|
PLearn 0.1
|
|
PLearn 0.1
|
#include <RandomVar.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| MixtureRandomVariable (const RVArray &components, const RandomVar &log_weights) | |
| MixtureRandomVariable. | |
| virtual char * | classname () |
| const RandomVar & | log_weights () |
| convenience inline: actual weights = softmax(log_weights) | |
| bool & | learn_the_weights () |
| virtual Var | logP (const Var &obs, const RVInstanceArray &RHS, RVInstanceArray *parameters_to_learn) |
| virtual Var | ElogP (const Var &obs, RVInstanceArray ¶meters_to_learn, const RVInstanceArray &RHS) |
| virtual void | setValueFromParentsValue () |
| virtual void | EMUpdate () |
| virtual void | EMBprop (const Vec obs, real posterior) |
| virtual void | EMEpochInitialize () |
| Initialization of an individual EMEpoch. | |
| virtual void | EMTrainingInitialize (const RVArray ¶meters_to_learn) |
| Initialization of EM training (before all the iterations start). | |
| virtual bool | isDiscrete () |
| most common default | |
| virtual bool | canStopEM () |
| virtual void | setKnownValues () |
| virtual void | unmarkAncestors () |
| clear not only the marked field but also that of parents | |
| virtual void | clearEMmarks () |
Protected Attributes | |
| RVArray | components |
| Note: THESE ARE NOT PARENTS IN THE GRAPHICAL MODEL. | |
| Vec | posteriors |
| temporaries used for EM: | |
| Vec | sum_posteriors |
| sum of posteriors over trianing data | |
| VarArray | componentsLogP |
| used in logP: | |
| Var | lw |
| = log(softmax(log_weights()->value())) | |
| Var | logp |
| result of last call to logP | |
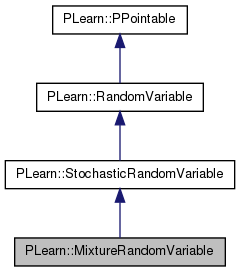
Definition at line 1243 of file RandomVar.h.
| PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::MixtureRandomVariable | ( | const RVArray & | components, |
| const RandomVar & | log_weights | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 2018 of file RandomVar.cc.
:StochasticRandomVariable(logweights,the_components[0]->length()), components(the_components), posteriors(logweights->length()), sum_posteriors(logweights->length()), componentsLogP(logweights->length()), lw(logweights->length()) { }
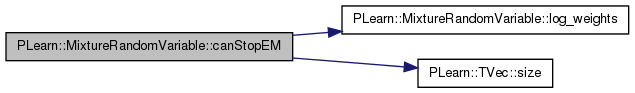
| bool PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::canStopEM | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Has the distribution seen enough EM iterations to meaningfully stop EM iterative training? This is a way for a RandomVariable sub-class to force continuation of the EM iterations beyond the criteria given by the caller of EM. the default just propagates to the unmarked parents.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 2183 of file RandomVar.cc.
References components, log_weights(), and PLearn::TVec< T >::size().
{
// propagate to components
bool can=log_weights()->canStopEM();
for (int i=0;i<components.size() && !can;i++)
can = components[i]->canStopEM();
return can;
}
| virtual char* PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::classname | ( | ) | [inline, virtual] |
Implements PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 1253 of file RandomVar.h.
{ return "MixtureRandomVariable"; }
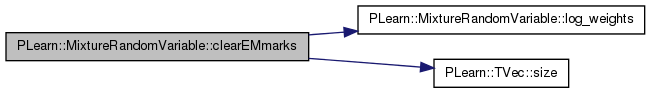
| void PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::clearEMmarks | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 2221 of file RandomVar.cc.
References components, PLearn::RandomVariable::EMmark, log_weights(), and PLearn::TVec< T >::size().
{
if (EMmark)
{
EMmark=false;
log_weights()->clearEMmarks();
for (int i=0;i<components.size();i++)
components[i]->clearEMmarks();
}
}
| Var PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::ElogP | ( | const Var & | obs, |
| RVInstanceArray & | parameters_to_learn, | ||
| const RVInstanceArray & | RHS | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Definition at line 2057 of file RandomVar.cc.
References components, componentsLogP, PLearn::exp(), PLearn::RandomVariable::isMarked(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::log(), log_weights(), PLearn::logadd(), logp, logP(), lw, PLearn::marginalize(), PLearn::RandomVariable::markRHSandSetKnownValues(), n, posteriors, PLearn::softmax(), PLearn::Var::subVec(), PLearn::sum(), PLearn::RVInstanceArray::swap_v_and_Vvalue(), unmarkAncestors(), PLearn::RandomVariable::value, and PLearn::vconcat().
Referenced by logP().
{
if (log_weights()->isMarked())
{
int n=posteriors.length();
// (1) using the "current" value of the parameters
Var weights = softmax(log_weights()->value);
lw = log(weights);
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
// componentsLogP[i] = log(P(obs|i)*P(i)) = log(P(obs,i))
componentsLogP[i] = components[i]->logP(obs,RHS) + lw->subVec(i,1);
// logp = log(P(obs)) = log(sum_i P(obs,i))
logp = logadd(vconcat(componentsLogP));
// now compute log-posteriors by normalization
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
// componentsLogP[i] = log(P(i|obs))=log(P(obs,i)/P(obs))
componentsLogP[i] = componentsLogP[i] - logp;
// (2) now put the "new" value of the parameters (swap with v fields)
parameters_to_learn.swap_v_and_Vvalue();
// unmark parents and re-compute value's in terms of ancestors' values
unmarkAncestors();
markRHSandSetKnownValues(RHS);
// (3) and compute the logP of each component weighted by its posterior
weights = softmax(log_weights()->value);
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
componentsLogP[i] = exp(components[i]->logP(obs,RHS,¶meters_to_learn)
+ componentsLogP[i]);
logp = sum(vconcat(componentsLogP));
// (4) now put back the "current" value of parameters in their value field
parameters_to_learn.swap_v_and_Vvalue();
// unmark parents and re-compute value's in terms of ancestors' values
unmarkAncestors();
markRHSandSetKnownValues(RHS);
return logp;
}
// else
// probably not feasible..., but try in case we know a trick
return PLearn::logP(ConditionalExpression
(RVInstance(marginalize(this,log_weights()),obs),
RHS),true,¶meters_to_learn);
}

************ EM STUFF ********** propagate posterior information to parents in order to perform an EMupdate at the end of an EMEpoch. In the case of mixture-like RVs and their components, the posterior is the probability of the component "this" given the observation "obs".
Implements PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 2133 of file RandomVar.cc.
References PLearn::apply(), components, componentsLogP, PLearn::TVec< T >::data(), PLearn::endl(), PLearn::exp(), learn_the_weights(), PLearn::Var::length(), logp, lw, n, posteriors, PLearn::safeexp(), PLearn::sum(), sum_posteriors, and PLearn::RandomVariable::value.
{
// ASSUME THAT AN FPROP HAS BEEN PERFORMED
// so that weights and componentsLogP hold appropriate value
//
// compute posterior vector for this observation
// posteriors = posterior*(components[i]->logP(obs)*weights/normalize)
real log_p = logp->value[0];
real *p = posteriors.data();
int n = lw->value.length();
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
p[i] = componentsLogP[i]->value[0] - log_p;
#ifdef _MSC_VER
apply(posteriors,posteriors,(tRealFunc)exp);
#else
apply(posteriors,posteriors,safeexp);
#endif
if (fabs(sum(posteriors)-1)>1e-5)
{
cout << "sum(posteriors) = " << sum(posteriors) << "!" << endl;
}
posteriors *= posterior;
if (learn_the_weights())
sum_posteriors+=posteriors;
// propagate to components
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
components[i]->EMBprop(obs,posteriors[i]);
}
| void PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::EMEpochInitialize | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Initialization of an individual EMEpoch.
the default just propagates to the unmarked parents
Reimplemented from PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 2123 of file RandomVar.cc.
References PLearn::TVec< T >::clear(), components, PLearn::RandomVariable::EMmark, learn_the_weights(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), and sum_posteriors.
{
if (EMmark) return;
RandomVariable::EMEpochInitialize();
if (learn_the_weights())
sum_posteriors.clear();
for (int i=0;i<components.size();i++)
components[i]->EMEpochInitialize();
}
| void PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::EMTrainingInitialize | ( | const RVArray & | parameters_to_learn | ) | [virtual] |
Initialization of EM training (before all the iterations start).
the default just propagates to the unmarked parents
Reimplemented from PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 2113 of file RandomVar.cc.
References components, PLearn::TVec< T >::contains(), PLearn::RandomVariable::EMmark, learn_the_weights(), log_weights(), and PLearn::TVec< T >::size().
{
if (EMmark) return;
EMmark=true;
learn_the_weights() = parameters_to_learn.contains(log_weights())
&& log_weights()->isConstant();
for (int i=0;i<components.size();i++)
components[i]->EMTrainingInitialize(parameters_to_learn);
}
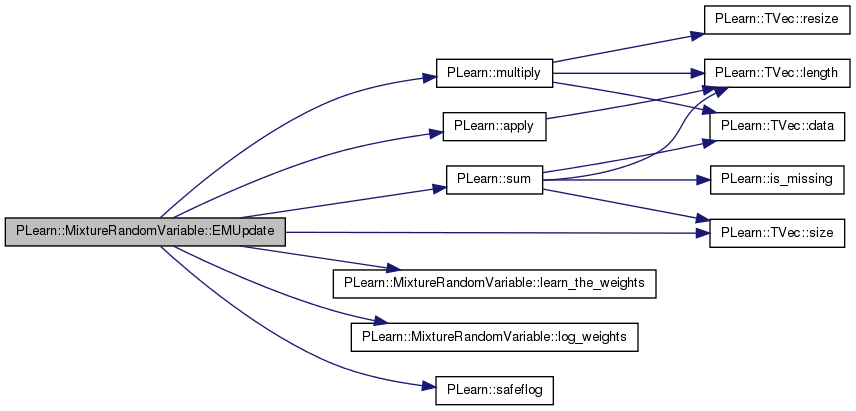
| void PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::EMUpdate | ( | ) | [virtual] |
update the fixed (non-random) parameters using internal learning mechanism, at end of an EMEpoch. the default just propagates to the unmarked parents.
Reimplemented from PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 2164 of file RandomVar.cc.
References PLearn::apply(), components, PLearn::RandomVariable::EMmark, learn_the_weights(), log_weights(), PLearn::multiply(), posteriors, PLearn::safeflog(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::sum(), sum_posteriors, and PLearn::RandomVariable::value.
{
if (EMmark) return;
EMmark=true;
// update weights
if (learn_the_weights())
{
real denom = sum(sum_posteriors);
if (denom>0)
{
multiply(sum_posteriors,real(1.0/denom),posteriors);
apply(posteriors,log_weights()->value->value,safeflog);
}
}
// propagate to components
for (int i=0;i<components.size();i++)
components[i]->EMUpdate();
}
| bool PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::isDiscrete | ( | ) | [virtual] |
most common default
Reimplemented from PLearn::StochasticRandomVariable.
Definition at line 2192 of file RandomVar.cc.
References components.
{
return components[0]->isDiscrete();
}
| bool& PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::learn_the_weights | ( | ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 1258 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), EMEpochInitialize(), EMTrainingInitialize(), and EMUpdate().
{ return learn_the_parameters[0]; }
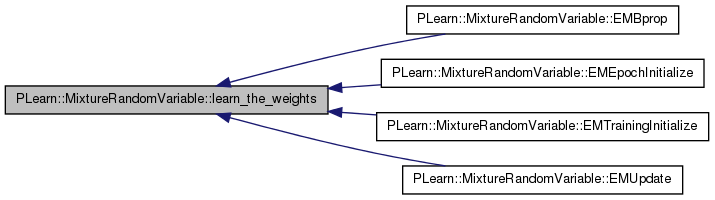
| const RandomVar& PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::log_weights | ( | ) | [inline] |
convenience inline: actual weights = softmax(log_weights)
Definition at line 1257 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by canStopEM(), clearEMmarks(), ElogP(), EMTrainingInitialize(), EMUpdate(), logP(), setKnownValues(), setValueFromParentsValue(), and unmarkAncestors().
{ return parents[0]; }
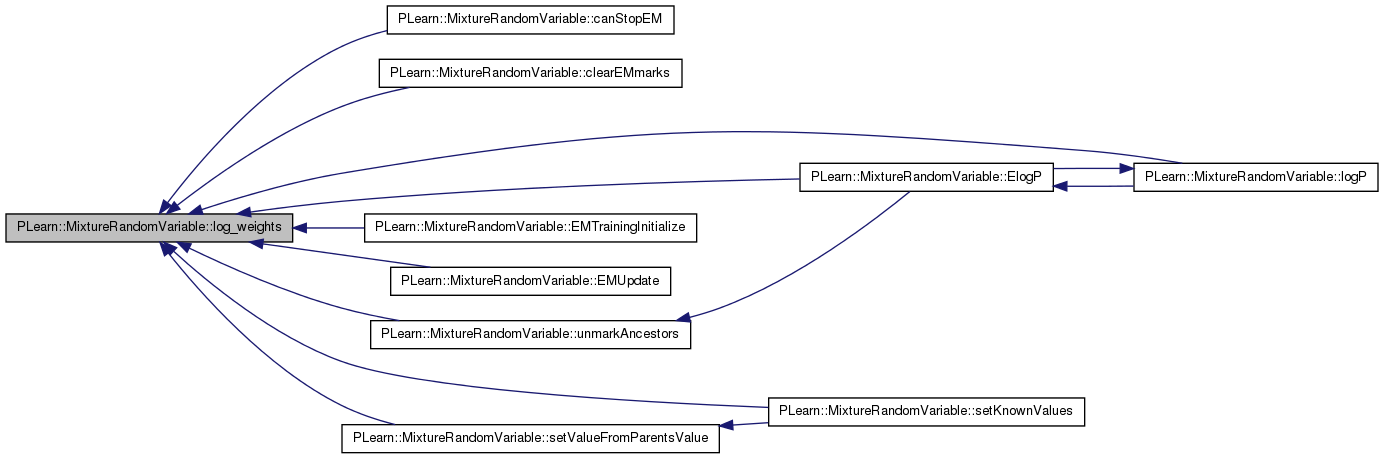
| Var PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::logP | ( | const Var & | obs, |
| const RVInstanceArray & | RHS, | ||
| RVInstanceArray * | parameters_to_learn | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
Construct a Var that computes logP(This = obs | RHS ). This function SHOULD NOT be used directly, but is called by the global function logP (same argument), which does proper massaging of the network before and after this call.
Implements PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 2027 of file RandomVar.cc.
References components, componentsLogP, ElogP(), PLearn::RandomVariable::isMarked(), PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::log(), log_weights(), PLearn::logadd(), logp, lw, PLearn::marginalize(), n, posteriors, PLearn::softmax(), PLearn::Var::subVec(), PLearn::RandomVariable::value, and PLearn::vconcat().
Referenced by ElogP().
{
if (parameters_to_learn!=0) return ElogP(obs,*parameters_to_learn,RHS);
if (log_weights()->isMarked())
{
int n=posteriors.length();
if (log_weights()->value->getName()[0]=='#')
log_weights()->value->setName("log_weights");
Var weights = softmax(log_weights()->value);
weights->setName("weights");
lw = log(weights);
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
componentsLogP[i] = components[i]->logP(obs,RHS) + lw->subVec(i,1);
logp = logadd(vconcat(componentsLogP));
return logp;
}
// else
// probably not feasible..., but try in case we know a trick
return PLearn::logP(ConditionalExpression
(RVInstance(marginalize(this,log_weights()),obs),RHS),true,0);
}
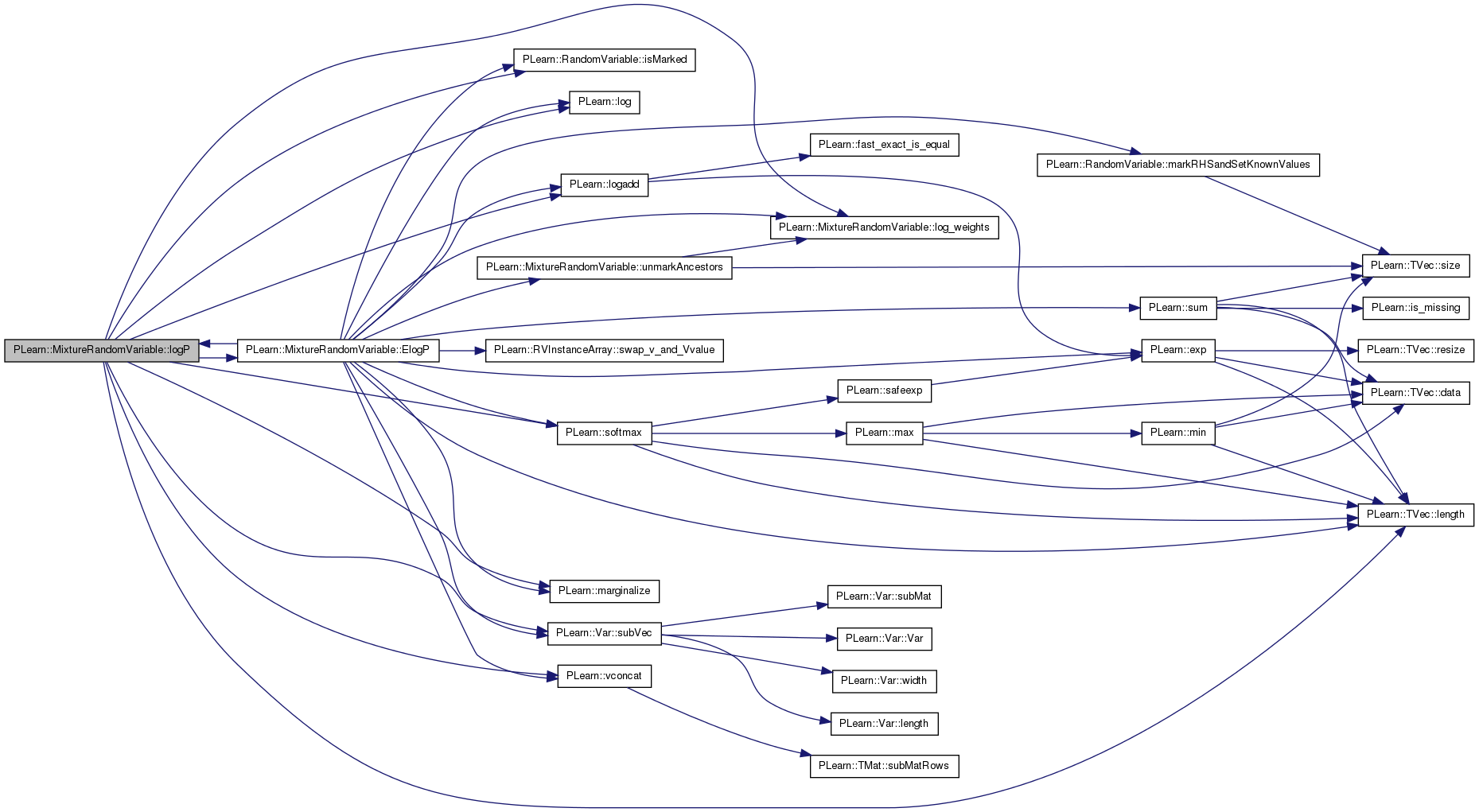

| void PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::setKnownValues | ( | ) | [virtual] |
traverse the graph of ancestors of this node and mark nodes which are deterministic descendents of marked nodes while setting their "value" field as a function of their parents.
Reimplemented from PLearn::StochasticRandomVariable.
Definition at line 2197 of file RandomVar.cc.
References components, log_weights(), PLearn::RandomVariable::marked, PLearn::RandomVariable::pmark, setValueFromParentsValue(), and PLearn::TVec< T >::size().
{
if (!pmark && !marked)
{
pmark = true;
log_weights()->setKnownValues();
for (int i=0;i<components.size();i++)
components[i]->setKnownValues();
setValueFromParentsValue();
}
}
| void PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::setValueFromParentsValue | ( | ) | [virtual] |
ALL BELOW THIS IS NOT NECESSARY FOR ORDINARY USERS < but may be necessary when writing subclasses. Note < however that normally the subclasses should not be < direct subclasses of RandomVariable but rather be < subclasses of StochasticRandomVariable and of < FunctionalRandomVariable.
define the formula that gives a value to this RV given its parent's value (sets the value field). If the RV is stochastic, the formula may also be "stochastic" (using SampleVariable's to define the Var).
Implements PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 2106 of file RandomVar.cc.
References components, log_weights(), PLearn::softmax(), PLearn::RandomVariable::value, and PLearn::RVArray::values().
Referenced by setKnownValues().
{
Var index = new MultinomialSampleVariable(softmax(log_weights()->value));
value = components.values()[index];
}

| void PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::unmarkAncestors | ( | ) | [virtual] |
clear not only the marked field but also that of parents
Reimplemented from PLearn::RandomVariable.
Definition at line 2209 of file RandomVar.cc.
References components, log_weights(), PLearn::RandomVariable::marked, PLearn::RandomVariable::pmark, and PLearn::TVec< T >::size().
Referenced by ElogP().
{
if (pmark)
{
marked=false;
pmark=false;
log_weights()->unmarkAncestors();
for (int i=0;i<components.size();i++)
components[i]->unmarkAncestors();
}
}

RVArray PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::components [protected] |
Note: THESE ARE NOT PARENTS IN THE GRAPHICAL MODEL.
component distributions.
Definition at line 1247 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by canStopEM(), clearEMmarks(), ElogP(), EMBprop(), EMEpochInitialize(), EMTrainingInitialize(), EMUpdate(), isDiscrete(), logP(), setKnownValues(), setValueFromParentsValue(), and unmarkAncestors().
Var PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::logp [protected] |
result of last call to logP
Definition at line 1284 of file RandomVar.h.
Var PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::lw [protected] |
= log(softmax(log_weights()->value()))
Definition at line 1283 of file RandomVar.h.
Vec PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::posteriors [protected] |
temporaries used for EM:
P(i-th component | obs), used in EM
Definition at line 1278 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by ElogP(), EMBprop(), EMUpdate(), and logP().
Vec PLearn::MixtureRandomVariable::sum_posteriors [protected] |
sum of posteriors over trianing data
Definition at line 1279 of file RandomVar.h.
Referenced by EMBprop(), EMEpochInitialize(), and EMUpdate().
 1.7.4
1.7.4