|
PLearn 0.1
|
|
PLearn 0.1
|
#include <plearn/io/load_and_save.h>#include <plearn/math/TMat_maths.h>#include "SurfaceMesh.h"#include "geometry.h"#include <plearn/misc/qld_interface.h>#include <plearn/ker/GaussianKernel.h>#include "Template.h"#include <glpk.h>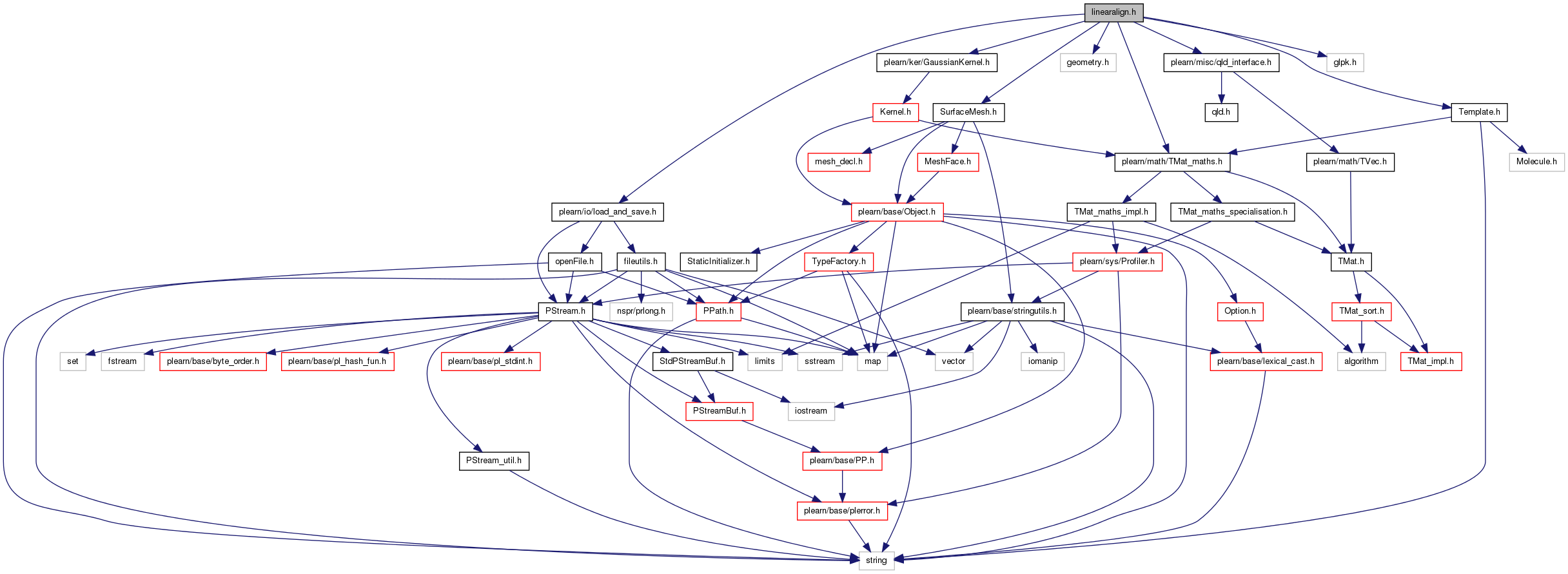
Go to the source code of this file.
Functions | |
| static void | nodekernel (const Mat &x, const Mat &y, const Mat &dev, real sigma, Mat &ans) |
| calculates the nodekernel...note that more the similarity more the nodekernel.its computing the exp(-distance).distance is computed taking into account the deviation and an additional scaling factor sigma | |
| static bool | compare (const pair< real, int > &a, const pair< real, int > &b) |
| static void | sortedIndexList (const Vec &tosort, vector< int > &slist) |
| static void | findRelevantWeights (const Mat &nkmat, vector< vector< bool > > &weights, int n) |
| given a node kernel it picks the top n node kernels in each row and column . | |
| static void | extractWeightList (const vector< vector< bool > > &wfilter, vector< pair< int, int > > &wlist) |
| static void | calculateEuclDist (const Mat &coords, Mat &dist) |
| static real | calcTransformation4 (const Mat &xmat, const Mat &ymat, const Mat &wij, const Mat &nk, Mat &rot, Vec &xm, Vec &ym) |
| see documenation about the alignment procedure. | |
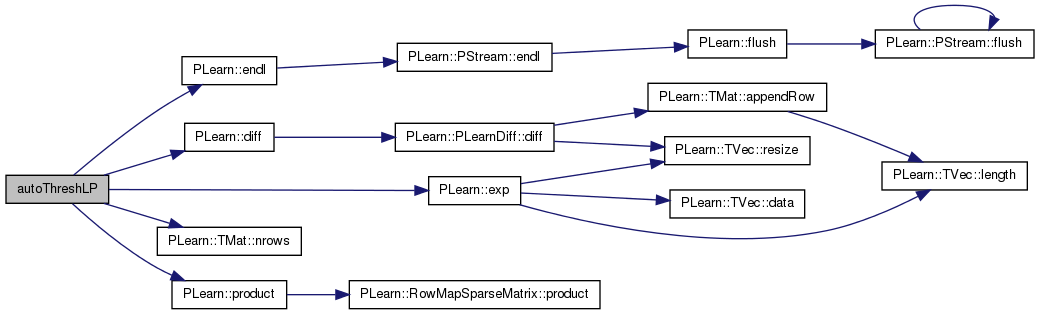
| static void | autoThreshLP (const Mat &dist1, const Mat &dist2, const Mat &nk, const vector< pair< int, int > > &wlist, const vector< vector< bool > > &wfilter, Mat &wm) |
| extension of calcLinearWeights ... | |
| static void | performLP (PMolecule name1, MoleculeTemplate name2, Mat &wm, bool isweighted) |
| given the molecule names , reads the vrml files and the properties and passes on the appropriate data to autoThreshLP. | |
| static void autoThreshLP | ( | const Mat & | dist1, |
| const Mat & | dist2, | ||
| const Mat & | nk, | ||
| const vector< pair< int, int > > & | wlist, | ||
| const vector< vector< bool > > & | wfilter, | ||
| Mat & | wm | ||
| ) | [static] |
extension of calcLinearWeights ...
uses fixed sigma and automatically selects suitable thresh from a fixed list. this is the version used for all calculations.
Definition at line 218 of file linearalign.h.
References a, b, PLearn::diff(), PLearn::endl(), PLearn::exp(), i, j, n, PLearn::TMat< T >::nrows(), and PLearn::product().
Referenced by performLP().
{
int nterms = 0;
int n = wlist.size();
int rows = dist1.nrows();
int cols = dist2.nrows();
int *ia = new int[1+50000];
int *ja = new int[1+50000];
double *ar = new double[1+50000];
const real sigma = 0.07;
vector< pair<int,int> > bpairs;
vector<real> products;
const double threshs[] = {0.7,0.75,0.8,0.85,0.9,0.95,0.97,0.98,0.99,0.995,0.999};
const int threshs_size = 11;
real thresh = threshs[0];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
int xa = wlist[i].first;
int ya = wlist[i].second;
int xb = wlist[j].first;
int yb = wlist[j].second;
if(nk[xa][ya]>thresh && nk[xb][yb]>thresh){
real d1 = dist1[xa][xb];
real d2 = dist2[ya][yb];
real diff = (d1-d2)*(d1-d2);
diff = diff/sigma*sigma;
real ekernel = exp(-diff);
real product = ekernel*nk[xa][ya]*nk[xb][yb];
if(product>thresh){
nterms++;
bpairs.push_back(pair<int,int>(i,j));
products.push_back(product);
}
}
}
}
//cout<<"number of quadratic constraints "<<nterms<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<threshs_size;i++){
if(nterms<0.15*n) break;
thresh = threshs[i];
nterms = 0;
for(unsigned int j=0;j<products.size();j++){
if(products[j]>thresh) nterms++;
}
}
// cout<<"threshold selected "<<thresh<<endl;
// cout<<"terms to be inserted "<<nterms<<endl;
int count = 1;
vector<real> row_bnds;
for(unsigned int k=0;k<products.size();k++){
if(products[k]>thresh){
int i = bpairs[k].first;
int j = bpairs[k].second;
int rownumber = rows + cols + (count+1)/2;
if (2 * n + count >= 50000) cout << "overflow" << endl;
ia[2*n + count] = rownumber;
ja[2*n + count] = i+1;
ar[2*n + count] = 1.0;
count++;
ia[2*n + count] = rownumber;
ja[2*n + count] = j+1;
ar[2*n + count] = 1.0;
row_bnds.push_back(1+products[k]);
count++;
}
}
//nconst = number of constraints
int nconst = rows+cols + nterms;
LPX *lp;
lp = lpx_create_prob();
lpx_set_int_parm(lp,LPX_K_MSGLEV,1);
lpx_set_obj_dir(lp,LPX_MIN);
lpx_add_cols(lp,n);
lpx_add_rows(lp,nconst);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
lpx_set_col_bnds(lp,i+1,LPX_DB,0.0,1.0);
}
//each weight appears in 2 constraints
//sconst : size of constraint vector
int sconst = 2*n + 2*nterms;
//generate row contraints
count = 1;
for(int i=0;i<rows;i++){
for(int j=0;j<cols;j++){
if(wfilter[i][j]){
ia[count] = i+1;
ja[count] = count;
ar[count] = 1.0;
ia[n+count] = j+rows+1;
ja[n+count] = count;
ar[n+count] = 1.0;
count++;
}
}
}
//generate the quadratic constraints
for(int i=0;i<nterms;i++){
lpx_set_row_bnds(lp,rows+cols+i+1,LPX_LO,row_bnds[i],0.0);
}
for(int i=0;i<rows+cols;i++){
lpx_set_row_bnds(lp,i+1,LPX_LO,1.0,0.0);
}
lpx_load_matrix(lp,sconst,ia,ja,ar);
//generate the linear coefficients of the weights which is just the nodekernels
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int a = wlist[i].first;
int b = wlist[i].second;
real coef = 1.0 - nk[a][b]; //+ lambda*abs(xcdist[a]-ycdist[b]);
lpx_set_obj_coef(lp,i+1,coef);
}
// time_t t1 = time(NULL);
lpx_simplex(lp);
// time_t t2 = time(NULL);
// cout<<difftime(t2,t1)<<endl;
wm = Mat(rows,cols,0.0);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
wm[wlist[i].first][wlist[i].second]=lpx_get_col_prim(lp,i+1);
}
lpx_delete_prob(lp);
free(ia);
free(ja);
free(ar);
}
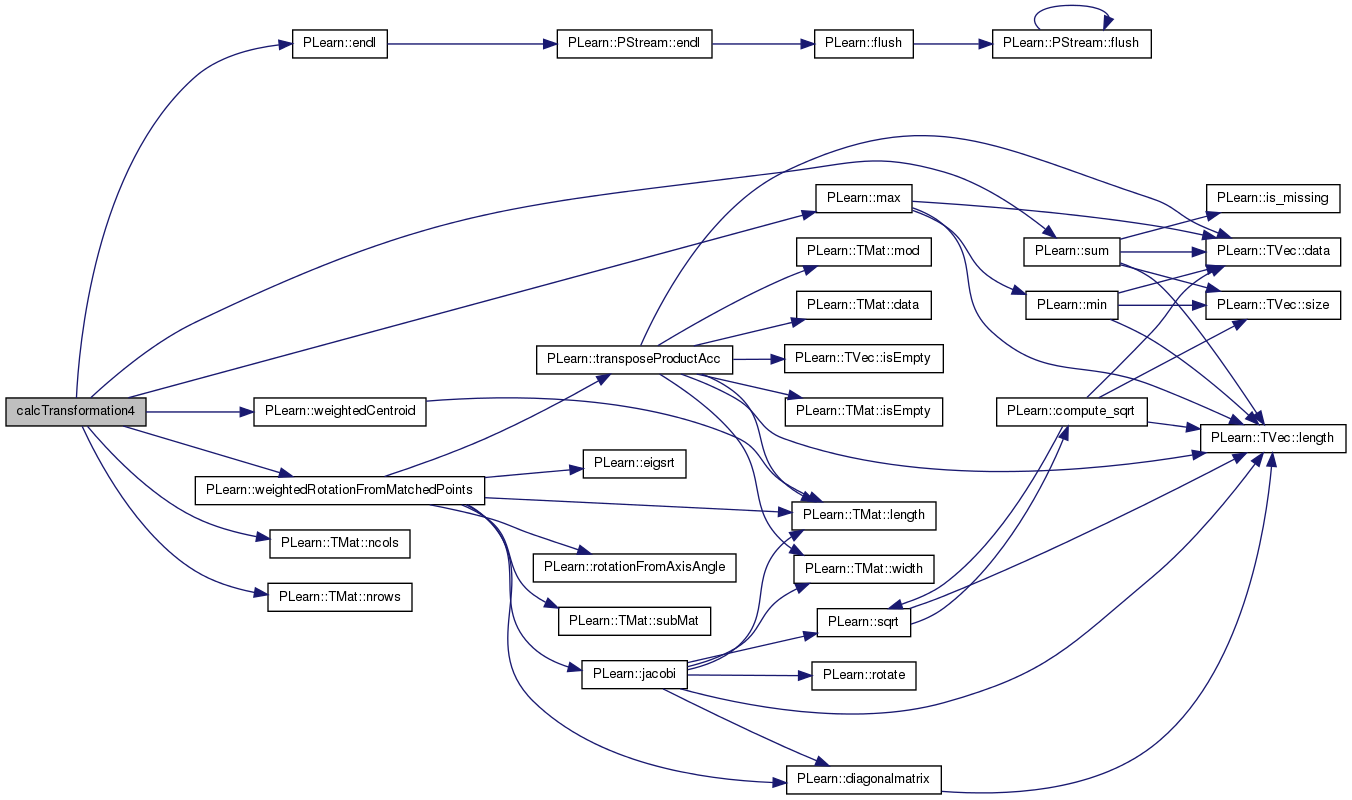
| static real calcTransformation4 | ( | const Mat & | xmat, |
| const Mat & | ymat, | ||
| const Mat & | wij, | ||
| const Mat & | nk, | ||
| Mat & | rot, | ||
| Vec & | xm, | ||
| Vec & | ym | ||
| ) | [static] |
see documenation about the alignment procedure.
this is the function being used to align
| xmat | coordinates of molecule x (to be transformed) |
| ymat | coordinates of molecule y |
| wij | weight matrix |
| nk | nodekernel |
| xm | weighted centroid of x |
| ym | weighted centroid of y |
Definition at line 167 of file linearalign.h.
References PLearn::endl(), i, j, PLearn::max(), PLearn::TMat< T >::ncols(), PLearn::TMat< T >::nrows(), PLearn::sum(), PLearn::weightedCentroid(), and PLearn::weightedRotationFromMatchedPoints().
{
int newn = xmat.nrows()+ymat.nrows();
Mat xmat2(newn,xmat.ncols());
Mat ymat2(newn,xmat.ncols());
Vec weights(newn);
for(int i=0;i<xmat.nrows();i++){
int max=0;
for(int j=0;j<ymat.nrows();j++){
if(wij[i][max]<wij[i][j]) max=j;
}
weights[i]=wij[i][max];
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
xmat2[i][j]=xmat[i][j];
ymat2[i][j]=ymat[max][j];
}
}
for(int i=0;i<ymat.nrows();i++){
int max=0;
for(int j=0;j<xmat.nrows();j++){
if(wij[max][i]<wij[j][i]) max=j;
}
weights[i+xmat.nrows()]=wij[max][i];
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
xmat2[i+xmat.nrows()][j]=xmat[max][j];
ymat2[i+xmat.nrows()][j]=ymat[i][j];
}
}
real sum = 0.0;
for(int i=0;i<xmat.nrows()+ymat.nrows();i++){
sum += weights[i];
}
real error;
rot = Mat(3,3);
xm = weightedCentroid(xmat,weights);
ym = weightedCentroid(ymat,weights);
xmat2 -= xm;
ymat2 -=ym;
rot = weightedRotationFromMatchedPoints(xmat2,ymat2,weights,error);
error /= sum;
cout<<"computation complete "<<error<<endl;
return error;
}
| coords | coordinates of the vertices among which distances are to be calculated |
| dist | euclidean distances will be reported in this mat |
Definition at line 141 of file linearalign.h.
References i, j, n, PLearn::TMat< T >::nrows(), and PLearn::sqrt().
Referenced by performLP().
{
int n = coords.nrows();
dist = Mat(n,n,0.0);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
for(int k=0;k<3;k++){
dist[i][j] += (coords[i][k]-coords[j][k])*(coords[i][k]-coords[j][k]);
}
dist[i][j] = sqrt(dist[i][j]);
}
}
}
Definition at line 47 of file linearalign.h.
| static void extractWeightList | ( | const vector< vector< bool > > & | wfilter, |
| vector< pair< int, int > > & | wlist | ||
| ) | [static] |
| wfilter | the boolean matrix containing info about which weights are to be considered |
| wlist | list of pairs of indices which will contain the same info as wfilter but it carries it in a list form. this makes it possible to traverse over the list of weights |
Definition at line 119 of file linearalign.h.
Referenced by performLP().
{
int nx = wfilter.size();
int count = 0;
for(int i=0;i<nx;i++){
int ny = wfilter[i].size();
for(int j=0;j<ny;j++){
if(wfilter[i][j]==true){
pair<int,int> w;
w.first = i;
w.second = j;
wlist.push_back(w);
count++;
}
}
}
//cout<<count<<" entries added to wlist"<<endl;
}
| static void findRelevantWeights | ( | const Mat & | nkmat, |
| vector< vector< bool > > & | weights, | ||
| int | n | ||
| ) | [static] |
given a node kernel it picks the top n node kernels in each row and column .
only these weights need to considered as all other weights will probably come out to be zero anyway. this way we can reduce the number of variables in our optimization problem
| nkmat | node kernel matrix |
| weights | this is a boolean matrix which will contain which weights are to be considered |
| n | minimum number of weights to be considered in a row or column |
Definition at line 77 of file linearalign.h.
References compare(), i, j, n, PLearn::TMat< T >::ncols(), PLearn::TMat< T >::nrows(), and w.
Referenced by performLP().
{
const int nx = nkmat.nrows();
const int ny = nkmat.ncols();
weights = vector< vector <bool> >(nx);
for(int i=0;i<nx;i++){
weights[i] = vector<bool>(ny,false);
}
/*n weights in each row be present*/
for(int i=0;i<nx;i++){
vector< pair<real,int> > w(ny);
for(int j=0;j<ny;j++){
w[j].first=nkmat[i][j];
w[j].second=j;
}
sort(w.begin(),w.end(),compare);
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
int k = w[ny - j -1].second;
weights[i][k] = true ;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<ny;i++){
vector< pair<real,int> > w(nx);
for(int j=0;j<nx;j++){
w[j].first=nkmat[j][i];
w[j].second=j;
}
sort(w.begin(),w.end(),compare);
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
int k = w[nx - j -1].second;
weights[k][i] = true ;
}
}
}

| static void nodekernel | ( | const Mat & | x, |
| const Mat & | y, | ||
| const Mat & | dev, | ||
| real | sigma, | ||
| Mat & | ans | ||
| ) | [static] |
calculates the nodekernel...note that more the similarity more the nodekernel.its computing the exp(-distance).distance is computed taking into account the deviation and an additional scaling factor sigma
| x | property matrix of first molecule |
| y | property matrix of the model (template) |
| sigma | additional scaling factor. |
| ans | the answer...i.e. the nodekernel matrix. ans is assigned a newly created matrix |
Definition at line 26 of file linearalign.h.
References PLearn::exp(), i, j, PLearn::TMat< T >::ncols(), PLearn::TMat< T >::nrows(), and PLERROR.
Referenced by performLP().
{
int xrows=x.nrows();
int yrows=y.nrows();
int cols=x.ncols();
if(cols!=y.ncols()){
PLERROR("The property matrices have different number of fields");
}
ans=Mat(xrows,yrows,0.0);
//cout<<"number of columns "<<cols<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<xrows;i++){
for(int j=0;j<yrows;j++){
for(int k=0;k<x.ncols();k++){
real term = (x[i][k]-y[j][k])/(dev[j][k]*sigma);
term *= term;
ans[i][j] += term;
}
ans[i][j] = exp(-ans[i][j]);
}
}
}

| static void performLP | ( | PMolecule | name1, |
| MoleculeTemplate | name2, | ||
| Mat & | wm, | ||
| bool | isweighted | ||
| ) | [static] |
given the molecule names , reads the vrml files and the properties and passes on the appropriate data to autoThreshLP.
this is the front end that is used.
| name1 | name of molecule to be aligned |
| name2 | name of molecule with which to align |
| wm | weight matrix |
| isweighted | take into account deviations ? |
Definition at line 351 of file linearalign.h.
References a, autoThreshLP(), b, calculateEuclDist(), PLearn::Molecule::chem, PLearn::endl(), extractWeightList(), findRelevantWeights(), PLearn::Molecule::geom, i, j, PLearn::PLearnError::message(), n, PLearn::TMat< T >::ncols(), nodekernel(), PLearn::TMat< T >::nrows(), PLERROR, and PLearn::TMat< T >::size().
{
try{
// cout<<"performing lp on "<<name1<<" "<<name2<<endl;
Mat xprpt,yprpt;
xprpt = name1->chem ;
yprpt = name2->chem ;
Mat dev;
// if(isweighted){
// load(name2+"Dev.mat",dev);
// }else{
dev=Mat(yprpt.nrows(),yprpt.ncols(),1.0);
// }
vector<int> common_prpt;
for(int i=0;i<yprpt.ncols();i++){
if(yprpt[0][i]<5000.0 && xprpt[0][i]<5000.0){
common_prpt.push_back(i);
}
}
Mat xprpt2(xprpt.nrows(),common_prpt.size(),0.0);
Mat yprpt2(yprpt.nrows(),common_prpt.size(),0.0);
Mat dev2(yprpt.nrows(),common_prpt.size(),0.0);
for(unsigned int j=0;j<common_prpt.size();j++){
int k = common_prpt[j];
for(int i=0;i<xprpt.nrows();i++){
xprpt2[i][j]=xprpt[i][k];
}
for(int i=0;i<yprpt.nrows();i++){
yprpt2[i][j]=yprpt[i][k];
dev2[i][j]=dev[i][k];
}
}
Mat nk;
nodekernel(xprpt2,yprpt2,dev2,0.3*common_prpt.size(),nk);
const int rows=nk.nrows();
const int cols=nk.ncols();
const int yjperxi = 5;
vector< vector<bool> > wfilter;
vector< pair<int,int> > wlist;
findRelevantWeights(nk,wfilter,yjperxi);
extractWeightList(wfilter,wlist);
const int n = wlist.size();
/*reading distances*/
Mat dist1,dist2;
calculateEuclDist(name1->geom,dist1);
calculateEuclDist(name2->geom,dist2);
if(dist1.nrows()!=rows || dist2.nrows()!=cols){
cout<<dist1.nrows()<<" "<<dist2.nrows()<<" "<<rows<<" "<<cols<<endl;
PLERROR("the dimensions in dist files and nkmat do not match\n");
}
Mat xmat,ymat;
xmat = name1->geom ;
ymat = name2->geom ;
//cout<<"got vertex coords"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int a = wlist[i].first;
int b = wlist[i].second;
if(a>=rows || b>=cols){
cout<<i<<" "<<a<<" "<<b<<endl;
}
}
//calcLinearWeights(dist1,dist2,nk,wlist,wfilter,sigma,thresh,wm);
autoThreshLP(dist1,dist2,nk,wlist,wfilter,wm);
//calcTransformation4(xmat,ymat,wm,nk,rot,xm,ym);
//writeAlignment(name1,xm,ym,rot,"lpw4");
}catch(PLearnError e){
cout<<e.message()<<endl;
}
}
| tosort | a plearn Vec which you want to sort |
| slist | it will contain the list of indices of tosort in a sorted manner. thus last entry of slist is the index of largest value in tosort |
Definition at line 55 of file linearalign.h.
References compare(), i, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), and n.
{
int n = tosort.length();
vector< pair<real,int> > ilist;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
pair<real,int> temp;
temp.first = tosort[i];
temp.second = i;
ilist.push_back(temp);
}
sort(ilist.begin(),ilist.end(),compare);
slist = vector<int>(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
slist[i] = ilist[i].second;
}
}
 1.7.4
1.7.4