|
PLearn 0.1
|
|
PLearn 0.1
|
#include <Func.h>
Public Types | |
| typedef Object | inherited |
Public Member Functions | |
| Function () | |
| Function. | |
| Function (const VarArray &the_inputs, const VarArray &the_outputs) | |
| Function (const VarArray &the_inputs, const VarArray ¶meters_to_optimize, const VarArray &the_outputs) | |
| virtual void | build () |
| simply calls inherited::build() then build_() | |
| virtual void | makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy (CopiesMap &copies) |
| Transforms a shallow copy into a deep copy. | |
| virtual string | classname () const |
| virtual OptionList & | getOptionList () const |
| virtual OptionMap & | getOptionMap () const |
| virtual RemoteMethodMap & | getRemoteMethodMap () const |
| virtual Function * | deepCopy (CopiesMap &copies) const |
| void | fprop (const Vec &in, const Vec &out) const |
| void | fprop (const Array< Vec > &in, const Array< Vec > &out) const |
| void | sizefprop (const Vec &in, const Vec &out) const |
| void | sizefprop (const Array< Vec > &in, const Array< Vec > &out) const |
| void | fbprop (const Vec &in, const Vec &out, const Vec &input_gradient, const Vec &output_gradient) |
| void | fbprop (const Array< Vec > &in, const Array< Vec > &out, const Array< Vec > &input_gradient, const Array< Vec > &output_gradient) |
| void | sizefbprop (const Vec &in, const Vec &out, const Vec &input_gradient, const Vec &output_gradient) |
| void | sizefbprop (const Array< Vec > &in, const Array< Vec > &out, const Array< Vec > &input_gradient, const Array< Vec > &output_gradient) |
| void | fbbprop (const Vec &in, const Vec &out, const Vec &gradient, const Mat &hessian) |
| given input, compute output, gradient (=doutput/dinput) and hessian (=d^2output/dinput^2) | |
| void | fbbpropAcc (const Vec &in, const Vec &out, const Vec &gradient, const Mat &hessian) |
| same thing but accumulate output, gradient and hessian | |
| void | rfprop (const Vec &in, const Vec &out, const Vec &input_rvalue, const Vec &output_rvalue, bool do_fprop=true) |
| void | recomputeParents () |
| recomputes the value of all the vars that influence the output but do not depend on the declared inputs (shared parameters for instance...) | |
| Func | differentiate () |
| Vec | operator() (const Vec &input) const |
| real | operator() (const Vec &input1, const Vec &input2) const |
| VarArray | operator() (const VarArray &new_inputs) const |
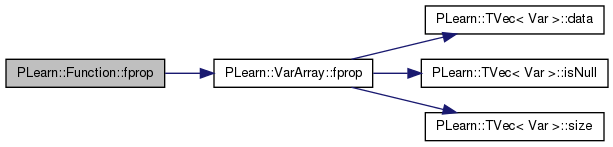
| void | verifyGradient (const Vec &in, real step=0.01, int which_component=0) |
| take the values given in the in Vec | |
| void | verifyHessian (const Vec &in, real step=0.01) |
| void | verifyGradient (real minval, real maxval, real step=0.01, int which_component=0) |
| take the values randomly between minval and maxval | |
| void | verifyGradient (real step=0.01, int which_component=0) |
| take the current values of the inputs variables | |
| void | verifySymbolicGradient (const Vec &in) |
| void | verifyrfprop (const Vec &in, real step=0.01) |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static string | _classname_ () |
| static OptionList & | _getOptionList_ () |
| static RemoteMethodMap & | _getRemoteMethodMap_ () |
| static Object * | _new_instance_for_typemap_ () |
| static bool | _isa_ (const Object *o) |
| static void | _static_initialize_ () |
| static const PPath & | declaringFile () |
Public Attributes | |
| VarArray | inputs |
| VarArray | parameters |
| nonInputSources | |
| VarArray | outputs |
| int | inputsize |
| int | outputsize |
| VarArray | fproppath |
| VarArray | bproppath |
| VarArray | parentspath |
| path on which to do a fprop to update the values of all the non-input direct parents on the fproppath (this will be called by method recomputeParents() ) | |
| Func | df |
| remembers the symbolic derivative | |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static StaticInitializer | _static_initializer_ |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static void | declareOptions (OptionList &ol) |
| Declares this class' options. | |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | build_ () |
| This does the actual building. | |
| typedef Object PLearn::Function::inherited |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
| PLearn::Function::Function | ( | ) |
| string PLearn::Function::_classname_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
| OptionList & PLearn::Function::_getOptionList_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::Function::_getRemoteMethodMap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
| Object * PLearn::Function::_new_instance_for_typemap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
| StaticInitializer Function::_static_initializer_ & PLearn::Function::_static_initialize_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
| void PLearn::Function::build | ( | ) | [virtual] |
simply calls inherited::build() then build_()
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 192 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::Object::build(), and build_().
{
inherited::build();
build_();
}
| void PLearn::Function::build_ | ( | ) | [private] |
This does the actual building.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 151 of file Func.cc.
References bproppath, fproppath, inputs, inputsize, PLearn::TVec< T >::isEmpty(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::VarArray::nelems(), PLearn::nonInputSources(), outputs, outputsize, parameters, parentspath, PLearn::propagationPath(), PLearn::propagationPathToParentsOfPath(), and recomputeParents().
Referenced by build(), and Function().
{
if(parameters.isEmpty())
parameters = nonInputSources(inputs, outputs);
inputsize = inputs.nelems();
outputsize = outputs.nelems();
fproppath = propagationPath(inputs, outputs);
if (fproppath.length()==0) // to handle the weird case in which there is no path from inputs to outputs
// but outputs still depends on parameters and we want to represent that dependency
{
fproppath = propagationPath(inputs & parameters, outputs);
bproppath = propagationPath(inputs & parameters, outputs);
}
else
bproppath = propagationPath(inputs, outputs);
parentspath = propagationPathToParentsOfPath(inputs, outputs);
recomputeParents();
//parameters_to_optimize.printNames();
//cout<<"**************Func::printInfo(inputs, outputs);"<<endl;
//printInfo(inputs, outputs);
//cout<<"**************Func::printInfo(parameters_to_optimize, outputs);"<<endl;
//printInfo(parameters_to_optimize,outputs);
//displayVarGraph(fproppath,true, 333, "ffpp", false);
//displayVarGraph(bproppath,true, 333, "fbpp", false);
// Let's see if getting everything in a single chunk of memory will improve efficiency...
// Hmm, doesn't seem to.
/*
VarArray criticalvars = the_inputs & fproppath;
int n = criticalvars.nelems();
Vec data(2*n);
criticalvars.makeSharedValue(data);
criticalvars.makeSharedGradient(data,n);
*/
}
| string PLearn::Function::classname | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
| void PLearn::Function::declareOptions | ( | OptionList & | ol | ) | [static, protected] |
Declares this class' options.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 135 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::OptionBase::buildoption, PLearn::declareOption(), PLearn::Object::declareOptions(), inputs, outputs, and parameters.
{
declareOption(ol, "inputs", &Function::inputs, OptionBase::buildoption,
"The list of input variabes of this function");
declareOption(ol, "parameters", &Function::parameters, OptionBase::buildoption,
"The list of parameters to optimize");
declareOption(ol, "outputs", &Function::outputs, OptionBase::buildoption,
"The list of output variables of this function");
// Now call the parent class' declareOptions
inherited::declareOptions(ol);
}
| static const PPath& PLearn::Function::declaringFile | ( | ) | [inline, static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
| Func PLearn::Function::differentiate | ( | ) |
Returns a Func that will compute the derivative of this function's output (expected to be a scalar) relative to the given input (of length inputsize) The computed derivative has (logically) also a length of inputsize. (This call uses symbolic gradient computation)
Definition at line 390 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::VarArray::clearSymbolicGradient(), df, PLearn::endl(), fproppath, g, i, inputs, PLearn::VarArray::nelems(), outputs, PLearn::VarArray::parents(), PLERROR, PLearn::propagationPath(), PLearn::VarArray::resizeRValue(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::VarArray::symbolicBprop(), and PLearn::VarArray::symbolicGradient().
Referenced by fbbprop(), fbbpropAcc(), verifyrfprop(), and verifySymbolicGradient().
{
if (outputs.size()>1)
PLERROR("In Function::differentiate cannot differentiate function with more than one output variable");
Var output = outputs[0];
if(df==0)
{
output->g = Var(1,"output->g");
output->g = 1.0; // fill gradient
fproppath.symbolicBprop();
// Give the symbolic gradient vars reasonable names
for(int i=0; i<fproppath.size(); i++)
{
if(!fproppath[i]->g)
{
string name = "gr_" + fproppath[i]->getName();
fproppath[i]->g->setName(name);
}
}
for(int i=0; i<inputs.size(); i++)
{
if(inputs[i]->g.isNull()) // must create it, even though it will remain 0
inputs[i]->g = Var(inputs[i]->length(), inputs[i]->width());
string name = "gr_" + inputs[i]->getName();
inputs[i]->g->setName(name);
}
VarArray dinputs = inputs.symbolicGradient();
// Sanity check:
if(dinputs.nelems() != inputs.nelems())
PLERROR("Problem in Function::differentiate() please send a bug report to vincentp@iro.umontreal.ca");
cerr << "i0: " << inputs[0]->classname() << endl;
cerr << "i1: " << inputs[1]->classname() << endl;
cerr << "di0: " << dinputs[0]->classname() << endl;
cerr << "di1: " << dinputs[1]->classname() << endl;
dinputs.resizeRValue();
cerr << "di0 = " << dinputs[0]->rvaluedata << endl;
df = Func(inputs, dinputs);
df->fproppath = propagationPath(fproppath.parents() & (VarArray)output->g, dinputs);
fproppath.clearSymbolicGradient();
}
return df;
}
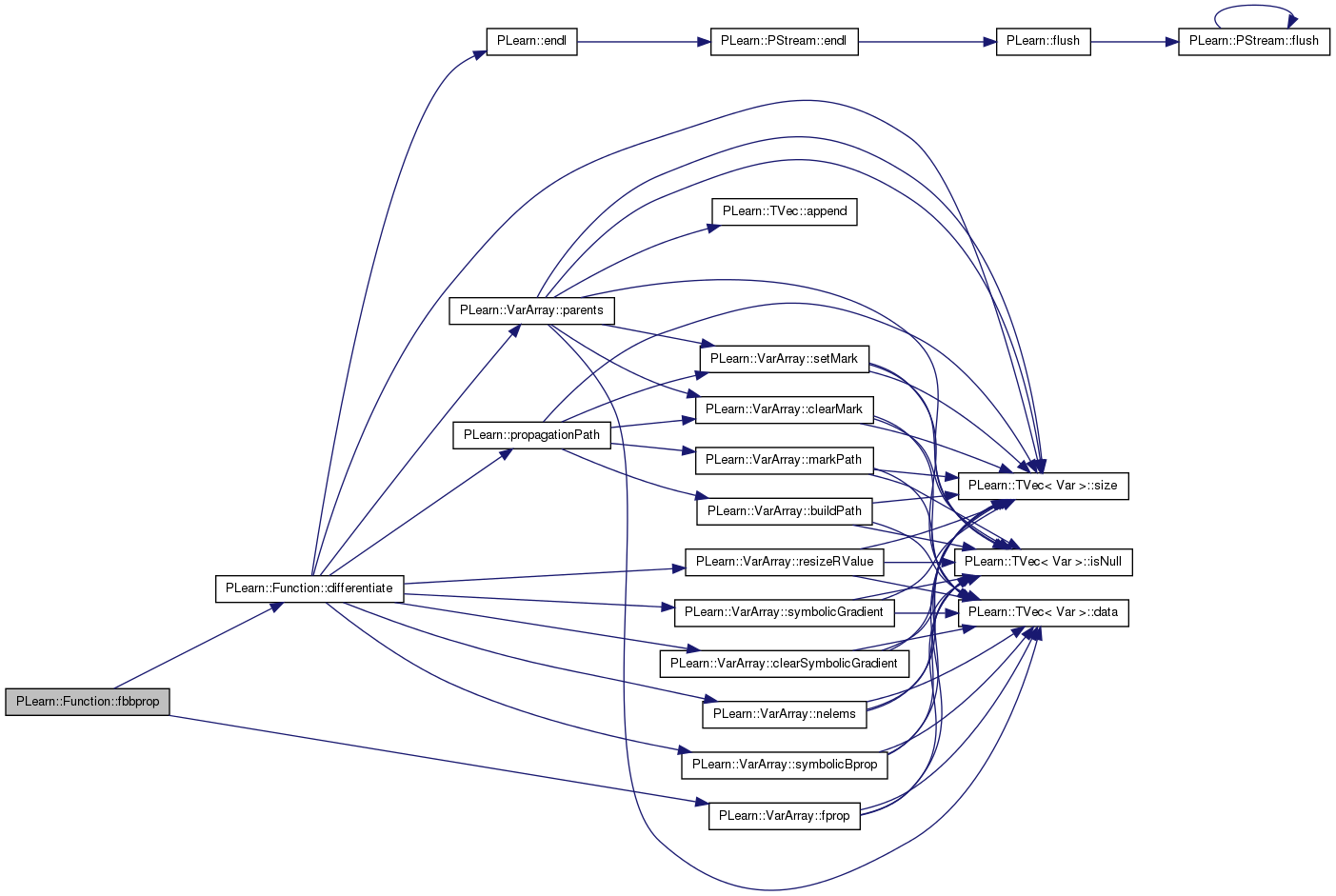
| void PLearn::Function::fbbprop | ( | const Vec & | in, |
| const Vec & | out, | ||
| const Vec & | gradient, | ||
| const Mat & | hessian | ||
| ) |
given input, compute output, gradient (=doutput/dinput) and hessian (=d^2output/dinput^2)
Definition at line 320 of file Func.cc.
References df, differentiate(), PLearn::VarArray::fprop(), fproppath, i, in, inputs, and outputs.
Referenced by verifyHessian(), and verifyrfprop().
{
if(df==0)
df = differentiate();
inputs << in; // inputs and df->inputs are supposed to be the same...
fproppath.fprop();
outputs >> output;
df->fproppath.fprop();
df->outputs >> gradient;
df->outputs.clearGradient();
int pos = 0;
for(int varnum=0; varnum<df->outputs.size(); varnum++)
{
Var& outputvar = df->outputs[varnum];
for(int i=0; i<outputvar->nelems(); i++)
{
df->inputs.clearGradient();
df->bproppath.clearGradient();
outputvar->gradient[i] = 1.0;
df->bproppath.bprop();
Vec hessian_row = hessian(pos++);
df->inputs.copyGradientTo(hessian_row);
outputvar->gradient[i] = 0.0;
}
}
}
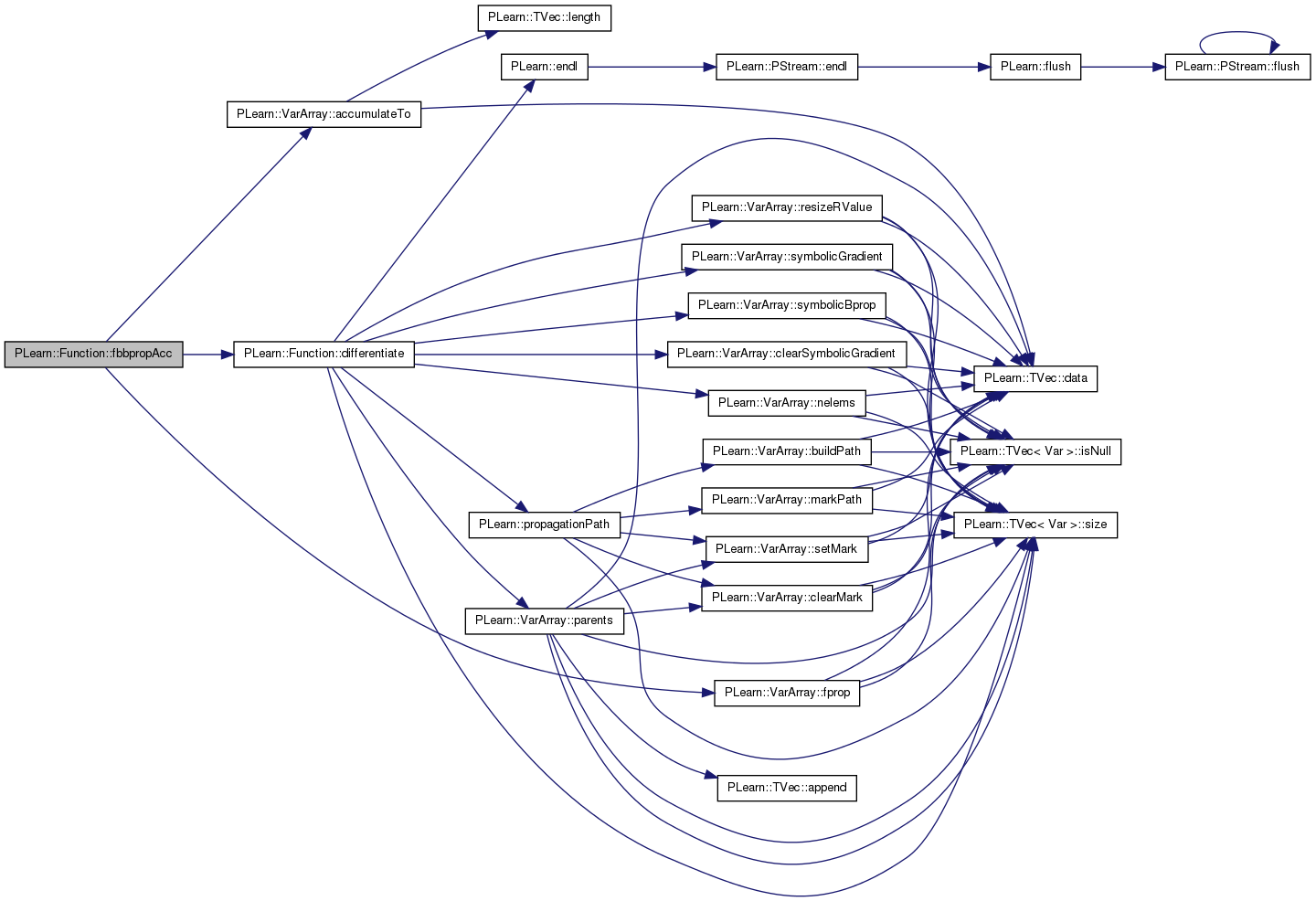
| void PLearn::Function::fbbpropAcc | ( | const Vec & | in, |
| const Vec & | out, | ||
| const Vec & | gradient, | ||
| const Mat & | hessian | ||
| ) |
same thing but accumulate output, gradient and hessian
Definition at line 349 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::VarArray::accumulateTo(), df, differentiate(), PLearn::VarArray::fprop(), fproppath, i, in, inputs, and outputs.
{
if(df==0)
df = differentiate();
inputs << in; // inputs and df->inputs are supposed to be the same...
fproppath.fprop();
outputs.accumulateTo(output);
df->fproppath.fprop();
df->outputs.accumulateTo(gradient);
df->outputs.clearGradient();
int pos = 0;
for(int varnum=0; varnum<df->outputs.size(); varnum++)
{
Var& outputvar = df->outputs[varnum];
for(int i=0; i<outputvar->nelems(); i++)
{
df->inputs.clearGradient();
df->bproppath.clearGradient();
outputvar->gradient[i] = 1.0;
df->bproppath.bprop();
Vec hessian_row = hessian(pos++);
df->inputs.accumulateGradientTo(hessian_row);
outputvar->gradient[i] = 0.0;
}
}
}
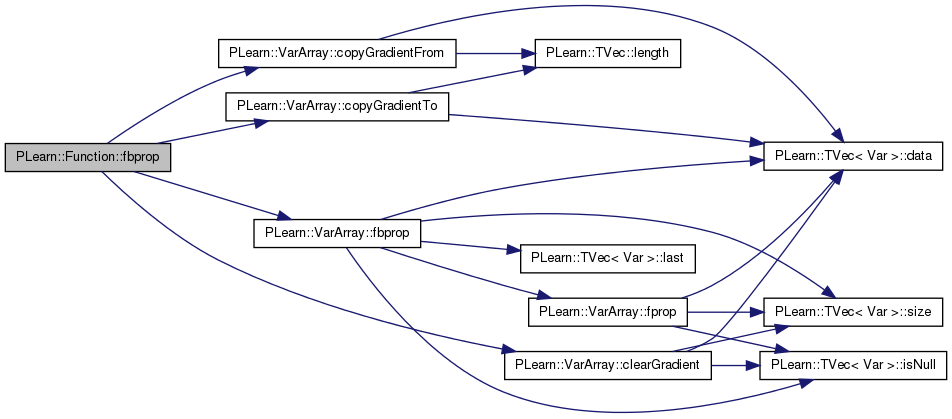
| void PLearn::Function::fbprop | ( | const Vec & | in, |
| const Vec & | out, | ||
| const Vec & | input_gradient, | ||
| const Vec & | output_gradient | ||
| ) |
when put_gradient_on_first_element_only, a gradient of 1 is put in only the first element of the output gradient this is a hack that is useful for having a SumOfVariable computing several costs in parallel, but backpropagating only through the first
Definition at line 248 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::VarArray::clearGradient(), PLearn::VarArray::copyGradientFrom(), PLearn::VarArray::copyGradientTo(), PLearn::VarArray::fbprop(), fproppath, in, inputs, outputs, and PLERROR.
Referenced by verifyGradient(), and verifySymbolicGradient().
{
inputs << in;
inputs.clearGradient();
fproppath.clearGradient();
outputs.copyGradientFrom(output_gradient);
fproppath.fbprop();
outputs >> out;
inputs.copyGradientTo(input_gradient);
#ifdef BOUNDCHECK
if (out.hasMissing())
PLERROR("Function::fbprop: detected MISSING_VALUE in function output!");
//static bool displayvargraph=false;
//if (displayvargraph)
// displayVarGraph(outputs,true);
#endif
}
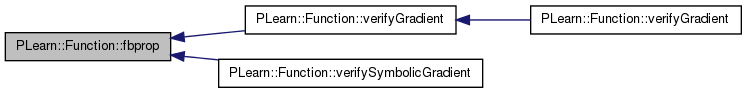
| void PLearn::Function::fbprop | ( | const Array< Vec > & | in, |
| const Array< Vec > & | out, | ||
| const Array< Vec > & | input_gradient, | ||
| const Array< Vec > & | output_gradient | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 268 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::VarArray::clearGradient(), PLearn::VarArray::copyGradientFrom(), PLearn::VarArray::copyGradientTo(), PLearn::VarArray::fbprop(), fproppath, in, inputs, outputs, and PLERROR.
{
inputs << in;
inputs.clearGradient();
fproppath.clearGradient();
outputs.copyGradientFrom(output_gradient);
fproppath.fbprop();
outputs >> out;
inputs.copyGradientTo(input_gradient);
#ifdef BOUNDCHECK
if (out.hasMissing())
PLERROR("Function::fbprop: detected MISSING_VALUE in function output!");
#endif
}
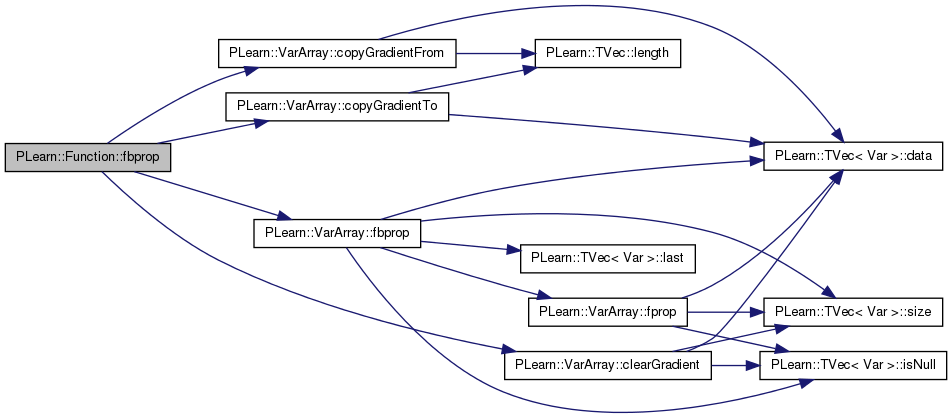
Definition at line 210 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::VarArray::fprop(), fproppath, in, inputs, and outputs.
Referenced by operator()(), rfprop(), verifyGradient(), and verifyHessian().
| OptionList & PLearn::Function::getOptionList | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
| OptionMap & PLearn::Function::getOptionMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::Function::getRemoteMethodMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
| void PLearn::Function::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy | ( | CopiesMap & | copies | ) | [virtual] |
Transforms a shallow copy into a deep copy.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 198 of file Func.cc.
References bproppath, PLearn::deepCopyField(), df, fproppath, inputs, PLearn::Object::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), outputs, parameters, and parentspath.
{
inherited::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(copies);
deepCopyField(inputs, copies);
deepCopyField(outputs, copies);
deepCopyField(fproppath, copies);
deepCopyField(bproppath, copies);
deepCopyField(parentspath, copies);
deepCopyField(df, copies);
deepCopyField(parameters, copies);
}

builds a whole new Var graph modeled after the current one but starting from new_inputs (instead of inputs) the resulting new_outputs var array is returned by the call All variables on the direct path from inputs to outputs are cloned but the parents of the cloned variables are the same as the originals (parents of the variables in the path are shared).
Definition at line 443 of file Func.cc.
References i, inputs, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::VarArray::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), PLearn::nonInputParentsOfPath(), outputs, PLERROR, and PLearn::TVec< T >::size().
{
CopiesMap copies;
// make sure the clones of the old inputs are the new inputs
for(int i=0; i<inputs.size(); i++)
{
if(new_inputs[i]->length()!=inputs[i]->length() || new_inputs[i]->width()!=inputs[i]->width())
PLERROR("In Function::operator()(const VarArray& new_inputs) dimensions of variables in new_inputs and inputs do not match");
copies[(Variable*)inputs[i]] = (Variable*)new_inputs[i];
if (!new_inputs[i]->nameIsSet() && inputs[i]->nameIsSet())
new_inputs[i]->setName(inputs[i]->getName());
}
// make sure that only the vars on the direct path from inputs to outputs
// get cloned but the clones should have the same parents as the
// originals so that gradients can be accumulated in these originals and
// then back propagated to shared sources.
VarArray parofpath = nonInputParentsOfPath(inputs, outputs);
for(int i=0; i<parofpath.size(); i++)
copies[(Variable*)parofpath[i]] = (Variable*)parofpath[i];
// do the deep copying
VarArray new_outputs = outputs;
new_outputs.makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(copies);
return new_outputs;
}
Definition at line 238 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::VarArray::copyFrom(), PLearn::VarArray::fprop(), fproppath, inputs, outputs, outputsize, PLERROR, and PLearn::TVec< T >::size().
{
if(inputs.size()!=2 || outputsize!=1)
PLERROR("You can only call real Function::operator()(const Vec& input1, const Vec& input2) for a function that has 2 input Vars and a single scalar output Var");
inputs[0]->copyFrom(input1);
inputs[1]->copyFrom(input2);
fproppath.fprop();
return outputs[0]->value[0];
}
Definition at line 434 of file Func.cc.
References fprop(), and outputsize.
{
Vec output(outputsize);
fprop(input,output);
return output;
}
| void PLearn::Function::recomputeParents | ( | ) |
recomputes the value of all the vars that influence the output but do not depend on the declared inputs (shared parameters for instance...)
Definition at line 387 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::VarArray::fprop(), and parentspath.
Referenced by build_().
{ parentspath.fprop(); }
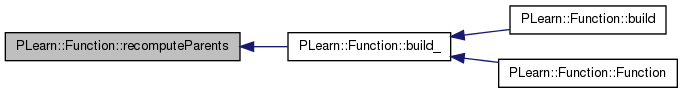
| void PLearn::Function::rfprop | ( | const Vec & | in, |
| const Vec & | out, | ||
| const Vec & | input_rvalue, | ||
| const Vec & | output_rvalue, | ||
| bool | do_fprop = true |
||
| ) |
Definition at line 378 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::VarArray::copyRValueFrom(), PLearn::VarArray::copyRValueTo(), fprop(), fproppath, inputs, outputs, and PLearn::VarArray::rfprop().
{
if (do_fprop) fprop(in,out);
inputs.copyRValueFrom(input_rvalue);
fproppath.rfprop();
outputs.copyRValueTo(output_rvalue);
}
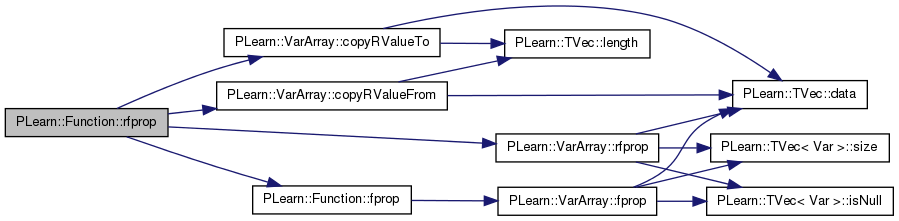
| void PLearn::Function::sizefbprop | ( | const Vec & | in, |
| const Vec & | out, | ||
| const Vec & | input_gradient, | ||
| const Vec & | output_gradient | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 284 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::VarArray::clearGradient(), PLearn::VarArray::copyGradientFrom(), PLearn::VarArray::copyGradientTo(), fproppath, in, inputs, outputs, PLERROR, and PLearn::VarArray::sizefbprop().
{
inputs << in;
inputs.clearGradient();
fproppath.clearGradient();
outputs.copyGradientFrom(output_gradient);
fproppath.sizefbprop();
outputs >> out;
inputs.copyGradientTo(input_gradient);
#ifdef BOUNDCHECK
if (out.hasMissing())
PLERROR("Function::fbprop: detected MISSING_VALUE in function output!");
//static bool displayvargraph=false;
//if (displayvargraph)
// displayVarGraph(outputs,true);
#endif
}
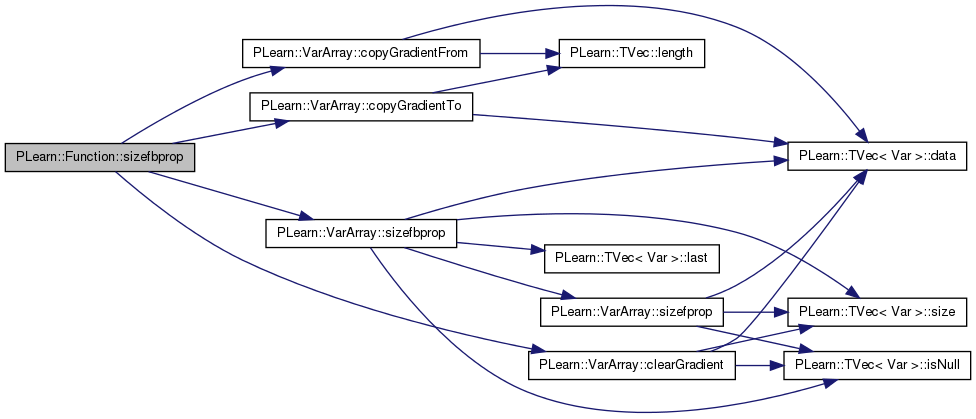
| void PLearn::Function::sizefbprop | ( | const Array< Vec > & | in, |
| const Array< Vec > & | out, | ||
| const Array< Vec > & | input_gradient, | ||
| const Array< Vec > & | output_gradient | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 304 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::VarArray::clearGradient(), PLearn::VarArray::copyGradientFrom(), PLearn::VarArray::copyGradientTo(), fproppath, in, inputs, outputs, PLERROR, and PLearn::VarArray::sizefbprop().
{
inputs << in;
inputs.clearGradient();
fproppath.clearGradient();
outputs.copyGradientFrom(output_gradient);
fproppath.sizefbprop();
outputs >> out;
inputs.copyGradientTo(input_gradient);
#ifdef BOUNDCHECK
if (out.hasMissing())
PLERROR("Function::fbprop: detected MISSING_VALUE in function output!");
#endif
}
take the values given in the in Vec
Definition at line 586 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::apply(), PLearn::argmax(), PLearn::TVec< T >::copy(), PLearn::dot(), PLearn::endl(), PLearn::FABS(), PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), fbprop(), fprop(), i, in, inputsize, PLearn::is_missing(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::max(), MISSING_VALUE, PLearn::norm(), outputsize, PLearn::perr, and PLWARNING.
Referenced by verifyGradient().
{
if(outputsize!=1)
PLWARNING("In Function::verifyGradient(...) Will verify gradient only for the first output");
Vec output(outputsize);
Vec output_gradient(outputsize);
output_gradient[which_component]=1.0;
Vec gradient(inputsize);
fbprop(input, output, gradient,output_gradient);
perr << "** Verifying gradient computation **" << endl;
perr << "Input: " << input << endl;
perr << "Output["<<which_component<<"]: " << output[which_component] << endl;
perr << "Computed gradient: " << gradient << endl;
//displayFunction(this,true);
// Now computing the gradient by finite difference
Vec newinput = input.copy();
Vec finitediffgradient(inputsize);
double doublestep = step+step;
for(int i=0; i<inputsize; i++)
{
real in = input[i];
newinput[i] = in+step;
fprop(newinput,output);
real out1 = output[which_component];
newinput[i] = in-step;
fprop(newinput,output);
real out2 = output[which_component];
finitediffgradient[i] = (out1-out2)/doublestep;
newinput[i] = input[i] = in;
}
// copy the original input into the VarArray
fprop(newinput,output);
perr << "Estimated gradient: " << finitediffgradient << endl;
perr << "-------------------" << endl;
perr << "relative difference: ";
// 'Safe' relative difference, that does not display a 'nan' when both
// computed and estimated gradients are zero.
Vec num = apply(gradient - finitediffgradient,FABS);
Vec denom = real(0.5)*apply(gradient + finitediffgradient,FABS);
for (int i = 0; i < num.length(); i++)
if (!fast_exact_is_equal(num[i], 0))
num[i] /= denom[i];
perr << num << endl;
// apply(gradient - finitediffgradient,(tRealFunc)fabs)/(0.5*apply(gradient + finitediffgradient,(tRealFunc)fabs));
perr << "-------------------" << endl;
perr << "max relative difference: ";
// As above, this is a 'safe' relative difference.
// TODO Question: are we re-doing the same computations as above?
num = apply(gradient - finitediffgradient,(tRealFunc)FABS);
denom = real(0.5)*apply(gradient + finitediffgradient,(tRealFunc)FABS);
for (int i = 0; i < num.length(); i++)
if (!fast_exact_is_equal(num[i], 0))
num[i] /= denom[i];
int pos = argmax(num);
perr << max(num) << " (at position " << pos << "/" << num.length()
<< ", computed = " << gradient[pos] << " and estimated = "
<< finitediffgradient[pos] << ")" << endl;
real norm_gradient = norm(gradient);
real norm_finitediffgradient = norm(finitediffgradient);
real cos_angle = fast_exact_is_equal(norm_gradient*norm_finitediffgradient,
0)
? MISSING_VALUE
: dot(gradient,finitediffgradient) /
(norm_gradient*norm_finitediffgradient);
if (cos_angle > 1)
cos_angle = 1; // Numerical imprecisions can lead to such situation.
perr << "cos(angle) : " << cos_angle << endl;
perr << "angle : " << ( is_missing(cos_angle) ? MISSING_VALUE
: acos(cos_angle) ) << endl;
}
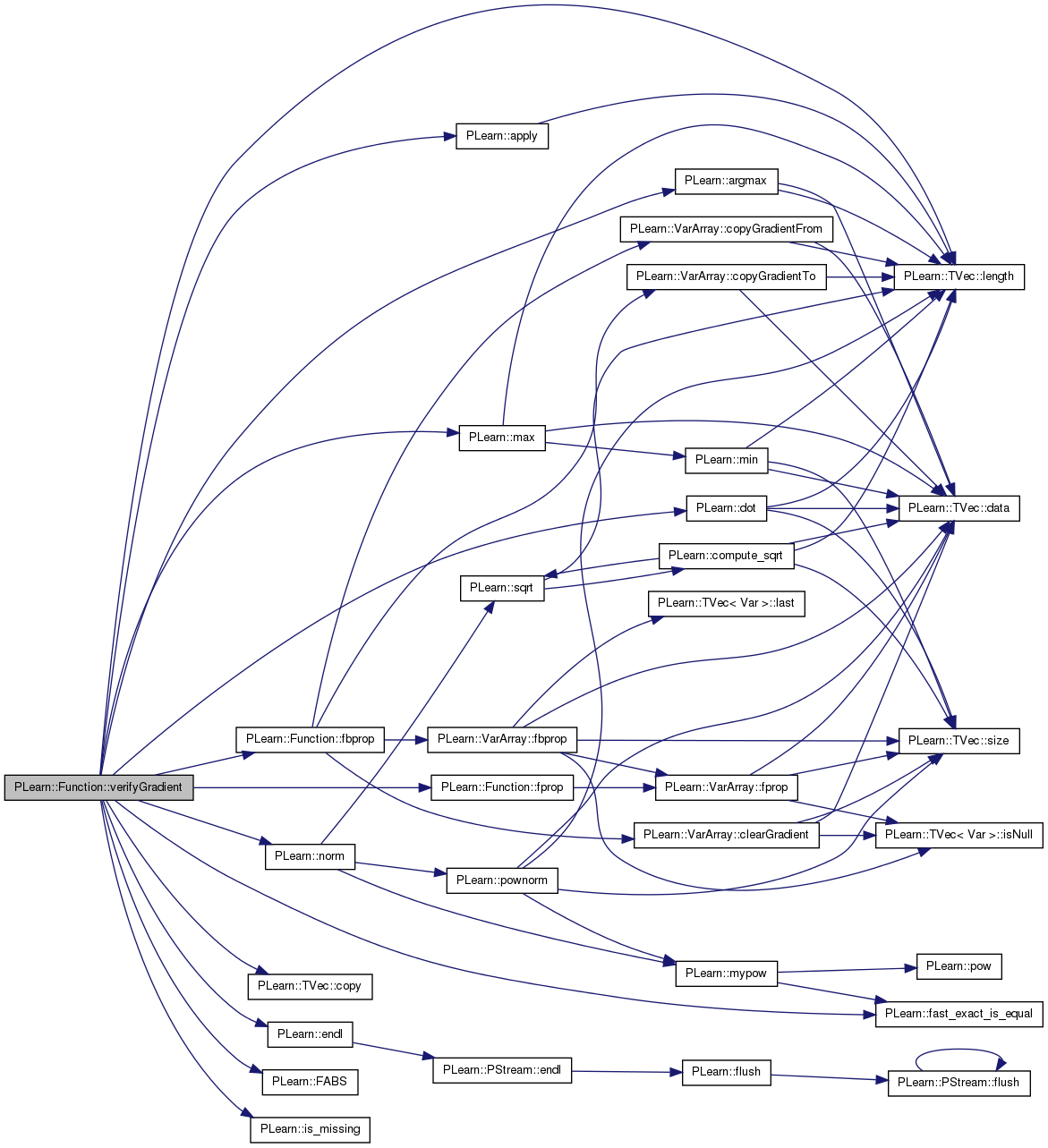

take the current values of the inputs variables
Definition at line 665 of file Func.cc.
References inputs, inputsize, and verifyGradient().
{
Vec input(inputsize);
inputs >> input;
verifyGradient(input, step, which_component);
}
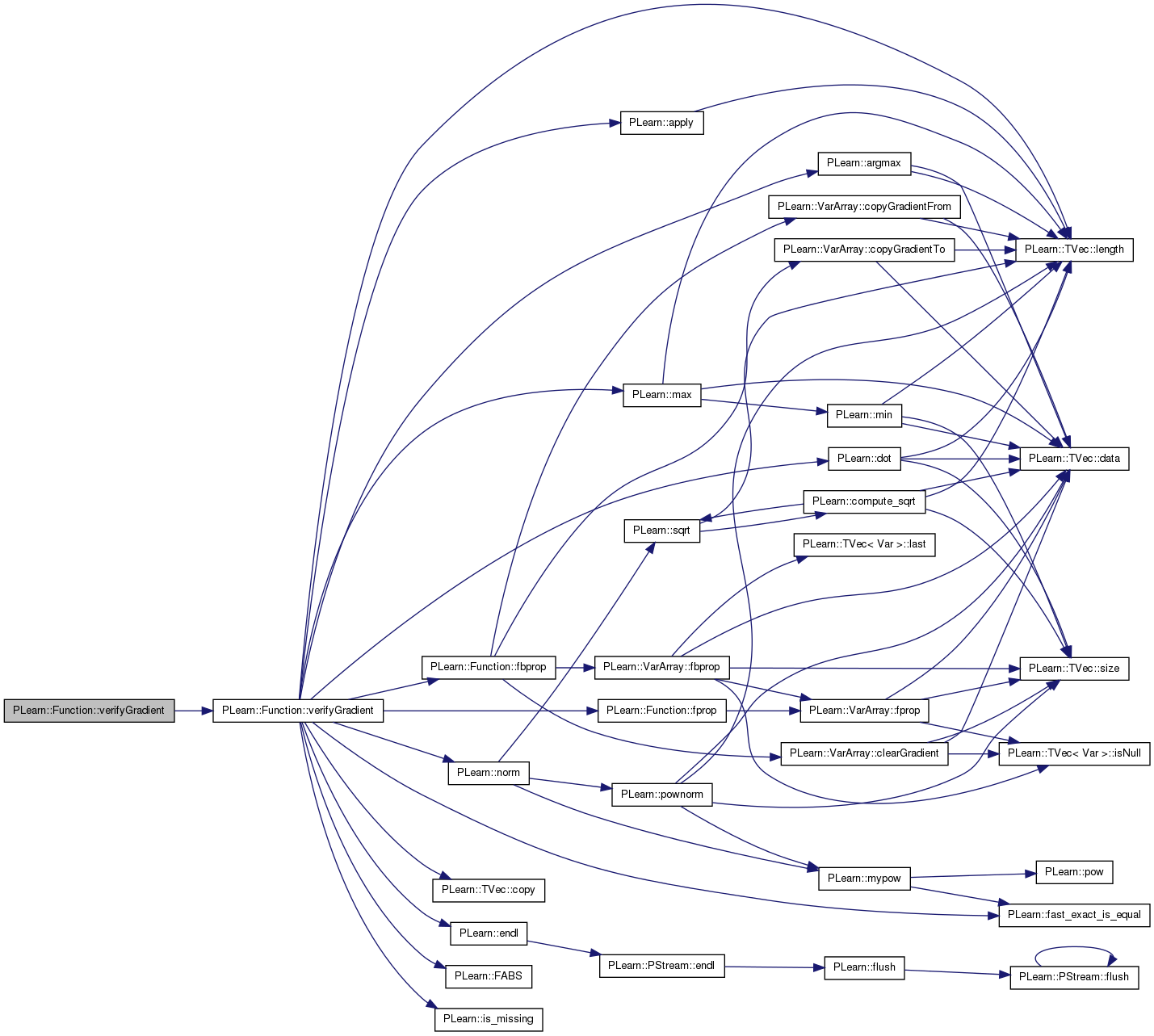
| void PLearn::Function::verifyGradient | ( | real | minval, |
| real | maxval, | ||
| real | step = 0.01, |
||
| int | which_component = 0 |
||
| ) |
take the values randomly between minval and maxval
Definition at line 658 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::fill_random_uniform(), inputsize, and verifyGradient().
{
Vec input(inputsize);
fill_random_uniform(input,minval, maxval);
verifyGradient(input, step, which_component);
}
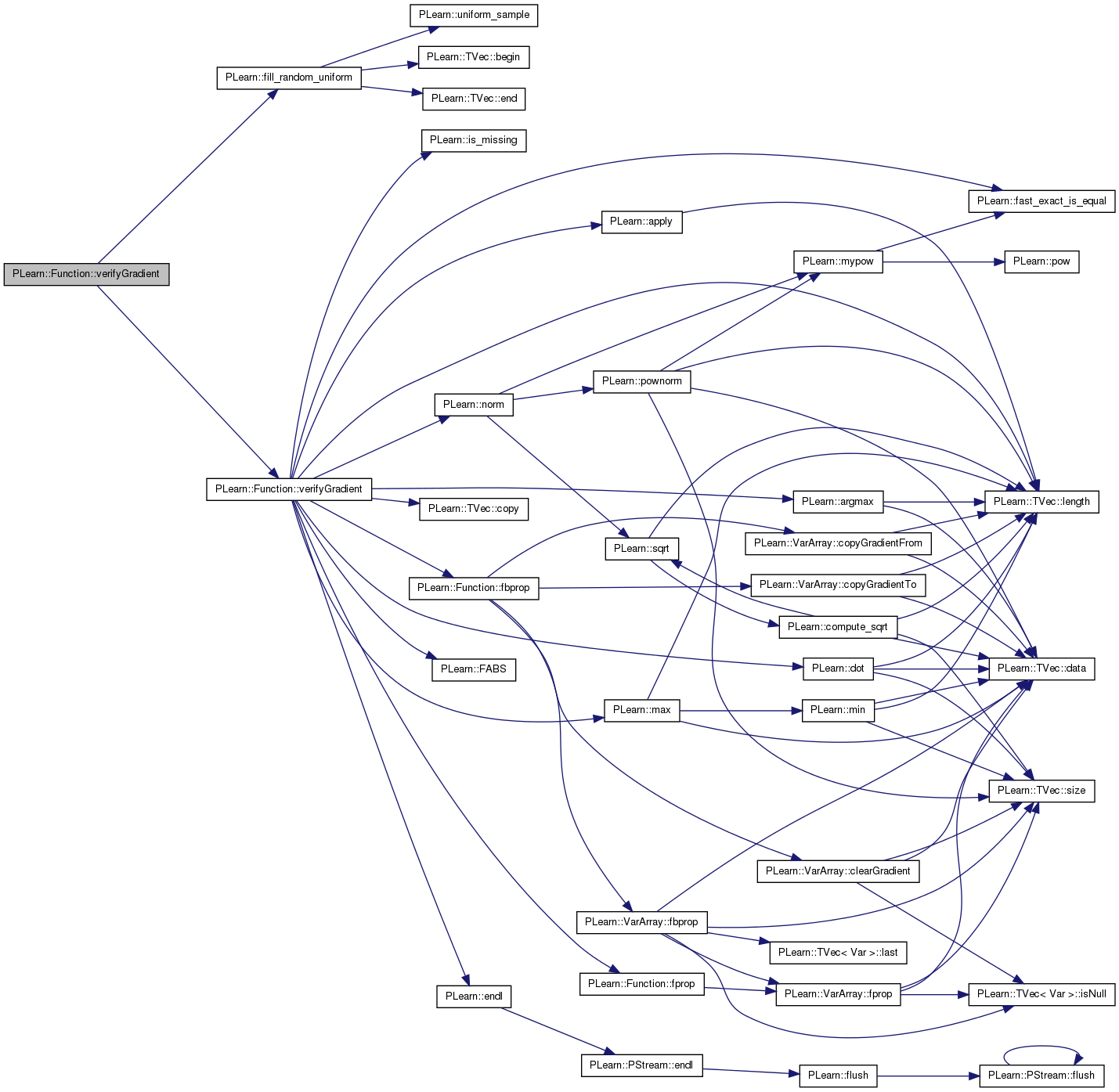
Definition at line 503 of file Func.cc.
References PLearn::TVec< T >::copy(), PLearn::endl(), fbbprop(), fprop(), i, inputsize, j, PLearn::max(), outputsize, and PLERROR.
{
// Job a Charles...
// Note: L'utilisation de l'option -DUSEDOUBLE dans le Makefile_option
// permet d'eviter certains problemes numeriques d'approximation
// et donc d'utiliser des valeurs de step plus petites
if(outputsize!=1)
PLERROR("In Function::verifyHessian(...) Can verify hessian only for output of size 1");
real out1,out2,out3,out4;
real doublestep = 2*step;
Vec output(1);
Vec gradient(inputsize);
Mat hessian(inputsize,inputsize);
fbbprop(input, output, gradient, hessian);
cerr << "** Verifying hessian computation **" << endl;
cerr << "Input: " << input;
cerr << "Output: " << output;
cerr << "Computed hessian: " << hessian;
// Now computing the gradient by finite difference
//
// f(x1+dx1,x2+dx2)-f(x1-dx1,x2+dx2)-f(x1+dx1,x2-dx2)+f(x1-dx1,x2-dx2)
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// 2 * dx1 * 2 * dx2
//
Vec newinput1 = input.copy();
Vec newinput2 = input.copy();
Vec newinput3 = input.copy();
Vec newinput4 = input.copy();
Mat finitediffhessian(inputsize,inputsize);
Mat rel(inputsize,inputsize);
double h,f;
for(int i=0; i<inputsize; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<inputsize; j++)
{
newinput1[i] = newinput1[i]-step;
newinput1[j] = newinput1[j]-step;
newinput2[i] = newinput2[i]+step;
newinput2[j] = newinput2[j]-step;
newinput3[i] = newinput3[i]-step;
newinput3[j] = newinput3[j]+step;
newinput4[i] = newinput4[i]+step;
newinput4[j] = newinput4[j]+step;
fprop(newinput1,output);
out1 = output[0];
fprop(newinput2,output);
out2 = output[0];
fprop(newinput3,output);
out3 = output[0];
fprop(newinput4,output);
out4 = output[0];
finitediffhessian(i,j) = ((out4-out3)/doublestep-(out2-out1)/doublestep)/doublestep;
newinput1[i] = input[i];
newinput1[j] = input[j];
newinput2[i] = input[i];
newinput2[j] = input[j];
newinput3[i] = input[i];
newinput3[j] = input[j];
newinput4[i] = input[i];
newinput4[j] = input[j];
}
}
cerr << "Estimated hessian: " << finitediffhessian;
cerr << "-------------------" << endl;
for (int i=0; i<inputsize; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<inputsize; j++)
{
h = hessian(i,j);
f = finitediffhessian(i,j);
rel(i,j) = 2*fabs(h-f)/(fabs(h)+fabs(f));
}
}
cerr << "relative difference: " << rel << endl;
cerr << "-------------------" << endl;
cerr << "max relative difference: " << max(rel) << endl;
}
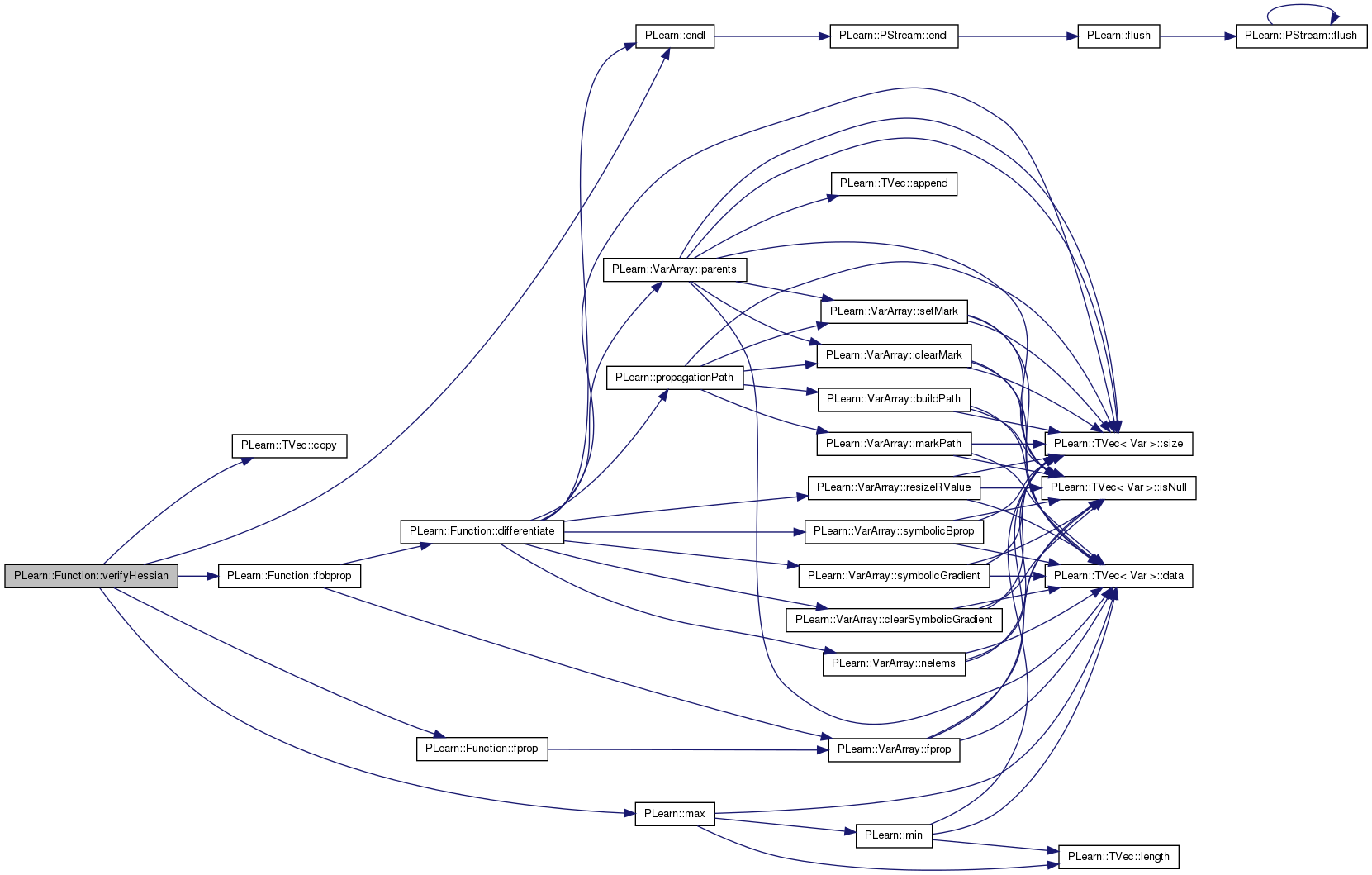
Definition at line 694 of file Func.cc.
References b, df, differentiate(), PLearn::endl(), PLearn::fast_exact_is_equal(), fbbprop(), i, inputsize, PLearn::max(), outputsize, and PLearn::transposeProduct().
{
//This is developed to make sure that the code of rfprop is correct.
Vec gradient(inputsize);
Vec rfpropRgradient(inputsize);
Vec fbbRgradient(inputsize);
Mat hessian(inputsize,inputsize);
Vec rel(inputsize);
Vec out(outputsize);
real b,r;
if(df==0)
df = differentiate();
fbbprop(in, out, gradient, hessian);
fbbRgradient = transposeProduct(hessian, gradient);
df->inputs.copyRValueFrom(gradient);
df->fproppath.rfprop();
df->outputs.copyRValueTo(rfpropRgradient);
for (int i=0; i<inputsize; i++)
{
b = fbbRgradient[i];
r = rfpropRgradient[i];
if (fast_exact_is_equal(b, 0) && fast_exact_is_equal(r, 0))
rel[i] = 0.0;
else rel[i] = fabs(b-r)/(fabs(b)+fabs(r));
}
cerr << "max relative difference of H*g between rfprop and fbbprop: " << max(rel) << endl;
//cerr << "max & min of rfprop rgradient: " << max(rfpropRgradient) << " " << min(rfpropRgradient) << endl;
//cerr << "max & min of fbb rgradient: " << max(fbbRgradient) << " " << min(fbbRgradient) << endl;
}
| void PLearn::Function::verifySymbolicGradient | ( | const Vec & | in | ) |
Checks that the gradient computed by a bprop on the function and the gradient computed by a fprop on the symbolic derivative of the function give the same results
Definition at line 675 of file Func.cc.
References df, differentiate(), PLearn::endl(), fbprop(), inputsize, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), outputsize, and PLERROR.
{
if(in.length()!=inputsize)
PLERROR("In Function::verifySymbolicGradient(const Vec& in) in does not have the size that this function expects");
Vec out(outputsize);
Vec output_gradient(outputsize,1.0);
Vec gradient1(inputsize);
fbprop(in,out,gradient1,output_gradient);
cout << "Bprop computed gradient: " << gradient1 << endl;
//cout << "Display f proppath" << endl;
//displayFunction(this, true, false);
Func df = differentiate();
//cout << "Display df proppath" << endl;
Vec gradient2 = df(in);
//displayFunction(df, true, false);
cout << "Symbolically computed gradient: " << gradient2 << endl;
}
Reimplemented from PLearn::Object.
Definition at line 93 of file Func.h.
Referenced by build_(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
remembers the symbolic derivative
Definition at line 96 of file Func.h.
Referenced by differentiate(), fbbprop(), fbbpropAcc(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), verifyrfprop(), and verifySymbolicGradient().
VarArray PLearn::Function::fproppath [mutable] |
Definition at line 92 of file Func.h.
Referenced by build_(), differentiate(), fbbprop(), fbbpropAcc(), fbprop(), fprop(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), operator()(), rfprop(), sizefbprop(), and sizefprop().
VarArray PLearn::Function::inputs [mutable] |
Definition at line 85 of file Func.h.
Referenced by build_(), declareOptions(), differentiate(), fbbprop(), fbbpropAcc(), fbprop(), fprop(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), operator()(), rfprop(), sizefbprop(), sizefprop(), and verifyGradient().
Definition at line 90 of file Func.h.
Referenced by build_(), verifyGradient(), verifyHessian(), verifyrfprop(), and verifySymbolicGradient().
VarArray PLearn::Function::outputs [mutable] |
Definition at line 87 of file Func.h.
Referenced by build_(), declareOptions(), differentiate(), fbbprop(), fbbpropAcc(), fbprop(), fprop(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), operator()(), rfprop(), sizefbprop(), and sizefprop().
Definition at line 91 of file Func.h.
Referenced by build_(), operator()(), verifyGradient(), verifyHessian(), verifyrfprop(), and verifySymbolicGradient().
VarArray PLearn::Function::parameters [mutable] |
nonInputSources
Definition at line 86 of file Func.h.
Referenced by build_(), declareOptions(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
path on which to do a fprop to update the values of all the non-input direct parents on the fproppath (this will be called by method recomputeParents() )
Definition at line 94 of file Func.h.
Referenced by build_(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), and recomputeParents().
 1.7.4
1.7.4