|
PLearn 0.1
|
|
PLearn 0.1
|
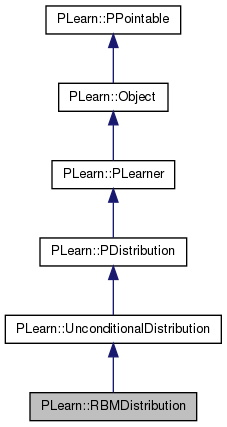
The first sentence should be a BRIEF DESCRIPTION of what the class does. More...
#include <RBMDistribution.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| RBMDistribution () | |
| Default constructor. | |
| virtual real | log_density (const Vec &x) const |
| Return log of probability density log(p(y)). | |
| virtual real | survival_fn (const Vec &y) const |
| Return survival function: P(Y>y). | |
| virtual real | cdf (const Vec &y) const |
| Return cdf: P(Y<y). | |
| virtual void | expectation (Vec &mu) const |
| Return E[Y]. | |
| virtual void | variance (Mat &cov) const |
| Return Var[Y]. | |
| virtual void | generate (Vec &y) const |
| Return a pseudo-random sample generated from the distribution. | |
| void | generateN (const Mat &Y) const |
| Overridden for efficiency purpose. | |
| virtual void | resetGenerator (long g_seed) |
| Reset the random number generator used by generate() using the given seed. | |
| virtual void | forget () |
| (Re-)initializes the PDistribution in its fresh state (that state may depend on the 'seed' option) and sets 'stage' back to 0 (this is the stage of a fresh learner!). | |
| virtual void | train () |
| The role of the train method is to bring the learner up to stage == nstages, updating the train_stats collector with training costs measured on-line in the process. | |
| virtual string | classname () const |
| virtual OptionList & | getOptionList () const |
| virtual OptionMap & | getOptionMap () const |
| virtual RemoteMethodMap & | getRemoteMethodMap () const |
| virtual RBMDistribution * | deepCopy (CopiesMap &copies) const |
| virtual void | build () |
| Simply call inherited::build() then build_(). | |
| virtual void | makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy (CopiesMap &copies) |
| Transforms a shallow copy into a deep copy. | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static string | _classname_ () |
| static OptionList & | _getOptionList_ () |
| static RemoteMethodMap & | _getRemoteMethodMap_ () |
| static Object * | _new_instance_for_typemap_ () |
| static bool | _isa_ (const Object *o) |
| static void | _static_initialize_ () |
| static const PPath & | declaringFile () |
Public Attributes | |
| PP< RBMModule > | rbm |
| real | n_gibbs_chains |
| VMat | sample_data |
| bool | unnormalized_density |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static StaticInitializer | _static_initializer_ |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static void | declareOptions (OptionList &ol) |
| Declares the class options. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| PP< ModuleLearner > | learner |
| Associated learner to train the RBM. | |
| TVec< Mat * > | ports_val |
| Vector of data passed to the fprop(..) method of the RBM. | |
| Mat | work1 |
| Temporary storage. | |
| Mat | work2 |
| Mat | work3 |
| Vec | workv1 |
| Temporary storage. | |
Private Types | |
| typedef UnconditionalDistribution | inherited |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | build_ () |
| This does the actual building. | |
The first sentence should be a BRIEF DESCRIPTION of what the class does.
Place the rest of the class programmer documentation here. Doxygen supports Javadoc-style comments. See http://www.doxygen.org/manual.html
Definition at line 59 of file RBMDistribution.h.
typedef UnconditionalDistribution PLearn::RBMDistribution::inherited [private] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 61 of file RBMDistribution.h.
| PLearn::RBMDistribution::RBMDistribution | ( | ) |
Default constructor.
Definition at line 54 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
:
n_gibbs_chains(-1),
unnormalized_density(false)
{}
| string PLearn::RBMDistribution::_classname_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 49 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
| OptionList & PLearn::RBMDistribution::_getOptionList_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 49 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::RBMDistribution::_getRemoteMethodMap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 49 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 49 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
| Object * PLearn::RBMDistribution::_new_instance_for_typemap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 49 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
| StaticInitializer RBMDistribution::_static_initializer_ & PLearn::RBMDistribution::_static_initialize_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 49 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
| void PLearn::RBMDistribution::build | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Simply call inherited::build() then build_().
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 106 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
References PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution::build(), and build_().
{
inherited::build();
build_();
}

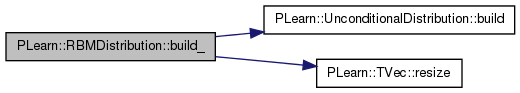
| void PLearn::RBMDistribution::build_ | ( | ) | [private] |
This does the actual building.
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 115 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
References PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution::build(), ports_val, PLearn::PDistribution::predicted_size, rbm, and PLearn::TVec< T >::resize().
Referenced by build().
{
if (!rbm)
return;
int n_ports = rbm->nPorts();
ports_val.resize(n_ports);
predicted_size = rbm->visible_layer->size;
// Rebuild the PDistribution object to take size into account.
inherited::build();
}

Return cdf: P(Y<y).
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 129 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
References PLERROR.
{
PLERROR("cdf not implemented for RBMDistribution"); return 0;
}
| string PLearn::RBMDistribution::classname | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 49 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
| void PLearn::RBMDistribution::declareOptions | ( | OptionList & | ol | ) | [static, protected] |
Declares the class options.
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 62 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
References PLearn::OptionBase::buildoption, PLearn::declareOption(), PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution::declareOptions(), n_gibbs_chains, rbm, sample_data, and unnormalized_density.
{
// ### Declare all of this object's options here.
// ### For the "flags" of each option, you should typically specify
// ### one of OptionBase::buildoption, OptionBase::learntoption or
// ### OptionBase::tuningoption. If you don't provide one of these three,
// ### this option will be ignored when loading values from a script.
// ### You can also combine flags, for example with OptionBase::nosave:
// ### (OptionBase::buildoption | OptionBase::nosave)
declareOption(ol, "rbm", &RBMDistribution::rbm,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Underlying RBM modeling the distribution.");
declareOption(ol, "n_gibbs_chains", &RBMDistribution::n_gibbs_chains,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Number of Gibbs chains ran in parallel when generating multiple\n"
"samples with generateN(). If <0, then there are as many chains as\n"
"samples. If in the (0,1) interval, then it is the given fraction of\n"
"the number of generated samples. If an integer >= 1, it is the\n"
"absolute number of chains that are run simultaneously. Each chain\n"
"will sample about N/n_chains samples, so as to obtain N samples.");
declareOption(ol, "unnormalized_density",
&RBMDistribution::unnormalized_density,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"If set to True, then the density will not be normalized (so the\n"
"partition function does not need to be computed). This means the\n"
"value returned by the 'log_density' method will instead be the\n"
"negative free energy of the visible input.");
declareOption(ol, "sample_data",
&RBMDistribution::sample_data,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"If provided, this data will be used to initialize the Gibbs\n"
"chains when generating samples.");
// Now call the parent class' declareOptions().
inherited::declareOptions(ol);
}

| static const PPath& PLearn::RBMDistribution::declaringFile | ( | ) | [inline, static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 138 of file RBMDistribution.h.
:
| RBMDistribution * PLearn::RBMDistribution::deepCopy | ( | CopiesMap & | copies | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 49 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
| void PLearn::RBMDistribution::expectation | ( | Vec & | mu | ) | const [virtual] |
Return E[Y].
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 137 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
References PLERROR.
{
PLERROR("In RBMDistribution::expectation - Not implemeted");
}
| void PLearn::RBMDistribution::forget | ( | ) | [virtual] |
(Re-)initializes the PDistribution in its fresh state (that state may depend on the 'seed' option) and sets 'stage' back to 0 (this is the stage of a fresh learner!).
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 145 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
References PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution::forget(), learner, PLearn::PDistribution::n_predicted, and rbm.
{
rbm->forget();
learner = NULL;
inherited::forget();
n_predicted = rbm->visible_layer->size;
}

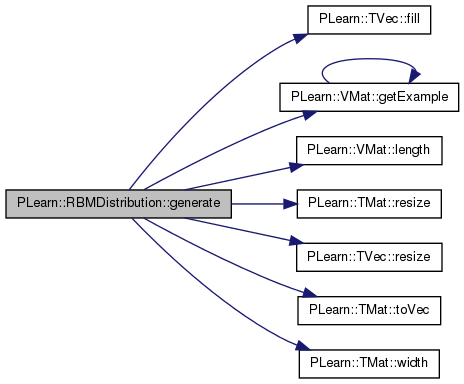
| void PLearn::RBMDistribution::generate | ( | Vec & | y | ) | const [virtual] |
Return a pseudo-random sample generated from the distribution.
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 156 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
References PLearn::TVec< T >::fill(), PLearn::VMat::getExample(), PLearn::VMat::length(), ports_val, PLearn::PLearner::random_gen, rbm, PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), sample_data, PLearn::TMat< T >::toVec(), PLearn::TMat< T >::width(), work1, work2, work3, and workv1.
{
work1.resize(0, 0);
ports_val.fill(NULL);
ports_val[rbm->getPortIndex("visible_sample")] = &work1;
if (sample_data) {
// Pick a random sample to initialize the Gibbs chain.
int init_i =
random_gen->uniform_multinomial_sample(sample_data->length());
real dummy_weight;
work3.resize(1, sample_data->inputsize());
Vec w3 = work3.toVec();
sample_data->getExample(init_i, w3, workv1, dummy_weight);
ports_val[rbm->getPortIndex("visible")] = &work2;
}
rbm->fprop(ports_val);
y.resize(work1.width());
y << work1(0);
}
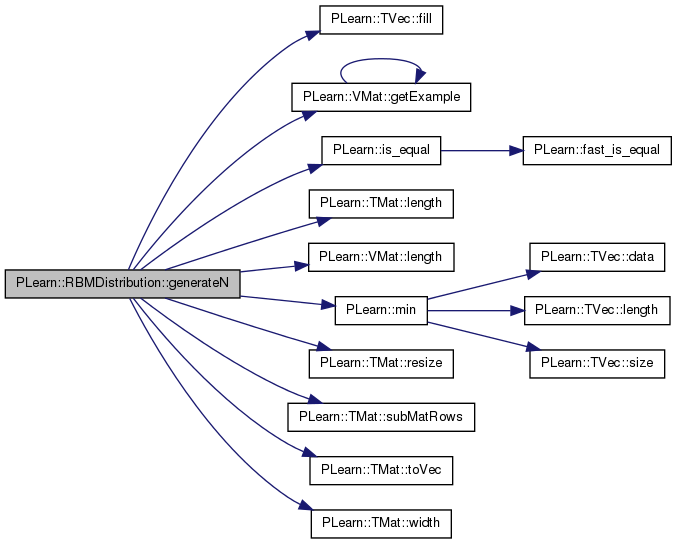
| void PLearn::RBMDistribution::generateN | ( | const Mat & | Y | ) | const [virtual] |
Overridden for efficiency purpose.
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 179 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
References PLearn::TVec< T >::fill(), PLearn::VMat::getExample(), i, PLearn::is_equal(), j, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::VMat::length(), PLearn::min(), n, n_gibbs_chains, PLCHECK, ports_val, PLearn::PLearner::random_gen, rbm, PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), sample_data, PLearn::TMat< T >::subMatRows(), PLearn::TMat< T >::toVec(), PLearn::PLearner::verbosity, PLearn::TMat< T >::width(), work1, work2, work3, and workv1.
{
int n = Y.length(); // Number of samples to obtain.
int n_chains = Y.length();
if (n_gibbs_chains > 0 && n_gibbs_chains < 1) {
// Fraction.
n_chains = min(1, int(round(n_gibbs_chains * n)));
} else if (n_gibbs_chains > 0) {
n_chains = int(round(n_gibbs_chains));
PLCHECK( is_equal(real(n_chains), n_gibbs_chains) );
}
int n_gibbs_samples = n / n_chains;
if (n % n_chains > 0)
n_gibbs_samples += 1;
work2.resize(n_chains * n_gibbs_samples, Y.width());
PP<ProgressBar> pb = verbosity && work2.length() > 10
? new ProgressBar("Gibbs sampling", work2.length())
: NULL;
int idx = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n_chains; j++) {
ports_val.fill(NULL);
if (sample_data) {
// Pick a sample to initialize the Gibbs chain.
int init_i;
if (n_chains == sample_data->length())
// We use each sample once and only once.
init_i = j;
else
// Pick the sample randomly.
init_i = random_gen->uniform_multinomial_sample(sample_data->length());
real dummy_weight;
work3.resize(1, sample_data->inputsize());
Vec w3 = work3.toVec();
sample_data->getExample(init_i, w3, workv1, dummy_weight);
ports_val[rbm->getPortIndex("visible")] = &work3;
}
// Crash if not in the specific case where we have sample data and we
// compute only 1 sample in each chain. This is because otherwise I
// (Olivier D.) am not sure the chain is properly (i) restarted for
// each new chain, and (ii) kept intact when continuing the same chain.
PLCHECK(sample_data && n_gibbs_samples == 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n_gibbs_samples; i++) {
work1.resize(0, 0);
ports_val[rbm->getPortIndex("visible_sample")] = &work1;
rbm->fprop(ports_val);
work2(idx) << work1;
idx++;
if (pb)
pb->update(idx);
}
}
if (n_gibbs_samples > 1)
// We shuffle rows to add more "randomness" since consecutive samples
// in the same Gibbs chain may be similar.
random_gen->shuffleRows(work2);
Y << work2.subMatRows(0, Y.length());
}
| OptionList & PLearn::RBMDistribution::getOptionList | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 49 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
| OptionMap & PLearn::RBMDistribution::getOptionMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 49 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::RBMDistribution::getRemoteMethodMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 49 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
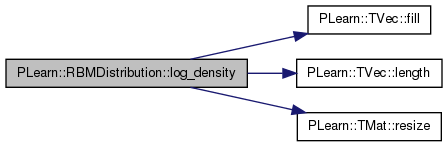
Return log of probability density log(p(y)).
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 240 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
References PLearn::TVec< T >::fill(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), ports_val, rbm, PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), unnormalized_density, work1, and work2.
{
ports_val.fill(NULL);
work1.resize(1, 0);
work2.resize(1, y.length());
work2 << y;
if (unnormalized_density)
ports_val[rbm->getPortIndex("energy")] = &work1;
else
ports_val[rbm->getPortIndex("neg_log_likelihood")] = &work1;
ports_val[rbm->getPortIndex("visible")] = &work2;
rbm->fprop(ports_val);
return -work1(0, 0);
}
| void PLearn::RBMDistribution::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy | ( | CopiesMap & | copies | ) | [virtual] |
Transforms a shallow copy into a deep copy.
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 258 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
References PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), and PLERROR.
{
inherited::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(copies);
// ### Call deepCopyField on all "pointer-like" fields
// ### that you wish to be deepCopied rather than
// ### shallow-copied.
// ### ex:
// deepCopyField(trainvec, copies);
// ### Remove this line when you have fully implemented this method.
PLERROR("RBMDistribution::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy not fully (correctly) implemented yet!");
}

| void PLearn::RBMDistribution::resetGenerator | ( | long | g_seed | ) | [virtual] |
Reset the random number generator used by generate() using the given seed.
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 275 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
References PLERROR, rbm, and PLearn::PDistribution::resetGenerator().
{
if (!rbm->random_gen)
PLERROR("In RBMDistribution::resetGenerator - The underlying RBM "
"must have a random number generator");
if (g_seed != 0)
rbm->random_gen->manual_seed(g_seed);
inherited::resetGenerator(g_seed);
}

Return survival function: P(Y>y).
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 288 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
References PLERROR.
{
PLERROR("survival_fn not implemented for RBMDistribution"); return 0;
}
| void PLearn::RBMDistribution::train | ( | ) | [virtual] |
The role of the train method is to bring the learner up to stage == nstages, updating the train_stats collector with training costs measured on-line in the process.
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 296 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
References learner, PLearn::PLearner::nstages, rbm, PLearn::PLearner::seed_, PLearn::PLearner::stage, PLearn::PLearner::train_set, and PLearn::PLearner::use_a_separate_random_generator_for_testing.
{
if (!learner) {
// First build the learner that will train a RBM.
learner = new ModuleLearner();
learner->module = rbm;
learner->seed_ = this->seed_;
learner->use_a_separate_random_generator_for_testing =
this->use_a_separate_random_generator_for_testing;
learner->input_ports = TVec<string>(1, "visible");
learner->target_ports.resize(0);
learner->cost_ports.resize(0);
learner->build();
learner->setTrainingSet(this->train_set);
}
learner->nstages = this->nstages;
learner->train();
this->stage = learner->stage;
}
| void PLearn::RBMDistribution::variance | ( | Mat & | cov | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 319 of file RBMDistribution.cc.
References PLERROR.
{
PLERROR("variance not implemented for RBMDistribution");
}
Reimplemented from PLearn::UnconditionalDistribution.
Definition at line 138 of file RBMDistribution.h.
PP<ModuleLearner> PLearn::RBMDistribution::learner [protected] |
Associated learner to train the RBM.
Definition at line 150 of file RBMDistribution.h.
Definition at line 68 of file RBMDistribution.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), and generateN().
TVec<Mat*> PLearn::RBMDistribution::ports_val [protected] |
Vector of data passed to the fprop(..) method of the RBM.
Definition at line 153 of file RBMDistribution.h.
Referenced by build_(), generate(), generateN(), and log_density().
Definition at line 66 of file RBMDistribution.h.
Referenced by build_(), declareOptions(), forget(), generate(), generateN(), log_density(), resetGenerator(), and train().
Definition at line 69 of file RBMDistribution.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), generate(), and generateN().
Definition at line 70 of file RBMDistribution.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), and log_density().
Mat PLearn::RBMDistribution::work1 [mutable, protected] |
Temporary storage.
Definition at line 156 of file RBMDistribution.h.
Referenced by generate(), generateN(), and log_density().
Mat PLearn::RBMDistribution::work2 [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 156 of file RBMDistribution.h.
Referenced by generate(), generateN(), and log_density().
Mat PLearn::RBMDistribution::work3 [mutable, protected] |
Definition at line 156 of file RBMDistribution.h.
Referenced by generate(), and generateN().
Vec PLearn::RBMDistribution::workv1 [mutable, protected] |
Temporary storage.
Definition at line 159 of file RBMDistribution.h.
Referenced by generate(), and generateN().
 1.7.4
1.7.4