|
PLearn 0.1
|
|
PLearn 0.1
|
Rational-Quadratic kernel that can be used for Automatic Relevance Determination. More...
#include <RationalQuadraticARDKernel.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| RationalQuadraticARDKernel () | |
| Default constructor. | |
| virtual real | evaluate (const Vec &x1, const Vec &x2) const |
| Compute K(x1,x2). | |
| virtual void | evaluate_all_i_x (const Vec &x, const Vec &k_xi_x, real squared_norm_of_x=-1, int istart=0) const |
| Fill k_xi_x with K(x_i, x), for all i from istart to istart + k_xi_x.length() - 1. | |
| virtual void | computeGramMatrix (Mat K) const |
| Compute entire Gram matrix. | |
| virtual void | computeGramMatrixDerivative (Mat &KD, const string &kernel_param, real epsilon=1e-6) const |
| Compute the derivative of the Gram matrix with respect to one of the kernel's parameters. | |
| virtual string | classname () const |
| virtual OptionList & | getOptionList () const |
| virtual OptionMap & | getOptionMap () const |
| virtual RemoteMethodMap & | getRemoteMethodMap () const |
| virtual RationalQuadraticARDKernel * | deepCopy (CopiesMap &copies) const |
| virtual void | build () |
| Post-constructor. | |
| virtual void | makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy (CopiesMap &copies) |
| Transforms a shallow copy into a deep copy. | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static string | _classname_ () |
| static OptionList & | _getOptionList_ () |
| static RemoteMethodMap & | _getRemoteMethodMap_ () |
| static Object * | _new_instance_for_typemap_ () |
| static bool | _isa_ (const Object *o) |
| static void | _static_initialize_ () |
| static const PPath & | declaringFile () |
Public Attributes | |
| real | m_isp_alpha |
| Inverse softplus of the alpha parameter in the rational-quadratic kernel. | |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static StaticInitializer | _static_initializer_ |
Protected Member Functions | |
| real | derivIspSignalSigma (int i, int j, int arg, real K) const |
| Derivative function with respect to isp_signal_sigma. | |
| real | derivIspGlobalSigma (int i, int j, int arg, real K) const |
| Derivative function with respect to isp_global_sigma. | |
| real | derivIspInputSigma (int i, int j, int arg, real K) const |
| Derivative function with respect to isp_input_sigma[arg]. | |
| real | derivIspAlpha (int i, int j, int arg, real K) const |
| Derivative function with respect to isp_alpha. | |
| void | computeGramMatrixDerivIspSignalSigma (Mat &KD) const |
| void | computeGramMatrixDerivIspInputSigma (Mat &KD, int arg) const |
| void | computeGramMatrixDerivIspAlpha (Mat &KD) const |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static void | declareOptions (OptionList &ol) |
| Declares the class options. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| Mat | m_pow_minus_alpha_minus_1 |
| Cached version of the K / k terms, namely: | |
Private Types | |
| typedef ARDBaseKernel | inherited |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | build_ () |
| This does the actual building. | |
Rational-Quadratic kernel that can be used for Automatic Relevance Determination.
This kernel can be interpreted as an infinite mixture of SquaredExponentialARDKernel (with different characteristic length-scales), allowing a greater variety of "interesting" functions to be generated. Similar to C.E. Rasmussen's GPML code (see http://www.gaussianprocess.org), this kernel is specified as:
k(x,y) = sf * [1 + (sum_i (x_i - y_i)^2 / w_i)/(2*alpha)]^(-alpha) * k_kron(x,y)
where sf is softplus(isp_signal_sigma), w_i is softplus(isp_global_sigma + isp_input_sigma[i]), and k_kron(x,y) is the result of the KroneckerBaseKernel evaluation, or 1.0 if there are no Kronecker terms. Note that since the Kronecker terms are incorporated multiplicatively, the very presence of the term associated to this kernel can be gated by the value of some input variable(s) (that are incorporated within one or more Kronecker terms).
Note that contrarily to previous versions that incorporated IID noise and Kronecker terms ADDITIVELY, this version does not add any noise at all (and as explained above incorporates the Kronecker terms multiplicatively). For best results, especially with moderately noisy data, IT IS IMPERATIVE to use whis kernel within a SummationKernel in conjunction with an IIDNoiseKernel, as follows (e.g. within a GaussianProcessRegressor):
kernel = SummationKernel(terms = [ RationalQuadraticARDKernel(), IIDNoiseKernel() ] )
In order to make its operations more robust when used with unconstrained optimization of hyperparameters, all hyperparameters of this kernel are specified in the inverse softplus domain. See IIDNoiseKernel for more explanations.
Definition at line 82 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.h.
typedef ARDBaseKernel PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::inherited [private] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 84 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.h.
| PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::RationalQuadraticARDKernel | ( | ) |
Default constructor.
Definition at line 81 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
Referenced by computeGramMatrixDerivative().
: m_isp_alpha(0.0) { }

| string PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::_classname_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 78 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
| OptionList & PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::_getOptionList_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 78 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::_getRemoteMethodMap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 78 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 78 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
| Object * PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::_new_instance_for_typemap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 78 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
| StaticInitializer RationalQuadraticARDKernel::_static_initializer_ & PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::_static_initialize_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 78 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
| void PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::build | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Post-constructor.
The normal implementation should call simply inherited::build(), then this class's build_(). This method should be callable again at later times, after modifying some option fields to change the "architecture" of the object.
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 104 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::build(), and build_().
{
// ### Nothing to add here, simply calls build_
inherited::build();
build_();
}

| void PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::build_ | ( | ) | [private] |
This does the actual building.
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 114 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::KroneckerBaseKernel::m_default_value.
Referenced by build().
{
// Ensure that we multiply in Kronecker terms
inherited::m_default_value = 1.0;
}

| string PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::classname | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 78 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
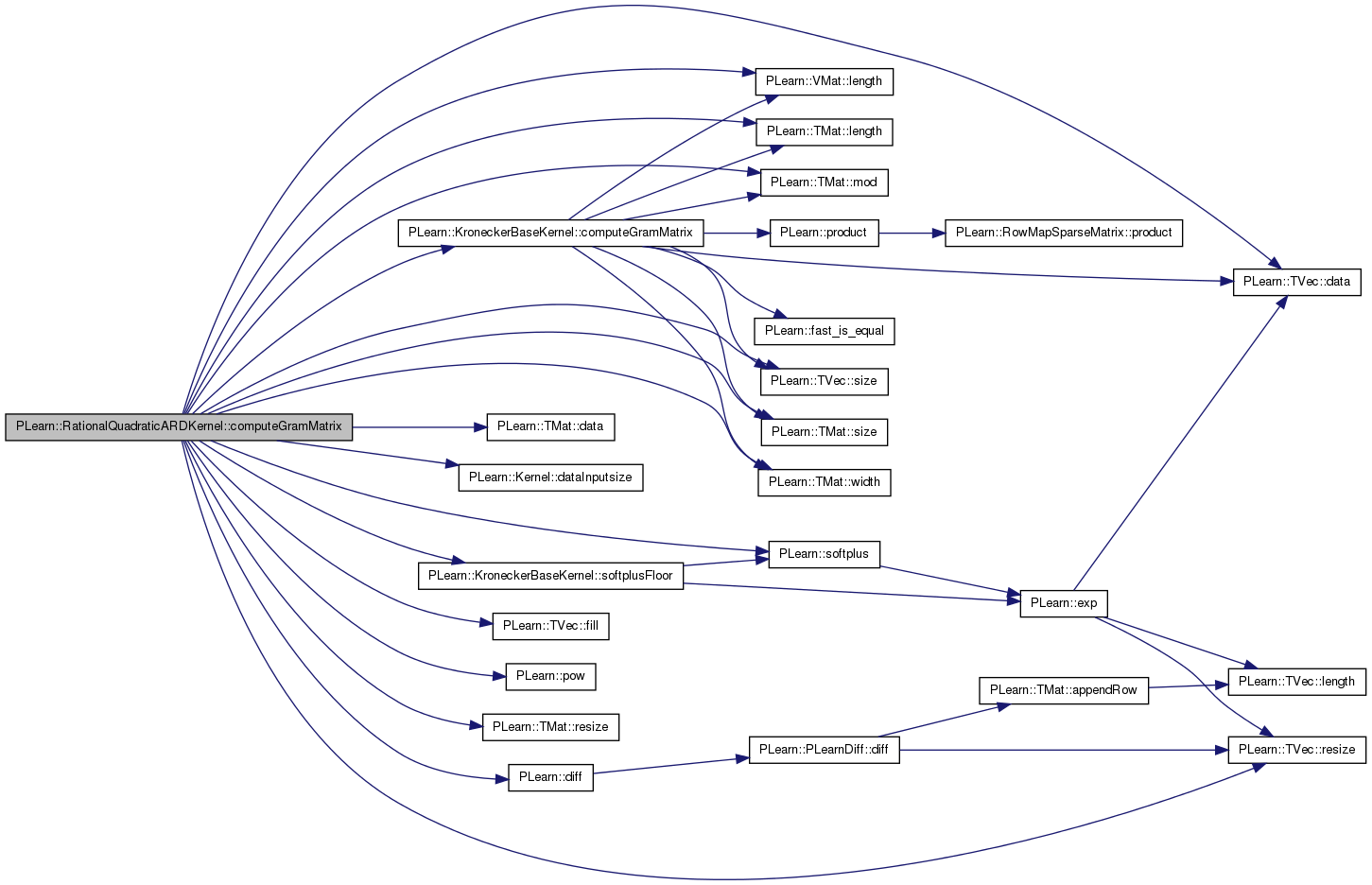
| void PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::computeGramMatrix | ( | Mat | K | ) | const [virtual] |
Compute entire Gram matrix.
Reimplemented from PLearn::KroneckerBaseKernel.
Definition at line 220 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::Kernel::cache_gram_matrix, PLearn::KroneckerBaseKernel::computeGramMatrix(), PLearn::TVec< T >::data(), PLearn::Kernel::data, PLearn::TMat< T >::data(), PLearn::Kernel::dataInputsize(), PLearn::diff(), PLearn::TVec< T >::fill(), PLearn::Kernel::gram_matrix, PLearn::Kernel::gram_matrix_is_cached, i, j, PLearn::VMat::length(), PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), m, PLearn::MemoryCachedKernel::m_data_cache, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_input_sigma, m_isp_alpha, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_global_sigma, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_input_sigma, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_signal_sigma, m_pow_minus_alpha_minus_1, PLearn::TMat< T >::mod(), n, PLASSERT, PLearn::pow(), PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::TMat< T >::size(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::softplus(), PLearn::KroneckerBaseKernel::softplusFloor(), and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
{
PLASSERT( !m_isp_input_sigma.size() || dataInputsize() == m_isp_input_sigma.size() );
PLASSERT( K.size() == 0 || m_data_cache.size() > 0 ); // Ensure data cached OK
// Compute Kronecker gram matrix. No need to cache it.
inherited::computeGramMatrix(K);
// Precompute some terms. Make sure that the alpha and input sigmas don't
// get too small
real sf = softplus(m_isp_signal_sigma);
real alpha = softplusFloor(m_isp_alpha, 1e-6);
m_input_sigma.resize(dataInputsize());
softplusFloor(m_isp_global_sigma, 1e-6);
m_input_sigma.fill(m_isp_global_sigma); // Still in ISP domain
for (int i=0, n=m_input_sigma.size() ; i<n ; ++i) {
if (m_isp_input_sigma.size() > 0) {
softplusFloor(m_isp_input_sigma[i], 1e-6);
m_input_sigma[i] += m_isp_input_sigma[i];
}
m_input_sigma[i] = softplus(m_input_sigma[i]);
}
// Prepare the cache for the pow terms
m_pow_minus_alpha_minus_1.resize(K.length(), K.width());
int pow_cache_mod = m_pow_minus_alpha_minus_1.mod();
real* pow_cache_row = m_pow_minus_alpha_minus_1.data();
// Compute Gram Matrix
int l = data->length();
int m = K.mod();
int n = dataInputsize();
int cache_mod = m_data_cache.mod();
real *data_start = &m_data_cache(0,0);
real *Ki = K[0]; // Start of current row
real *Kij; // Current element along row
real *input_sigma_data = m_input_sigma.data();
real *xi = data_start;
for (int i=0 ; i<l
; ++i, xi += cache_mod, pow_cache_row+=pow_cache_mod, Ki+=m)
{
Kij = Ki;
real *xj = data_start;
real *pow_cache_cur = pow_cache_row;
// This whole loop can be optimized further when a Kronecker term is 0
for (int j=0; j<=i; ++j, xj += cache_mod) {
// Kernel evaluation per se
real *x1 = xi;
real *x2 = xj;
real *p_inpsigma = input_sigma_data;
real sum_wt = 0.0;
int k = n;
// Use Duff's device to unroll the following loop:
// while (k--) {
// real diff = *x1++ - *x2++;
// sum_wt += (diff * diff) / *p_inpsigma++;
// }
real diff;
switch (k % 8) {
case 0: do { diff = *x1++ - *x2++; sum_wt += (diff*diff) / *p_inpsigma++;
case 7: diff = *x1++ - *x2++; sum_wt += (diff*diff) / *p_inpsigma++;
case 6: diff = *x1++ - *x2++; sum_wt += (diff*diff) / *p_inpsigma++;
case 5: diff = *x1++ - *x2++; sum_wt += (diff*diff) / *p_inpsigma++;
case 4: diff = *x1++ - *x2++; sum_wt += (diff*diff) / *p_inpsigma++;
case 3: diff = *x1++ - *x2++; sum_wt += (diff*diff) / *p_inpsigma++;
case 2: diff = *x1++ - *x2++; sum_wt += (diff*diff) / *p_inpsigma++;
case 1: diff = *x1++ - *x2++; sum_wt += (diff*diff) / *p_inpsigma++;
} while((k -= 8) > 0);
}
// Multiplicatively update kernel matrix (already pre-filled with
// Kronecker terms, or 1.0 if no Kronecker terms, as per build_).
real inner_pow = 1 + sum_wt / (2.*alpha);
real pow_alpha = pow(inner_pow, -alpha);
real Kij_cur = *Kij * sf * pow_alpha; // Mind *Kij here
*pow_cache_cur++ = Kij_cur / inner_pow;
*Kij++ = Kij_cur;
}
}
if (cache_gram_matrix) {
gram_matrix.resize(l,l);
gram_matrix << K;
gram_matrix_is_cached = true;
}
}
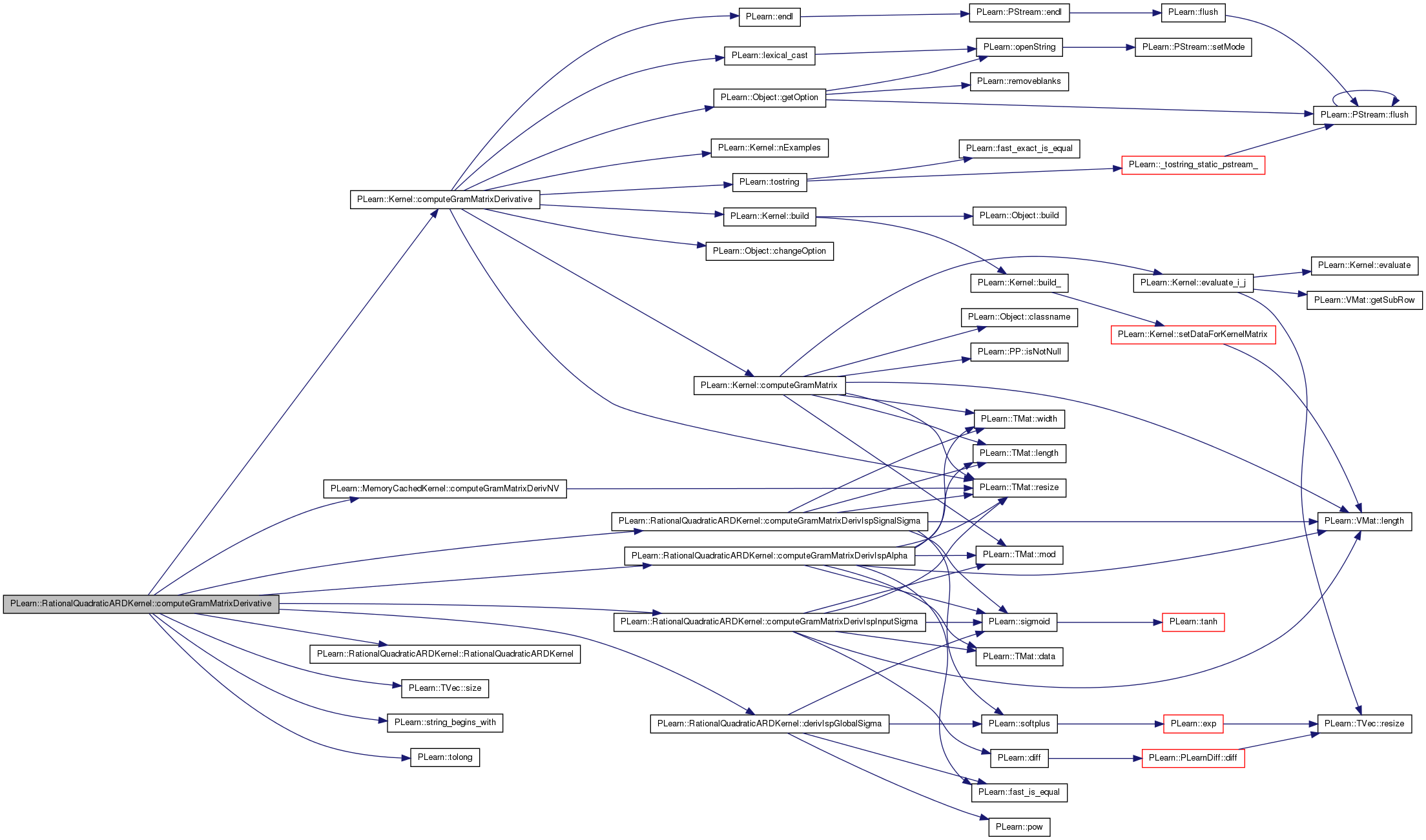
| void PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::computeGramMatrixDerivative | ( | Mat & | KD, |
| const string & | kernel_param, | ||
| real | epsilon = 1e-6 |
||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Compute the derivative of the Gram matrix with respect to one of the kernel's parameters.
Analytic derivatives are implemented for this kernel.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Kernel.
Definition at line 313 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::Kernel::computeGramMatrixDerivative(), computeGramMatrixDerivIspAlpha(), computeGramMatrixDerivIspInputSigma(), computeGramMatrixDerivIspSignalSigma(), PLearn::MemoryCachedKernel::computeGramMatrixDerivNV(), derivIspGlobalSigma(), PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_input_sigma, PLASSERT, RationalQuadraticARDKernel(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::string_begins_with(), and PLearn::tolong().
{
static const string ISS("isp_signal_sigma");
static const string IGS("isp_global_sigma");
static const string IIS("isp_input_sigma[");
static const string IAL("isp_alpha");
if (kernel_param == ISS) {
computeGramMatrixDerivIspSignalSigma(KD);
// computeGramMatrixDerivNV<
// RationalQuadraticARDKernel,
// &RationalQuadraticARDKernel::derivIspSignalSigma>(KD, this, -1);
}
else if (kernel_param == IGS) {
computeGramMatrixDerivNV<
RationalQuadraticARDKernel,
&RationalQuadraticARDKernel::derivIspGlobalSigma>(KD, this, -1);
}
else if (string_begins_with(kernel_param, IIS) &&
kernel_param[kernel_param.size()-1] == ']')
{
int arg = tolong(kernel_param.substr(
IIS.size(), kernel_param.size() - IIS.size() - 1));
PLASSERT( arg < m_isp_input_sigma.size() );
computeGramMatrixDerivIspInputSigma(KD, arg);
// computeGramMatrixDerivNV<
// RationalQuadraticARDKernel,
// &RationalQuadraticARDKernel::derivIspInputSigma>(KD, this, arg);
}
else if (kernel_param == IAL) {
computeGramMatrixDerivIspAlpha(KD);
// computeGramMatrixDerivNV<
// RationalQuadraticARDKernel,
// &RationalQuadraticARDKernel::derivIspAlpha>(KD, this, -1);
}
else
inherited::computeGramMatrixDerivative(KD, kernel_param, epsilon);
// Compare against finite differences
// Mat KD1;
// Kernel::computeGramMatrixDerivative(KD1, kernel_param, epsilon);
// cerr << "Kernel hyperparameter: " << kernel_param << endl;
// cerr << "Analytic derivative (200th row):" << endl
// << KD(200) << endl
// << "Finite differences:" << endl
// << KD1(200) << endl;
}
| void PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::computeGramMatrixDerivIspAlpha | ( | Mat & | KD | ) | const [protected] |
Definition at line 506 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::data(), PLearn::Kernel::data, PLearn::fast_is_equal(), PLearn::Kernel::gram_matrix, i, j, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::VMat::length(), m_isp_alpha, m_pow_minus_alpha_minus_1, PLearn::TMat< T >::mod(), pl_log, PLASSERT_MSG, PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), PLearn::sigmoid(), and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
Referenced by computeGramMatrixDerivative().
{
// Precompute some terms
real alpha_sigmoid = sigmoid(m_isp_alpha);
// Compute Gram Matrix derivative w.r.t. isp_alpha
int l = data->length();
PLASSERT_MSG(
gram_matrix.width() == l && gram_matrix.length() == l,
"To compute the derivative with respect to 'isp_alpha', the\n"
"Gram matrix must be precomputed and cached in RationalQuadraticARDKernel.");
// Variables that walk over the pre-computed kernel matrix (K)
int k_mod = gram_matrix.mod();
real *Ki = &gram_matrix(0,0); // Current row of kernel matrix
real *Kij; // Current element of kernel matrix
// Variables that walk over the pow cache
int pow_cache_mod = m_pow_minus_alpha_minus_1.mod();
real *pow_cache_row = m_pow_minus_alpha_minus_1.data();
real *pow_cache_cur;
// Variables that walk over the kernel derivative matrix (KD)
KD.resize(l,l);
real* KDi = KD.data(); // Start of row i
real* KDij; // Current element on row i
int KD_mod = KD.mod();
// Iterate on rows of derivative matrix
for (int i=0 ; i<l ; ++i, Ki += k_mod,
KDi += KD_mod, pow_cache_row += pow_cache_mod)
{
Kij = Ki;
KDij = KDi;
pow_cache_cur = pow_cache_row;
// Iterate on columns of derivative matrix
for (int j=0 ; j <= i ; ++j, ++Kij, ++pow_cache_cur)
{
real pow_cur = *pow_cache_cur;
if (fast_is_equal(pow_cur, 0))
*KDij++ = 0.;
else {
real K = *Kij;
real k = K / pow_cur;
real KD_cur = alpha_sigmoid * K * (1 - pl_log(k) - 1/k);
// Set into derivative matrix
*KDij++ = KD_cur;
}
}
}
}

| void PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::computeGramMatrixDerivIspInputSigma | ( | Mat & | KD, |
| int | arg | ||
| ) | const [protected] |
Definition at line 453 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::data(), PLearn::Kernel::data, PLearn::diff(), i, j, PLearn::VMat::length(), PLearn::MemoryCachedKernel::m_data_cache, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_input_sigma, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_global_sigma, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_input_sigma, m_pow_minus_alpha_minus_1, PLearn::TMat< T >::mod(), PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), and PLearn::sigmoid().
Referenced by computeGramMatrixDerivative().
{
// Precompute some terms
real input_sigma_arg = m_input_sigma[arg];
real input_sigma_sq = input_sigma_arg * input_sigma_arg;
real input_sigmoid = sigmoid(m_isp_global_sigma + m_isp_input_sigma[arg]);
// Compute Gram Matrix derivative w.r.t. isp_input_sigma[arg]
int l = data->length();
// Variables that walk over the data matrix
int cache_mod = m_data_cache.mod();
real *data_start = &m_data_cache(0,0);
real *xi = data_start+arg; // Iterator on data rows
// Variables that walk over the pow cache
int pow_cache_mod = m_pow_minus_alpha_minus_1.mod();
real *pow_cache_row = m_pow_minus_alpha_minus_1.data();
real *pow_cache_cur;
// Variables that walk over the kernel derivative matrix (KD)
KD.resize(l,l);
real* KDi = KD.data(); // Start of row i
real* KDij; // Current element on row i
int KD_mod = KD.mod();
// Iterate on rows of derivative matrix
for (int i=0 ; i<l ; ++i, xi += cache_mod, KDi += KD_mod,
pow_cache_row += pow_cache_mod)
{
KDij = KDi;
real *xj = data_start+arg; // Inner iterator on data rows
pow_cache_cur = pow_cache_row;
// Iterate on columns of derivative matrix
for (int j=0 ; j <= i
; ++j, xj += cache_mod, ++pow_cache_cur)
{
real diff = *xi - *xj;
real sq_diff = diff * diff;
real KD_cur = 0.5 * *pow_cache_cur *
input_sigmoid * sq_diff / input_sigma_sq;
// Set into derivative matrix
*KDij++ = KD_cur;
}
}
}

| void PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::computeGramMatrixDerivIspSignalSigma | ( | Mat & | KD | ) | const [protected] |
Definition at line 437 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::Kernel::data, PLearn::Kernel::gram_matrix, PLearn::TMat< T >::length(), PLearn::VMat::length(), PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_signal_sigma, PLASSERT_MSG, PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), PLearn::sigmoid(), PLearn::softplus(), and PLearn::TMat< T >::width().
Referenced by computeGramMatrixDerivative().
{
int l = data->length();
KD.resize(l,l);
PLASSERT_MSG(
gram_matrix.width() == l && gram_matrix.length() == l,
"To compute the derivative with respect to 'isp_signal_sigma', the\n"
"Gram matrix must be precomputed and cached in SquaredExponentialARDKernel.");
KD << gram_matrix;
KD *= sigmoid(m_isp_signal_sigma)/softplus(m_isp_signal_sigma);
}

| void PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::declareOptions | ( | OptionList & | ol | ) | [static, protected] |
Declares the class options.
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 88 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::OptionBase::buildoption, PLearn::declareOption(), PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::declareOptions(), and m_isp_alpha.
{
declareOption(
ol, "isp_alpha",
&RationalQuadraticARDKernel::m_isp_alpha,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Inverse softplus of the alpha parameter in the rational-quadratic kernel.\n"
"Default value=0.0");
// Now call the parent class' declareOptions
inherited::declareOptions(ol);
}
| static const PPath& PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::declaringFile | ( | ) | [inline, static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 123 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.h.
:
| RationalQuadraticARDKernel * PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::deepCopy | ( | CopiesMap & | copies | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 78 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
| real PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::derivIspAlpha | ( | int | i, |
| int | j, | ||
| int | arg, | ||
| real | K | ||
| ) | const [protected] |
Derivative function with respect to isp_alpha.
Definition at line 422 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::fast_is_equal(), m_isp_alpha, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_signal_sigma, pl_log, PLearn::pow(), PLearn::sigmoid(), and PLearn::softplus().
{
// The rational quadratic gives us:
// K = s * k^(-alpha) * kron
// where kron is 0 or 1. Rederive the value of k == (K/s)^(-1/alpha)
if (fast_is_equal(K, 0.))
return 0.;
real alpha = softplus(m_isp_alpha);
real k = pow(K / softplus(m_isp_signal_sigma), real(-1.) / alpha);
return sigmoid(m_isp_alpha) * K * (1 - pl_log(k) - 1 / k);
}
| real PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::derivIspGlobalSigma | ( | int | i, |
| int | j, | ||
| int | arg, | ||
| real | K | ||
| ) | const [protected] |
Derivative function with respect to isp_global_sigma.
Definition at line 377 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::fast_is_equal(), m_isp_alpha, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_global_sigma, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_signal_sigma, PLearn::pow(), PLearn::sigmoid(), and PLearn::softplus().
Referenced by computeGramMatrixDerivative().
{
// The rational quadratic gives us:
// K = s * k^(-alpha) * kron
// where kron is 0 or 1. Rederive the value of k == (K/s)^(-1/alpha)
if (fast_is_equal(K, 0.))
return 0.;
real alpha = softplus(m_isp_alpha);
real k = pow(K / softplus(m_isp_signal_sigma), real(-1.) / alpha);
real inner = (k - 1) * alpha * sigmoid(m_isp_global_sigma) / softplus(m_isp_global_sigma);
return (K / k) * inner;
// Note: in the above expression for 'inner' there is the implicit
// assumption that the input_sigma[i] are zero, which allows the
// sigmoid/softplus term to be factored out of the norm summation.
}

| real PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::derivIspInputSigma | ( | int | i, |
| int | j, | ||
| int | arg, | ||
| real | K | ||
| ) | const [protected] |
Derivative function with respect to isp_input_sigma[arg].
Definition at line 400 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::MemoryCachedKernel::dataRow(), PLearn::diff(), PLearn::fast_is_equal(), m_isp_alpha, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_global_sigma, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_input_sigma, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_signal_sigma, PLearn::pow(), PLearn::sigmoid(), and PLearn::softplus().
{
// The rational quadratic gives us:
// K = s * k^(-alpha) * kron
// where kron is 0 or 1. Rederive the value of k == (K/s)^(-1/alpha)
if (fast_is_equal(K, 0.))
return 0.;
real alpha = softplus(m_isp_alpha);
Vec& row_i = *dataRow(i);
Vec& row_j = *dataRow(j);
real k = pow(K / softplus(m_isp_signal_sigma), real(-1.) / alpha);
real diff = row_i[arg] - row_j[arg];
real sq_diff = diff * diff;
real inner = m_isp_global_sigma + m_isp_input_sigma[arg];
real sig_inn = sigmoid(inner);
real spl_inn = softplus(inner);
return 0.5 * (K / k) * sig_inn * sq_diff / (spl_inn * spl_inn);
}
| real PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::derivIspSignalSigma | ( | int | i, |
| int | j, | ||
| int | arg, | ||
| real | K | ||
| ) | const [protected] |
Derivative function with respect to isp_signal_sigma.
Definition at line 369 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_signal_sigma, PLearn::sigmoid(), and PLearn::softplus().
{
return K*sigmoid(m_isp_signal_sigma)/softplus(m_isp_signal_sigma);
}
| real PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::evaluate | ( | const Vec & | x1, |
| const Vec & | x2 | ||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Compute K(x1,x2).
Reimplemented from PLearn::KroneckerBaseKernel.
Definition at line 132 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::TVec< T >::data(), PLearn::diff(), PLearn::KroneckerBaseKernel::evaluate(), PLearn::fast_is_equal(), i, m_isp_alpha, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_global_sigma, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_input_sigma, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_signal_sigma, n, PLASSERT, PLearn::pow(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), and PLearn::softplus().
{
PLASSERT( x1.size() == x2.size() );
PLASSERT( !m_isp_input_sigma.size() || x1.size() == m_isp_input_sigma.size() );
real gating_term = inherited::evaluate(x1,x2);
if (fast_is_equal(gating_term, 0.0))
return 0.0;
if (x1.size() == 0)
return softplus(m_isp_signal_sigma) * gating_term;
const real* px1 = x1.data();
const real* px2 = x2.data();
real sf = softplus(m_isp_signal_sigma);
real alpha = softplus(m_isp_alpha);
real sum_wt = 0.0;
if (m_isp_input_sigma.size() > 0) {
const real* pinpsig = m_isp_input_sigma.data();
for (int i=0, n=x1.size() ; i<n ; ++i) {
real diff = *px1++ - *px2++;
real sqdiff = diff * diff;
sum_wt += sqdiff / softplus(m_isp_global_sigma + *pinpsig++);
}
}
else {
real global_sigma = softplus(m_isp_global_sigma);
for (int i=0, n=x1.size() ; i<n ; ++i) {
real diff = *px1++ - *px2++;
real sqdiff = diff * diff;
sum_wt += sqdiff / global_sigma;
}
}
// Gate by Kronecker term
return sf * pow(1 + sum_wt / (real(2.)*alpha), -alpha) * gating_term;
}
| void PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::evaluate_all_i_x | ( | const Vec & | x, |
| const Vec & | k_xi_x, | ||
| real | squared_norm_of_x = -1, |
||
| int | istart = 0 |
||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Fill k_xi_x with K(x_i, x), for all i from istart to istart + k_xi_x.length() - 1.
Reimplemented from PLearn::Kernel.
Definition at line 174 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::Kernel::data, PLearn::TVec< T >::data(), PLearn::Kernel::dataInputsize(), PLearn::MemoryCachedKernel::dataRow(), PLearn::diff(), PLearn::KroneckerBaseKernel::evaluate(), PLearn::fast_is_equal(), PLearn::TVec< T >::fill(), i, j, PLearn::VMat::length(), PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_input_sigma, m_isp_alpha, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_global_sigma, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_input_sigma, PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::m_isp_signal_sigma, PLearn::min(), n, PLearn::pow(), PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), and PLearn::softplus().
{
if (x1.size() == 0) {
k_xi_x.fill(0.0);
return;
}
// Precompute some terms
real sf = softplus(m_isp_signal_sigma);
real alpha = softplus(m_isp_alpha);
m_input_sigma.resize(dataInputsize());
for (int i=0, n=m_input_sigma.size() ; i<n ; ++i)
m_input_sigma[i] = softplus(m_isp_global_sigma + m_isp_input_sigma[i]);
const real* px1_start = x1.data();
const real* pinpsig_start = m_input_sigma.data();
int i_max = min(istart + k_xi_x.size(), data->length());
int j = 0;
for (int i=istart ; i<i_max ; ++i, ++j) {
Vec* train_row = dataRow(i);
const real* px2 = train_row->data();
const real* px1 = px1_start;
real gating_term = inherited::evaluate(x1,*train_row);
if (fast_is_equal(gating_term, 0.0)) {
k_xi_x[j] = 0.0;
continue;
}
real sum_wt = 0.0;
const real* pinpsig = pinpsig_start;
for (int i=0, n=x1.size() ; i<n ; ++i) {
real diff = *px1++ - *px2++;
real sqdiff = diff * diff;
sum_wt += sqdiff / *pinpsig++;
}
// Gate by Kronecker term
k_xi_x[j] = sf * pow(1 + sum_wt / (real(2.)*alpha), -alpha) * gating_term;
}
}
| OptionList & PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::getOptionList | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 78 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
| OptionMap & PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::getOptionMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 78 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::getRemoteMethodMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 78 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
| void PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy | ( | CopiesMap & | copies | ) | [virtual] |
Transforms a shallow copy into a deep copy.
Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 123 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.cc.
References PLearn::deepCopyField(), m_pow_minus_alpha_minus_1, and PLearn::ARDBaseKernel::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
{
inherited::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(copies);
deepCopyField(m_pow_minus_alpha_minus_1, copies);
}

Reimplemented from PLearn::ARDBaseKernel.
Definition at line 123 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.h.
Inverse softplus of the alpha parameter in the rational-quadratic kernel.
Default value=0.0
Definition at line 91 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.h.
Referenced by computeGramMatrix(), computeGramMatrixDerivIspAlpha(), declareOptions(), derivIspAlpha(), derivIspGlobalSigma(), derivIspInputSigma(), evaluate(), and evaluate_all_i_x().
Mat PLearn::RationalQuadraticARDKernel::m_pow_minus_alpha_minus_1 [mutable, protected] |
Cached version of the K / k terms, namely:
pow(1 + sum_wt / (2*alpha), -alpha-1) * sf * kron
This is useful for computing derivatives,
Definition at line 164 of file RationalQuadraticARDKernel.h.
Referenced by computeGramMatrix(), computeGramMatrixDerivIspAlpha(), computeGramMatrixDerivIspInputSigma(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
 1.7.4
1.7.4