|
PLearn 0.1
|
|
PLearn 0.1
|
#include <RandomVar.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| ProductRandomVariable (MatRandomVar input1, MatRandomVar input2) | |
| RandomVariable Product. | |
| virtual char * | classname () |
| void | setValueFromParentsValue () |
| set the field value from the values of the parents | |
| bool | invertible (const Var &obs, RVInstanceArray &unobserved_parents, Var **JacobianCorrection) |
| functions specific to FunctionalRandomVariable's | |
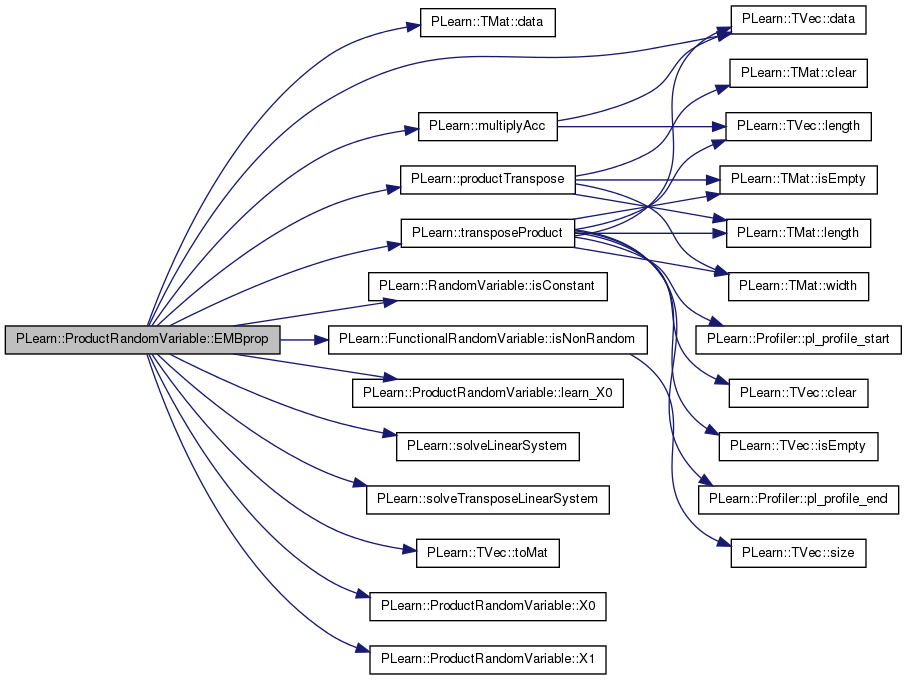
| void | EMBprop (const Vec obs, real post) |
| void | EMTrainingInitialize (const RVArray ¶meters_to_learn) |
| Initialization of EM training (before all the iterations start). | |
| void | EMEpochInitialize () |
| Initialization of an individual EMEpoch. | |
| void | EMUpdate () |
| const RandomVar & | X0 () |
| convenience inline's | |
| const RandomVar & | X1 () |
| viewed as nx1 vector | |
| bool | learn_X0 () |
| stuff for EM | |
| bool | learn_X1 () |
Public Attributes | |
| int | m |
| int | n |
| int | l |
| dimensions of the matrices Y(mxl) = X0(mxn) * X1(nxl) | |
| bool | scalars |
| = (m==1 && n==1 && l==1); | |
| bool | learn_something |
| Mat | X0numerator |
| mxn matrix, used in the case X0 is learned | |
| Mat | X1numerator |
| nxl vector, used in the case X1 is learned | |
| Mat | denom |
| nxn matrix denominator | |
| Mat | tmp1 |
| temporary matrices to avoid allocating in loops | |
| Mat | tmp2 |
| Mat | tmp3 |
| Vec | vtmp3 |
| Vec version of tmp3. | |
| Vec | tmp4 |
* X0 and X1 are Vec and product is element by element
Y = X0 * X1
where Y is an mxl matrix (or a vector viewed as mx1 or 1xl), X0 is an mxn matrix, or a vector which must be 1xn or mx1, X1 is an nxl matrix, or a vector which must be nx1 or 1xl; this includes the special cases where one or the other is scalar (n=1 or l=1), or both are scalar (m=n=l=1).
if both X0 and X1 are observed, and one of them is learnable, then it can be learned by EM (p_t denotes posterior for example t, and y_t the output observation for example t):
Note that sometimes the nxn matrix to invert is a 1x1 scalar.
Definition at line 1417 of file RandomVar.h.
| PLearn::ProductRandomVariable::ProductRandomVariable | ( | MatRandomVar | input1, |
| MatRandomVar | input2 | ||
| ) |
RandomVariable Product.
Definition at line 1587 of file RandomVar.cc.
References l, m, n, PLERROR, and scalars.
: FunctionalRandomVariable(input1 & input2, input1->value->matValue.length(), input2->value->matValue.width()), m(input1->value->matValue.length()), n(input1->value->matValue.width()), l(input2->value->matValue.width()), learn_something(false) { if (n != input2->value->matValue.length()) PLERROR("ProductRandomVariable(X0,X1): X0(%d,%d)'s width (%d) must match" "X1(%d,%d)'s length (%d)", input1->value->matValue.length(), input1->value->matValue.width(), input1->value->matValue.width(), input2->value->matValue.length(), input2->value->matValue.width(), input2->value->matValue.length()); scalars = (m==1 && n==1 && l==1); }
| virtual char* PLearn::ProductRandomVariable::classname | ( | ) | [inline, virtual] |
Implements PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 1424 of file RandomVar.h.
{ return "ProductRandomVariable"; }
************ EM STUFF ********** propagate posterior information to parents in order to perform an EMupdate at the end of an EMEpoch. In the case of mixture-like RVs and their components, the posterior is the probability of the component "this" given the observation "obs".
Implements PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 1683 of file RandomVar.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::data(), PLearn::TVec< T >::data(), denom, PLearn::RandomVariable::isConstant(), PLearn::FunctionalRandomVariable::isNonRandom(), l, learn_something, learn_X0(), m, PLearn::multiplyAcc(), PLERROR, PLearn::productTranspose(), scalars, PLearn::solveLinearSystem(), PLearn::solveTransposeLinearSystem(), tmp1, tmp2, tmp3, PLearn::TVec< T >::toMat(), PLearn::transposeProduct(), vtmp3, X0(), X0numerator, X1(), and X1numerator.
{
if (learn_something)
{
if (learn_X0())
{
if (scalars)
{
// do the special scalar case separately for efficiency
real x1 = *(X1()->value->value.data());
real y = *obs.data();
*X0numerator.data() += posterior * y * x1;
*denom.data() += posterior * x1 * x1;
// propagate EMBprop to X1
if (!X1()->isNonRandom())
{
real x0 = *(X0()->value->value.data());
if (x0==0.0)
PLERROR("ProductRandomVariable: can't divide by X0==0");
*tmp3.data() = y / x0;
X1()->EMBprop(vtmp3,posterior);
}
}
else
{
Mat matObs = obs.toMat(m,l);
Mat& x1 = X1()->value->matValue;
// numerator += posterior * obs * x1'
productTranspose(tmp1, matObs,x1);
multiplyAcc(X0numerator, tmp1,posterior);
// denominator += posterior * x1 * x1'
productTranspose(tmp2, x1,x1);
multiplyAcc(denom, tmp2,posterior);
// propagate EMBprop to X1
if (!X1()->isNonRandom())
{
Mat& x0 = X0()->value->matValue;
// solve x0 * tmp3 = matObs
solveLinearSystem(x0,matObs,tmp3);
X1()->EMBprop(vtmp3,posterior);
}
}
}
else // learn_X1()
{
if (scalars)
{
// do the special scalar case separately for efficiency
real x0 = *(X0()->value->value.data());
*X1numerator.data() += posterior * *obs.data() * x0;
*denom.data() += posterior * x0 * x0;
// propagate EMBprop to X0
if (!X0()->isNonRandom())
{
real x1 = *(X1()->value->value.data());
if (x1==0.0)
PLERROR("ProductRandomVariable: can't divide by X1==0");
*tmp3.data() = obs[0] / x1;
X0()->EMBprop(vtmp3,posterior);
}
}
else
{
Mat matObs = obs.toMat(m,l);
Mat& x0 = X0()->value->matValue;
// numerator += posterior * x0' * obs
transposeProduct(tmp1, x0,matObs);
multiplyAcc(X1numerator, tmp1,posterior);
// denominator += posterior * x0' * x0
transposeProduct(tmp2, x0,x0);
multiplyAcc(denom, tmp2,posterior);
// propagate EMBprop to X0
if (!X0()->isNonRandom())
{
Mat& x1 = X1()->value->matValue;
// solve tmp3 * x1 = matObs
solveTransposeLinearSystem(x1,matObs,tmp3);
X1()->EMBprop(vtmp3,posterior);
}
}
}
}
else
{
if (scalars)
{
if (!X1()->isNonRandom())
{
real x0 = *(X0()->value->value.data());
if (x0==0.0)
PLERROR("ProductRandomVariable: can't divide by X0==0");
*tmp3.data() = obs[0] / x0;
X1()->EMBprop(vtmp3,posterior);
}
if (!X0()->isNonRandom())
{
real x1 = *(X1()->value->value.data());
if (x1==0.0)
PLERROR("ProductRandomVariable: can't divide by X1==0");
*tmp3.data() = obs[0] / x1;
X0()->EMBprop(vtmp3,posterior);
}
}
else
{
if (!X1()->isConstant())
{
Mat matObs = obs.toMat(m,l);
Mat& x0 = X0()->value->matValue;
solveLinearSystem(x0,matObs,tmp3); // solve x0 * tmp3 = matObs
X1()->EMBprop(vtmp3,posterior);
}
if (!X0()->isConstant())
{
Mat matObs = obs.toMat(m,l);
Mat& x1 = X1()->value->matValue;
// solve tmp3 * x1 = matObs
solveTransposeLinearSystem(x1,matObs,tmp3);
X1()->EMBprop(vtmp3,posterior);
}
}
}
}
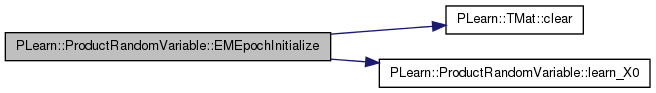
| void PLearn::ProductRandomVariable::EMEpochInitialize | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Initialization of an individual EMEpoch.
the default just propagates to the unmarked parents
Reimplemented from PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 1669 of file RandomVar.cc.
References PLearn::TMat< T >::clear(), denom, PLearn::RandomVariable::EMmark, learn_something, learn_X0(), X0numerator, and X1numerator.
{
if (EMmark) return;
RandomVariable::EMEpochInitialize();
if (learn_something)
{
denom.clear();
if (learn_X0())
X0numerator.clear();
else
X1numerator.clear();
}
}
| void PLearn::ProductRandomVariable::EMTrainingInitialize | ( | const RVArray & | parameters_to_learn | ) | [virtual] |
Initialization of EM training (before all the iterations start).
the default just propagates to the unmarked parents
Reimplemented from PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 1633 of file RandomVar.cc.
References denom, PLearn::FunctionalRandomVariable::isNonRandom(), l, learn_something, learn_X0(), learn_X1(), m, n, PLERROR, PLearn::TMat< T >::resize(), PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), tmp1, tmp2, tmp3, tmp4, PLearn::TMat< T >::toVec(), vtmp3, X0(), X0numerator, X1(), and X1numerator.
{
RandomVariable::EMTrainingInitialize(parameters_to_learn);
if (learn_X0() && learn_X1())
PLERROR("ProductRandomVariable: can't learn both X0 and X1");
if (learn_X0() || learn_X1())
{
denom.resize(n,n);
tmp2.resize(n,n);
tmp4.resize(n);
learn_something=true;
if (learn_X0())
{
X0numerator.resize(m,n);
tmp1.resize(m,n);
if (!X1()->isNonRandom())
{
tmp3.resize(m,l);
vtmp3 = tmp3.toVec();
}
}
else
{
X1numerator.resize(n,l);
tmp1.resize(n,l);
if (!X0()->isNonRandom())
{
tmp3.resize(n,m);
vtmp3 = tmp3.toVec();
}
}
}
else
learn_something=false;
}
| void PLearn::ProductRandomVariable::EMUpdate | ( | ) | [virtual] |
update the fixed (non-random) parameters using internal learning mechanism, at end of an EMEpoch. the default just propagates to the unmarked parents.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 1807 of file RandomVar.cc.
References denom, PLearn::RandomVariable::EMmark, PLearn::RandomVariable::isConstant(), learn_something, learn_X0(), scalars, PLearn::solveLinearSystemByCholesky(), PLearn::solveTransposeLinearSystemByCholesky(), tmp2, tmp4, PLearn::RandomVariable::value, X0(), X0numerator, X1(), and X1numerator.
{
if (EMmark) return;
EMmark=true;
if (learn_something)
{
if (learn_X0())
{
if (scalars)
{
if (denom(0,0)>0)
X0()->value->value[0] = X0numerator(0,0)/denom(0,0);
}
else
solveTransposeLinearSystemByCholesky(denom,X0numerator,
X0()->value->matValue,
&tmp2,&tmp4);
if (!X1()->isConstant())
X1()->EMUpdate();
}
else // learn_X1()
{
if (scalars)
{
if (denom(0,0)>0)
X1()->value->value[0] = X1numerator(0,0)/denom(0,0);
}
else
solveLinearSystemByCholesky(denom,X1numerator,
X1()->value->matValue,
&tmp2,&tmp4);
if (!X0()->isConstant())
X0()->EMUpdate();
}
}
else
{
if (!X0()->isConstant())
X0()->EMUpdate();
if (!X1()->isConstant())
X1()->EMUpdate();
}
}
| bool PLearn::ProductRandomVariable::invertible | ( | const Var & | obs, |
| RVInstanceArray & | unobserved_parents, | ||
| Var ** | JacobianCorrection | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
functions specific to FunctionalRandomVariable's
!< SUBCLASS WRITERS: IMPLEMENT FUNCTIONS BELOW //!<
check whether it is possible to invert the function which maps the given unobserved parents to the observed value of the RV (obs). If invertible, do the inversion, and set the value fields of the RVInstances to Var's which are functionally dependent on obs. If the absolute value of the Jacobian of the map from the unobserved parents to this R.V.'s value is different from 1, then JacobianCorrection should point to a Var that is the logarithm of the determinant of this Jacobian (first derivatives) matrix. If the function is not invertible but it is possible to write P(Y==obs | unobserved_parents) in terms of the unobserved_parents logP functions, then the sub-class writer should instead redefine the logP function appropriately.
Reimplemented from PLearn::FunctionalRandomVariable.
Definition at line 1610 of file RandomVar.cc.
References PLearn::abs(), PLearn::det(), PLearn::leftPseudoInverse(), PLearn::log(), PLearn::product(), PLearn::rightPseudoInverse(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::RandomVariable::value, X0(), and X1().
{
if (unobserved_parents.size()==2)
return false; // can't invert if two parents are unobserved
if (unobserved_parents[0].V == X0())
{
unobserved_parents[0].v =
product(obs,rightPseudoInverse(X1()->value));
**JacobianCorrection = log(abs(det(X1()->value)));
}
else
{
unobserved_parents[0].v =
product( leftPseudoInverse(X0()->value), obs);
**JacobianCorrection = log(abs(det(X0()->value)));
}
return true;
}
| bool PLearn::ProductRandomVariable::learn_X0 | ( | ) | [inline] |
stuff for EM
Definition at line 1440 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), EMEpochInitialize(), EMTrainingInitialize(), and EMUpdate().
{ return learn_the_parameters[0]; }
| bool PLearn::ProductRandomVariable::learn_X1 | ( | ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 1441 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMTrainingInitialize().
{ return learn_the_parameters[1]; }

| void PLearn::ProductRandomVariable::setValueFromParentsValue | ( | ) | [virtual] |
set the field value from the values of the parents
Implements PLearn::FunctionalRandomVariable.
Definition at line 1603 of file RandomVar.cc.
References PLearn::RandomVariable::marked, PLearn::RandomVariable::value, X0(), and X1().
| const RandomVar& PLearn::ProductRandomVariable::X0 | ( | ) | [inline] |
convenience inline's
viewed as mxn matrix
Definition at line 1435 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), EMTrainingInitialize(), EMUpdate(), invertible(), and setValueFromParentsValue().
| const RandomVar& PLearn::ProductRandomVariable::X1 | ( | ) | [inline] |
viewed as nx1 vector
Definition at line 1436 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), EMTrainingInitialize(), EMUpdate(), invertible(), and setValueFromParentsValue().
nxn matrix denominator
Definition at line 1445 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), EMEpochInitialize(), EMTrainingInitialize(), and EMUpdate().
dimensions of the matrices Y(mxl) = X0(mxn) * X1(nxl)
Definition at line 1420 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), EMTrainingInitialize(), and ProductRandomVariable().
Definition at line 1442 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), EMEpochInitialize(), EMTrainingInitialize(), and EMUpdate().
Definition at line 1420 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), EMTrainingInitialize(), and ProductRandomVariable().
Definition at line 1420 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMTrainingInitialize(), and ProductRandomVariable().
= (m==1 && n==1 && l==1);
Definition at line 1437 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), EMUpdate(), and ProductRandomVariable().
temporary matrices to avoid allocating in loops
Definition at line 1446 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), and EMTrainingInitialize().
Definition at line 1447 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), EMTrainingInitialize(), and EMUpdate().
Definition at line 1448 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), and EMTrainingInitialize().
Definition at line 1450 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMTrainingInitialize(), and EMUpdate().
Vec version of tmp3.
Definition at line 1449 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), and EMTrainingInitialize().
mxn matrix, used in the case X0 is learned
Definition at line 1443 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), EMEpochInitialize(), EMTrainingInitialize(), and EMUpdate().
nxl vector, used in the case X1 is learned
Definition at line 1444 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), EMEpochInitialize(), EMTrainingInitialize(), and EMUpdate().
 1.7.4
1.7.4