| static const PPath& PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::declaringFile | ( | ) | [inline, static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 151 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.h.
:
//##### Not Options #####################################################
| RBMLocalMultinomialLayer * PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::deepCopy | ( | CopiesMap & | copies | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 138 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 798 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::bias, and PLearn::dot().
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::fprop | ( | const Vec & | input, |
| const Vec & | rbm_bias, | ||
| Vec & | output | ||
| ) | const [virtual] |
forward propagation with provided bias
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 291 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References area_length, area_width, i, images_length, images_size, images_width, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::input_size, j, n_images, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::output_size, PLASSERT, PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::softmax(), PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), PLearn::TVec< T >::subVec(), and PLearn::TVec< T >::toMat().
{
PLASSERT( input.size() == input_size );
PLASSERT( rbm_bias.size() == input_size );
output.resize( output_size );
// inefficient
Vec input_plus_bias = input + rbm_bias;
for (int l=0; l<n_images; l++)
{
Mat input_image = input_plus_bias
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat output_image = output
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
for (int i=0; i<images_length; i+=area_length)
for (int j=0; j<images_width; j+=area_width)
softmax(
input_image.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width),
output_image.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width)
);
}
}
forward propagation
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 263 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References area_length, area_width, PLearn::RBMLayer::bias, i, images_length, images_size, images_width, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::input_size, j, n_images, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::output_size, PLASSERT, PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::softmax(), PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), PLearn::TVec< T >::subVec(), and PLearn::TVec< T >::toMat().
{
PLASSERT( input.size() == input_size );
output.resize( output_size );
// inefficient
Vec input_plus_bias = input + bias;
for (int l=0; l<n_images; l++)
{
Mat input_image = input_plus_bias
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat output_image = output
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
for (int i=0; i<images_length; i+=area_length)
for (int j=0; j<images_width; j+=area_width)
softmax(
input_image.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width),
output_image.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width)
);
}
}

Computes the negative log-likelihood of target given the internal activations of the layer.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 585 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References area_length, area_size, area_width, PLearn::TMat< T >::begin(), computeExpectation(), PLearn::RBMLayer::expectation, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), PLearn::TMat< T >::hasMissing(), i, images_length, images_size, images_width, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::input_size, PLearn::is_equal(), j, m, PLearn::min(), n_images, pl_log, PLASSERT, PLASSERT_MSG, PLERROR, PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), PLearn::TVec< T >::subVec(), PLearn::sum(), and PLearn::TVec< T >::toMat().
{
computeExpectation();
PLASSERT( target.size() == input_size );
real nll = 0;
for (int l=0; l<n_images; l++)
{
Mat target_image = target
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat expectation_image = expectation
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
for (int i=0; i<images_length; i+=area_length)
for (int j=0; j<images_width; j+= area_width)
{
Mat target_area = target_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat expectation_area = expectation_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
#ifdef BOUNDCHECK
if (!target_area.hasMissing())
{
PLASSERT_MSG( min(target_area) >= 0.,
"Elements of \"target_areal\" should be"
" positive" );
// Ensure the distribution probabilities sum to 1. We relax a
// bit the default tolerance as probabilities using
// exponentials could suffer numerical imprecisions.
if (!is_equal( sum(target_area), 1., 1., 1e-5, 1e-5 ))
PLERROR("In RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::fpropNLL -"
" Elements of \"target_area\" should sum to 1"
" (found a sum = %f)",
sum(target_area));
}
#endif
TMatElementIterator<real> p_tgt = target_area.begin();
TMatElementIterator<real> p_exp = expectation_area.begin();
for (int m=0; m<area_size; m++, p_tgt++, p_exp++)
{
if (!fast_exact_is_equal(*p_tgt, 0))
nll -= *p_tgt * pl_log(*p_exp);
}
}
}
return nll;
}
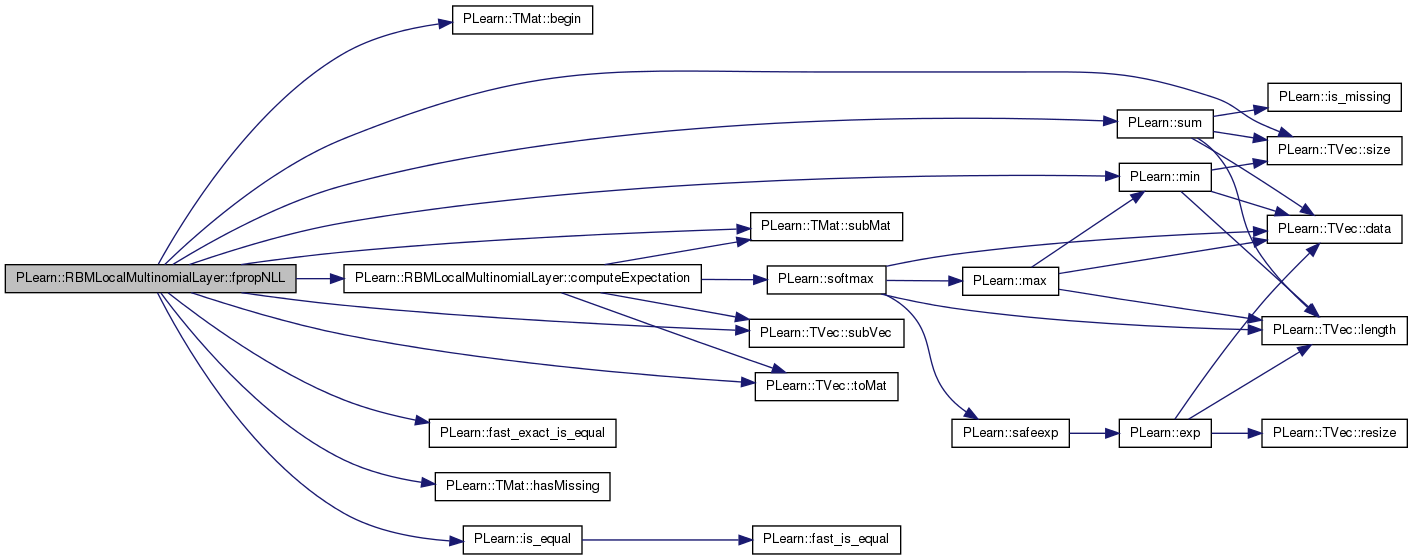
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::fpropNLL | ( | const Mat & | targets, |
| const Mat & | costs_column | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 637 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References area_length, area_size, area_width, PLearn::RBMLayer::batch_size, PLearn::TMat< T >::begin(), computeExpectations(), PLearn::RBMLayer::expectations, PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), PLearn::TMat< T >::hasMissing(), i, images_length, images_size, images_width, PLearn::OnlineLearningModule::input_size, PLearn::is_equal(), j, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), m, PLearn::min(), n_images, pl_log, PLASSERT, PLASSERT_MSG, PLERROR, PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), PLearn::sum(), and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
{
computeExpectations();
PLASSERT( targets.width() == input_size );
PLASSERT( targets.length() == batch_size );
PLASSERT( costs_column.width() == 1 );
PLASSERT( costs_column.length() == batch_size );
for (int k=0; k<batch_size; k++) // loop over minibatch
{
real nll = 0;
for (int l=0; l<n_images; l++)
{
Mat target_image = targets(k)
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat expectation_image = expectations(k)
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
for (int i=0; i<images_length; i+=area_length)
for (int j=0; j<images_width; j+= area_width)
{
Mat target_area = target_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat expectation_area = expectation_image
.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
#ifdef BOUNDCHECK
if (!target_area.hasMissing())
{
PLASSERT_MSG( min(target_area) >= 0.,
"Elements of \"target_areal\" should be"
" positive" );
// Ensure the distribution probabilities sum to 1. We relax a
// bit the default tolerance as probabilities using
// exponentials could suffer numerical imprecisions.
if (!is_equal( sum(target_area), 1., 1., 1e-5, 1e-5 ))
PLERROR("In RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::fpropNLL -"
" Elements of \"target_area\" should sum"
" to 1 (found a sum = %f) at row %d",
sum(target_area), k);
}
#endif
TMatElementIterator<real> p_tgt = target_area.begin();
TMatElementIterator<real> p_exp = expectation_area.begin();
for (int m=0; m<area_size; m++, p_tgt++, p_exp++)
{
if (!fast_exact_is_equal(*p_tgt, 0))
nll -= *p_tgt * pl_log(*p_exp);
}
}
}
costs_column(k, 0) = nll;
}
}
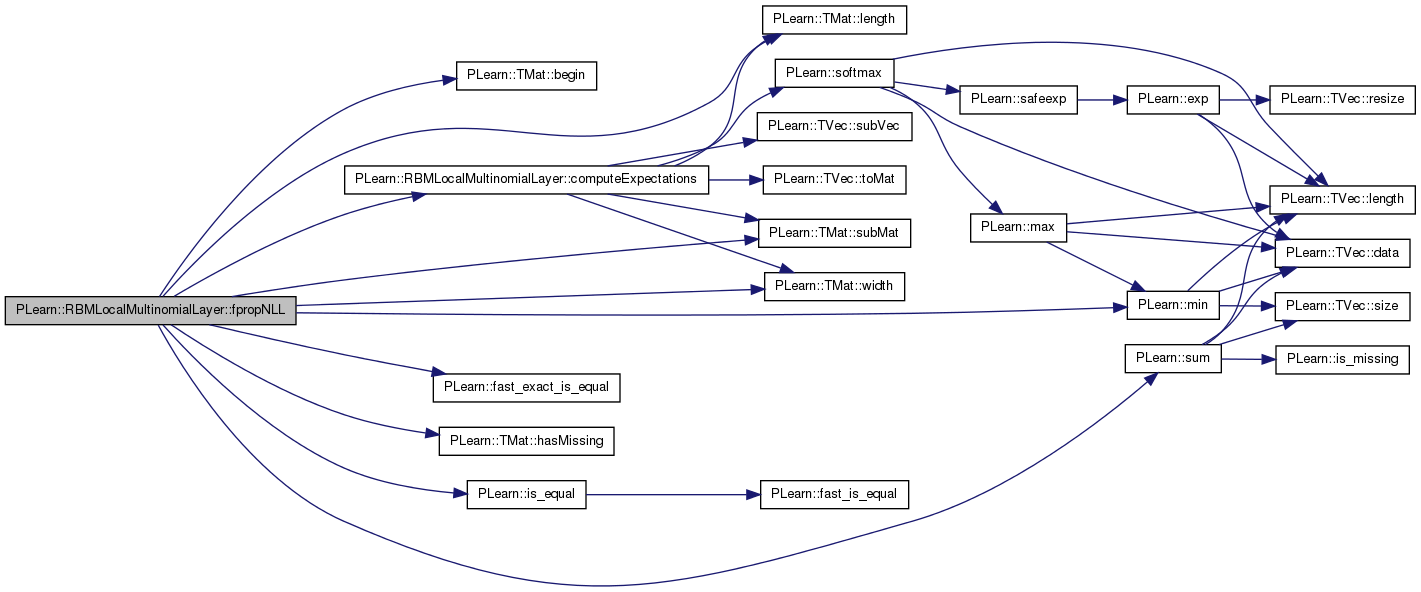
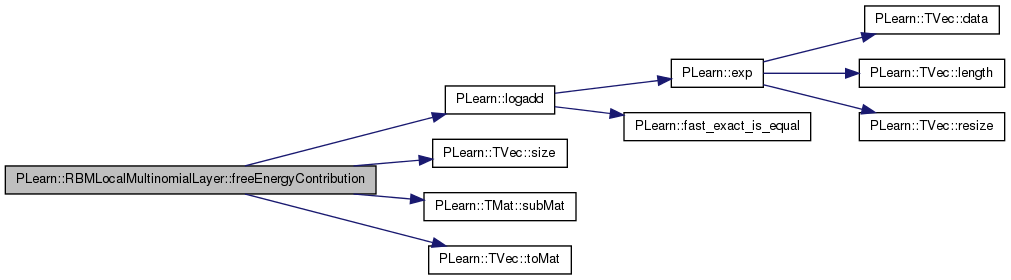
| real PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::freeEnergyContribution | ( | const Vec & | unit_activations | ) | const [virtual] |
Computes 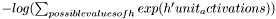 This quantity is used for computing the free energy of a sample x in the OTHER layer of an RBM, from which unit_activations was computed.
This quantity is used for computing the free energy of a sample x in the OTHER layer of an RBM, from which unit_activations was computed.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 804 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References area_length, area_width, i, images_length, images_width, PLearn::logadd(), n_areas, n_images, PLASSERT, PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::RBMLayer::size, PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), and PLearn::TVec< T >::toMat().
{
PLASSERT( activation_values.size() == size );
// result =
// -\sum_{i=0}^{n_areas-1} log(\sum_{j=0}^{area_size-1} exp(a_{ij}))
real result = 0;
Mat activation_images = activation_values
.toMat(n_images*images_length, images_width);
for (int i=0; i<n_areas; i++)
{
Mat activation_area = activation_images
.subMat((i/images_width)*area_length,
(i*area_width) % images_width,
area_length,
area_width);
result -= logadd(activation_area);
}
return result;
}
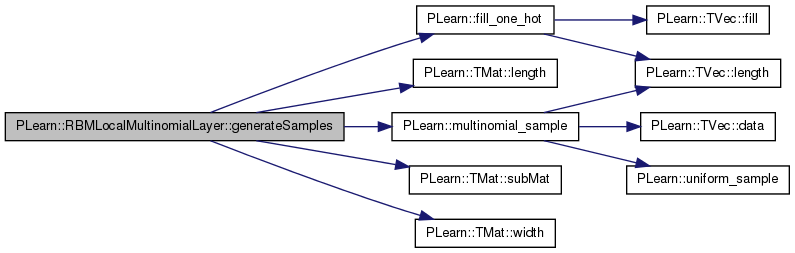
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::generateSample | ( | ) | [virtual] |
generate a sample, and update the sample field
Implements PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 145 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References area_length, area_width, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectation, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectation_is_up_to_date, PLearn::fill_one_hot(), i, images_length, images_size, images_width, j, PLearn::multinomial_sample(), n_images, PLASSERT_MSG, PLCHECK_MSG, PLearn::RBMLayer::random_gen, PLearn::RBMLayer::sample, PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), PLearn::TVec< T >::subVec(), and PLearn::TVec< T >::toMat().
{
PLASSERT_MSG(random_gen,
"random_gen should be initialized before generating samples");
PLCHECK_MSG(expectation_is_up_to_date, "Expectation should be computed "
"before calling generateSample()");
for (int l=0; l<n_images; l++)
{
Mat expectation_image = expectation
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat sample_image = sample
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
for (int i=0; i<images_length; i+=area_length)
for (int j=0; j<images_width; j+=area_width)
{
Mat expectation_area =
expectation_image.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat sample_area =
sample_image.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
int index = multinomial_sample(random_gen, expectation_area);
fill_one_hot(sample_area, index, real(0), real(1));
}
}
}
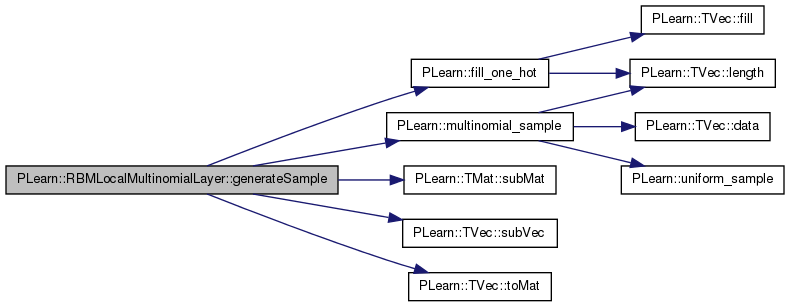
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::generateSamples | ( | ) | [virtual] |
batch version
Implements PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 175 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References area_length, area_width, PLearn::RBMLayer::batch_size, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectations, PLearn::RBMLayer::expectations_are_up_to_date, PLearn::fill_one_hot(), i, images_length, images_size, images_width, j, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::multinomial_sample(), n_images, PLASSERT, PLASSERT_MSG, PLCHECK_MSG, PLearn::RBMLayer::random_gen, PLearn::RBMLayer::samples, PLearn::RBMLayer::size, PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
{
PLASSERT_MSG(random_gen,
"random_gen should be initialized before generating samples");
PLCHECK_MSG(expectations_are_up_to_date, "Expectations should be computed "
"before calling generateSamples()");
PLASSERT( samples.width() == size && samples.length() == batch_size );
for (int k = 0; k < batch_size; k++)
for (int l=0; l<n_images; l++)
{
Mat expectation_image = expectations(k)
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
Mat sample_image = samples(k)
.subVec(l*images_size, images_size)
.toMat(images_length, images_width);
for (int i=0; i<images_length; i+=area_length)
for (int j=0; j<images_width; j+=area_width)
{
Mat expectation_area =
expectation_image.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
Mat sample_area =
sample_image.subMat(i, j, area_length, area_width);
int index = multinomial_sample(random_gen,
expectation_area);
fill_one_hot(sample_area, index, real(0), real(1));
}
}
}
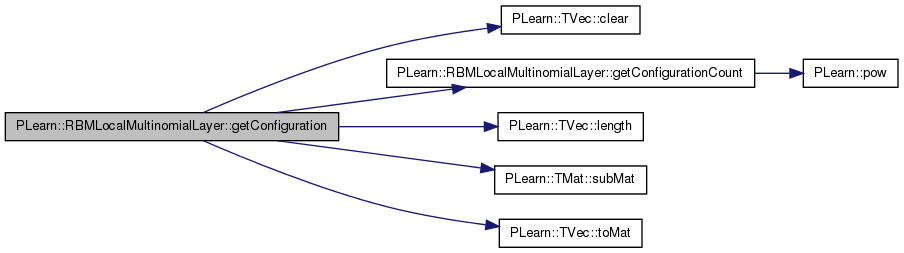
Computes the conf_index configuration of the layer.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 840 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References area_length, area_size, area_width, PLearn::TVec< T >::clear(), getConfigurationCount(), i, images_length, images_width, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), n_areas, n_images, PLASSERT, PLearn::RBMLayer::size, PLearn::TMat< T >::subMat(), and PLearn::TVec< T >::toMat().
{
PLASSERT( output.length() == size );
PLASSERT( conf_index >= 0 && conf_index < getConfigurationCount() );
output.clear();
Mat output_images = output.toMat(n_images*images_length, images_width);
for (int i=0; i<n_areas; i++)
{
int area_conf_index = conf_index % area_size;
conf_index /= area_size;
Mat output_area = output_images
.subMat((i/images_width)*area_length,
(i*area_width) % images_width,
area_length,
area_width );
output_area(area_conf_index/area_width, area_conf_index%area_width)=1;
}
}
| int PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::getConfigurationCount | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Returns a number of different configurations the layer can be in.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 827 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References area_size, i, PLearn::RBMLayer::INFINITE_CONFIGURATIONS, n_areas, and PLearn::pow().
Referenced by getConfiguration().
{
real approx_count = pow(real(area_size), n_areas);
int count = 1;
if (approx_count > 1e30)
count = INFINITE_CONFIGURATIONS;
else
for (int i=0; i<n_areas; i++)
count *= area_size;
return count;
}


| OptionList & PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::getOptionList | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 138 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
| OptionMap & PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::getOptionMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 138 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::getRemoteMethodMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 138 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
| void PLearn::RBMLocalMultinomialLayer::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy | ( | CopiesMap & | copies | ) | [virtual] |
Transforms a shallow copy into a deep copy.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 793 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.cc.
References PLearn::RBMLayer::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
{
inherited::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(copies);
}

Reimplemented from PLearn::RBMLayer.
Definition at line 151 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.h.
Length of the areas to consider.
Definition at line 69 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), computeExpectations(), declareOptions(), fprop(), fpropNLL(), freeEnergyContribution(), generateSample(), generateSamples(), and getConfiguration().
Definition at line 76 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropUpdate(), build_(), declareOptions(), fpropNLL(), getConfiguration(), and getConfigurationCount().
Width of the areas to consider.
Definition at line 72 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), computeExpectations(), declareOptions(), fprop(), fpropNLL(), freeEnergyContribution(), generateSample(), generateSamples(), and getConfiguration().
Length of each of the images.
Definition at line 63 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), computeExpectations(), declareOptions(), fprop(), fpropNLL(), freeEnergyContribution(), generateSample(), generateSamples(), and getConfiguration().
Definition at line 75 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), computeExpectations(), declareOptions(), fprop(), fpropNLL(), generateSample(), and generateSamples().
Width of each of the images.
Definition at line 66 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), computeExpectations(), declareOptions(), fprop(), fpropNLL(), freeEnergyContribution(), generateSample(), generateSamples(), and getConfiguration().
Definition at line 77 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by build_(), freeEnergyContribution(), getConfiguration(), and getConfigurationCount().
Number of images present at the same time in the input vector.
Definition at line 60 of file RBMLocalMultinomialLayer.h.
Referenced by bpropUpdate(), build_(), computeExpectation(), computeExpectations(), declareOptions(), fprop(), fpropNLL(), freeEnergyContribution(), generateSample(), generateSamples(), and getConfiguration().
 1.7.4
1.7.4