|
PLearn 0.1
|
|
PLearn 0.1
|
Does the same thing as Hinton's deep belief nets. More...
#include <GaussianDBNRegression.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| GaussianDBNRegression () | |
| Default constructor. | |
| virtual real | density (const Vec &y) const |
| Return probability density p(y | x) | |
| virtual real | log_density (const Vec &y) const |
| Return log of probability density log(p(y | x)). | |
| virtual real | survival_fn (const Vec &y) const |
| Return survival function: P(Y>y | x). | |
| virtual real | cdf (const Vec &y) const |
| Return cdf: P(Y<y | x). | |
| virtual void | expectation (Vec &mu) const |
| Return E[Y | x]. | |
| virtual void | variance (Mat &cov) const |
| Return Var[Y | x]. | |
| virtual void | generate (Vec &y) const |
| Return a pseudo-random sample generated from the conditional distribution, of density p(y | x). | |
| virtual bool | setPredictorPredictedSizes (int the_predictor_size, int the_predicted_size, bool call_parent=true) |
| Generates a pseudo-random sample x from the reversed conditional distribution, of density p(x | y) (and NOT p(y | x)). | |
| virtual void | setPredictor (const Vec &predictor, bool call_parent=true) const |
| Set the value for the predictor part of a conditional probability. | |
| virtual void | forget () |
| (Re-)initializes the PDistribution in its fresh state (that state may depend on the 'seed' option). | |
| virtual void | train () |
| The role of the train method is to bring the learner up to stage == nstages, updating the train_stats collector with training costs measured on-line in the process. | |
| virtual void | computeCostsFromOutputs (const Vec &input, const Vec &output, const Vec &target, Vec &costs) const |
| Compute a cost, depending on the type of the first output : if it is the density or the log-density: NLL if it is the expectation: NLL and class error. | |
| virtual TVec< string > | getTestCostNames () const |
| Return [ "NLL" ] (the only cost computed by a PDistribution). | |
| virtual string | classname () const |
| virtual OptionList & | getOptionList () const |
| virtual OptionMap & | getOptionMap () const |
| virtual RemoteMethodMap & | getRemoteMethodMap () const |
| virtual GaussianDBNRegression * | deepCopy (CopiesMap &copies) const |
| virtual void | build () |
| Simply calls inherited::build() then build_(). | |
| virtual void | makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy (CopiesMap &copies) |
| Transforms a shallow copy into a deep copy. | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static string | _classname_ () |
| static OptionList & | _getOptionList_ () |
| static RemoteMethodMap & | _getRemoteMethodMap_ () |
| static Object * | _new_instance_for_typemap_ () |
| static bool | _isa_ (const Object *o) |
| static void | _static_initialize_ () |
| static const PPath & | declaringFile () |
Public Attributes | |
| real | learning_rate |
| ### declare public option fields (such as build options) here Start your comments with Doxygen-compatible comments such as //! | |
| real | weight_decay |
| The weight decay. | |
| string | initialization_method |
| The method used to initialize the weights: | |
| int | n_layers |
| Number of layers, including input layer and last layer, but not target layer. | |
| TVec< PP< RBMLayer > > | layers |
| Layers that learn representations of the input, layers[0] is input layer, layers[n_layers-1] is last layer. | |
| PP< RBMLayer > | last_layer |
| last_layer is layer[n_layers-1] | |
| PP< RBMLayer > | target_layer |
| Target (or label) layer. | |
| TVec< PP< RBMLLParameters > > | params |
| RBMParameters linking the unsupervised layers. | |
| PP< RBMQLParameters > | input_params |
| Parameters linking input layer[0] and layer[1]. | |
| PP< RBMLQParameters > | target_params |
| Parameters linking target_layer and last_layer. | |
| TVec< int > | training_schedule |
| Number of examples to use during each of the different greedy steps of the training phase. | |
| string | fine_tuning_method |
| Method for fine-tuning the whole network after greedy learning. | |
| bool | use_sample_rather_than_expectation_in_positive_phase_statistics |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static StaticInitializer | _static_initializer_ |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual void | greedyStep (const Vec &predictor, int params_index) |
| virtual void | fineTuneByGradientDescent (const Vec &input) |
| void | fineTuneByGradientDescentLastLayer (const Vec &input) |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static void | declareOptions (OptionList &ol) |
| Declares the class options. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| TVec< Vec > | activation_gradients |
| gradients of cost wrt the activations (output of params) | |
| TVec< Vec > | expectation_gradients |
| gradients of cost wrt the expectations (output of layers) | |
| Vec | output_gradient |
| gradient wrt output activations | |
Private Types | |
| typedef PDistribution | inherited |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | build_ () |
| This does the actual building. | |
| void | build_layers () |
| Build the layers. | |
| void | build_params () |
| Build the parameters if needed. | |
Does the same thing as Hinton's deep belief nets.
Definition at line 60 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
typedef PDistribution PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::inherited [private] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 62 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
| PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::GaussianDBNRegression | ( | ) |
Default constructor.
Definition at line 64 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References PLearn::PLearner::random_gen.
:
learning_rate(0.),
weight_decay(0.),
use_sample_rather_than_expectation_in_positive_phase_statistics(false)
{
random_gen = new PRandom();
}
| string PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::_classname_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 59 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
| OptionList & PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::_getOptionList_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 59 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::_getRemoteMethodMap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 59 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 59 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
| Object * PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::_new_instance_for_typemap_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 59 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
| StaticInitializer GaussianDBNRegression::_static_initializer_ & PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::_static_initialize_ | ( | ) | [static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 59 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::build | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Simply calls inherited::build() then build_().
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 156 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References PLearn::PDistribution::build(), and build_().
{
// ### Nothing to add here, simply calls build_().
inherited::build();
build_();
}
| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::build_ | ( | ) | [private] |
This does the actual building.
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 166 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References build_layers(), build_params(), PLearn::endl(), fine_tuning_method, initialization_method, layers, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::lowerstring(), n_layers, PLERROR, and training_schedule.
Referenced by build().
{
MODULE_LOG << "build_() called" << endl;
n_layers = layers.length();
if( n_layers <= 1 )
return;
// check value of initialization_method
string im = lowerstring( initialization_method );
if( im == "" || im == "uniform_sqrt" )
initialization_method = "uniform_sqrt";
else if( im == "uniform_linear" )
initialization_method = im;
else if( im == "zero" )
initialization_method = im;
else
PLERROR( "RBMParameters::build_ - initialization_method\n"
"\"%s\" unknown.\n", initialization_method.c_str() );
MODULE_LOG << " initialization_method = \"" << initialization_method
<< "\"" << endl;
// check value of fine_tuning_method
string ftm = lowerstring( fine_tuning_method );
if( ftm == "" | ftm == "none" )
fine_tuning_method = "";
else if( ftm == "cd" | ftm == "contrastive_divergence" )
fine_tuning_method = "CD";
else if( ftm == "egd" | ftm == "error_gradient_descent" )
fine_tuning_method = "EGD";
else if( ftm == "ws" | ftm == "wake_sleep" )
fine_tuning_method = "WS";
else
PLERROR( "GaussianDBNRegression::build_ - fine_tuning_method \"%s\"\n"
"is unknown.\n", fine_tuning_method.c_str() );
MODULE_LOG << " fine_tuning_method = \"" << fine_tuning_method << "\""
<< endl;
//TODO: build structure to store gradients during gradient descent
if( training_schedule.length() != n_layers )
training_schedule = TVec<int>( n_layers, 1000000 );
MODULE_LOG << " training_schedule = " << training_schedule << endl;
MODULE_LOG << endl;
build_layers();
build_params();
}

| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::build_layers | ( | ) | [private] |
Build the layers.
Definition at line 213 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References PLearn::endl(), i, PLearn::PLearner::inputsize(), PLearn::PLearner::inputsize_, last_layer, layers, n_layers, PLearn::PDistribution::n_predicted, PLearn::PDistribution::n_predictor, PLASSERT, PLearn::PLearner::random_gen, setPredictorPredictedSizes(), and target_layer.
Referenced by build_().
{
MODULE_LOG << "build_layers() called" << endl;
if( inputsize_ >= 0 )
{
PLASSERT( layers[0]->size + target_layer->size == inputsize() );
setPredictorPredictedSizes( layers[0]->size,
target_layer->size, false );
MODULE_LOG << " n_predictor = " << n_predictor << endl;
MODULE_LOG << " n_predicted = " << n_predicted << endl;
}
for( int i=0 ; i<n_layers ; i++ )
layers[i]->random_gen = random_gen;
target_layer->random_gen = random_gen;
last_layer = layers[n_layers-1];
}

| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::build_params | ( | ) | [private] |
Build the parameters if needed.
Definition at line 233 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References activation_gradients, PLearn::endl(), expectation_gradients, i, initialization_method, input_params, last_layer, layers, learning_rate, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), n_layers, PLearn::PDistribution::n_predicted, output_gradient, params, PLERROR, PLearn::PLearner::random_gen, PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), target_layer, and target_params.
Referenced by build_().
{
MODULE_LOG << "build_params() called" << endl;
if( params.length() == 0 )
{
input_params = new RBMQLParameters() ;
params.resize( n_layers-1 );
for( int i=1 ; i<n_layers-1 ; i++ )
params[i] = new RBMLLParameters();
// params[0] is not being using, it is not being created
}
else if( params.length() != n_layers-1 )
PLERROR( "GaussianDBNRegression::build_params - params.length() should\n"
"be equal to layers.length()-1 (%d != %d).\n",
params.length(), n_layers-1 );
activation_gradients.resize( n_layers+1 );
expectation_gradients.resize( n_layers+1 );
output_gradient.resize( n_predicted );
input_params->down_units_types = layers[0]->units_types;
input_params->up_units_types = layers[1]->units_types;
input_params->learning_rate = learning_rate;
input_params->initialization_method = initialization_method;
input_params->random_gen = random_gen;
input_params->build();
activation_gradients[0].resize( input_params->down_layer_size );
expectation_gradients[0].resize( input_params->down_layer_size );
for( int i=1 ; i<n_layers-1 ; i++ )
{
//TODO: call changeOptions instead
params[i]->down_units_types = layers[i]->units_types;
params[i]->up_units_types = layers[i+1]->units_types;
params[i]->learning_rate = learning_rate;
params[i]->initialization_method = initialization_method;
params[i]->random_gen = random_gen;
params[i]->build();
activation_gradients[i].resize( params[i]->down_layer_size );
expectation_gradients[i].resize( params[i]->down_layer_size );
}
if( target_layer && !target_params )
target_params = new RBMLQParameters();
//TODO: call changeOptions instead
target_params->down_units_types = last_layer->units_types;
target_params->up_units_types = target_layer->units_types;
target_params->learning_rate = learning_rate;
target_params->initialization_method = initialization_method;
target_params->random_gen = random_gen;
target_params->build();
}

Return cdf: P(Y<y | x).
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 331 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References PLERROR.
{
PLERROR("cdf not implemented for GaussianDBNRegression"); return 0;
}
| string PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::classname | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 59 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
Referenced by train().

| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::computeCostsFromOutputs | ( | const Vec & | input, |
| const Vec & | output, | ||
| const Vec & | target, | ||
| Vec & | costs | ||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Compute a cost, depending on the type of the first output : if it is the density or the log-density: NLL if it is the expectation: NLL and class error.
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 837 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References c, PLearn::PDistribution::computeCostsFromOutputs(), i, PLearn::TVec< T >::length(), PLearn::PDistribution::outputs_def, PLearn::PDistribution::predicted_part, PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::PDistribution::splitCond(), and PLearn::square().
{
char c = outputs_def[0];
if( c == 'l' || c == 'd' )
inherited::computeCostsFromOutputs(input, output, target, costs);
else if( c == 'e' )
{
costs.resize( 1 );
costs[0] = .0 ;
splitCond(input);
int output_size = output.length();
for(int i=0 ; i<output_size ; ++i) {
costs[0] += square(output[i] - predicted_part[i]) ;
}
costs[0] /= output_size ;
}
}
| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::declareOptions | ( | OptionList & | ol | ) | [static, protected] |
Declares the class options.
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 75 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References PLearn::OptionBase::buildoption, PLearn::declareOption(), PLearn::PDistribution::declareOptions(), fine_tuning_method, initialization_method, input_params, layers, learning_rate, PLearn::OptionBase::learntoption, n_layers, params, target_layer, target_params, training_schedule, use_sample_rather_than_expectation_in_positive_phase_statistics, and weight_decay.
{
declareOption(ol, "learning_rate", &GaussianDBNRegression::learning_rate,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Learning rate");
declareOption(ol, "weight_decay", &GaussianDBNRegression::weight_decay,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Weight decay");
declareOption(ol, "initialization_method",
&GaussianDBNRegression::initialization_method,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"The method used to initialize the weights:\n"
" - \"uniform_linear\" = a uniform law in [-1/d, 1/d]\n"
" - \"uniform_sqrt\" = a uniform law in [-1/sqrt(d),"
" 1/sqrt(d)]\n"
" - \"zero\" = all weights are set to 0,\n"
"where d = max( up_layer_size, down_layer_size ).\n");
declareOption(ol, "training_schedule",
&GaussianDBNRegression::training_schedule,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Number of examples to use during each of the different"
" greedy\n"
"steps of the training phase.\n");
declareOption(ol, "fine_tuning_method",
&GaussianDBNRegression::fine_tuning_method,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Method for fine-tuning the whole network after greedy"
" learning.\n"
"One of:\n"
" - \"none\"\n"
" - \"CD\" or \"contrastive_divergence\"\n"
" - \"EGD\" or \"error_gradient_descent\"\n"
" - \"WS\" or \"wake_sleep\".\n");
declareOption(ol, "layers", &GaussianDBNRegression::layers,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Layers that learn representations of the input,"
" unsupervisedly.\n"
"layers[0] is input layer.\n");
declareOption(ol, "target_layer", &GaussianDBNRegression::target_layer,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Target (or label) layer");
declareOption(ol, "params", &GaussianDBNRegression::params,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"RBMParameters linking the unsupervised layers.\n"
"params[i] links layers[i] and layers[i+1], except for"
"params[n_layers-1],\n"
"that links layers[n_layers-1] and last_layer.\n");
declareOption(ol, "target_params", &GaussianDBNRegression::target_params,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Parameters linking target_layer and last_layer");
declareOption(ol, "input_params", &GaussianDBNRegression::input_params,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"Parameters linking layer[0] and layer[1]");
declareOption(ol, "use_sample_rather_than_expectation_in_positive_phase_statistics",
&GaussianDBNRegression::use_sample_rather_than_expectation_in_positive_phase_statistics,
OptionBase::buildoption,
"In positive phase statistics use output->sample * input\n"
"rather than output->expectation * input.\n");
declareOption(ol, "n_layers", &GaussianDBNRegression::n_layers,
OptionBase::learntoption,
"Number of unsupervised layers, including input layer");
// Now call the parent class' declareOptions().
inherited::declareOptions(ol);
}
| static const PPath& PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::declaringFile | ( | ) | [inline, static] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 232 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
:
//##### Protected Options ###############################################
| GaussianDBNRegression * PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::deepCopy | ( | CopiesMap & | copies | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 59 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
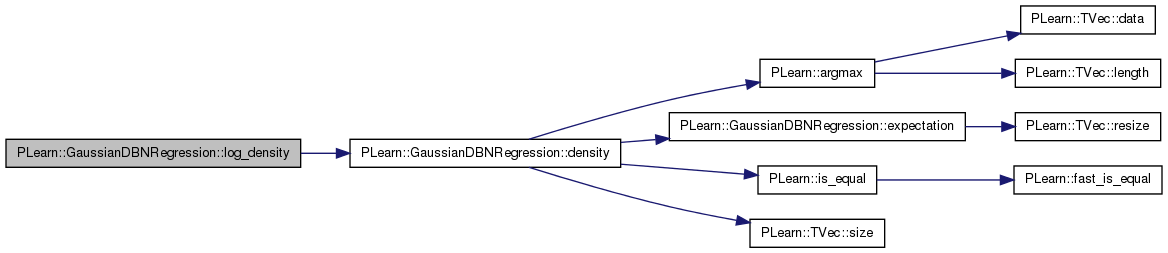
Return probability density p(y | x)
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 367 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References PLearn::argmax(), expectation(), i, PLearn::is_equal(), PLearn::PDistribution::n_predicted, PLASSERT, PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), and PLearn::PDistribution::store_expect.
Referenced by log_density().
{
PLASSERT( y.size() == n_predicted );
// TODO: 'y'[0] devrait plutot etre l'entier "index" lui-meme!
int index = argmax( y );
// If y != onehot( index ), then density is 0
if( !is_equal( y[index], 1. ) )
return 0;
for( int i=0 ; i<n_predicted ; i++ )
if( !is_equal( y[i], 0 ) && i != index )
return 0;
expectation( store_expect );
return store_expect[index];
}
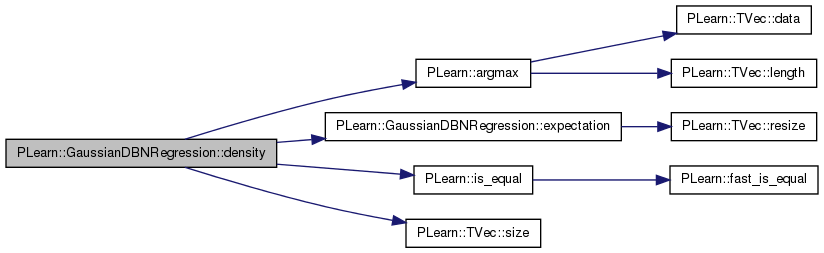

| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::expectation | ( | Vec & | mu | ) | const [virtual] |
Return E[Y | x].
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 339 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References i, input_params, last_layer, layers, n_layers, params, PLearn::PDistribution::predicted_size, PLearn::PDistribution::predictor_part, PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), target_layer, and target_params.
Referenced by density(), fineTuneByGradientDescent(), fineTuneByGradientDescentLastLayer(), greedyStep(), and train().
{
mu.resize( predicted_size );
// Propagate input (predictor_part) until penultimate layer
layers[0]->expectation << predictor_part;
input_params->setAsDownInput(layers[0]->expectation) ;
layers[1]->getAllActivations( (RBMQLParameters*) input_params );
layers[1]->computeExpectation();
for( int i=1 ; i<n_layers-1 ; i++ )
{
params[i]->setAsDownInput( layers[i]->expectation );
layers[i+1]->getAllActivations( (RBMLLParameters*) params[i] );
layers[i+1]->computeExpectation();
}
target_params->setAsDownInput( last_layer->expectation );
target_layer->getAllActivations( (RBMLQParameters*) target_params );
target_layer->computeExpectation();
mu << target_layer->expectation;
}


| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::fineTuneByGradientDescent | ( | const Vec & | input | ) | [protected, virtual] |
Definition at line 785 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References activation_gradients, expectation(), expectation_gradients, i, input_params, layers, n_layers, output_gradient, params, PLearn::PDistribution::predicted_part, PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::PDistribution::splitCond(), target_layer, and target_params.
{
// split input in predictor_part and predicted_part
splitCond(input);
// compute predicted_part expectation, conditioned on predictor_part
// (forward pass)
expectation( output_gradient );
int target_size = predicted_part.size() ;
expectation_gradients[n_layers].resize(target_size) ;
for(int i=0 ; i < target_size ; ++i) {
expectation_gradients[n_layers][i] = 2 * (output_gradient[i] - predicted_part[i]) ;
}
target_layer->bpropUpdate( target_layer->activations,
target_layer->expectation,
activation_gradients[n_layers] ,
expectation_gradients[n_layers]) ;
target_params->bpropUpdate( layers[n_layers-1]->expectation,
target_layer->activations,
expectation_gradients[n_layers-1],
activation_gradients[n_layers] );
for( int i=n_layers-1 ; i>1 ; i-- )
{
layers[i]->bpropUpdate( layers[i]->activations,
layers[i]->expectation,
activation_gradients[i],
expectation_gradients[i] );
params[i-1]->bpropUpdate( layers[i-1]->expectation,
layers[i]->activations,
expectation_gradients[i-1],
activation_gradients[i] );
}
layers[1]->bpropUpdate( layers[1]->activations,
layers[1]->expectation,
activation_gradients[1],
expectation_gradients[1] );
input_params->bpropUpdate( layers[0]->expectation,
layers[1]->activations,
expectation_gradients[0],
activation_gradients[1] );
}
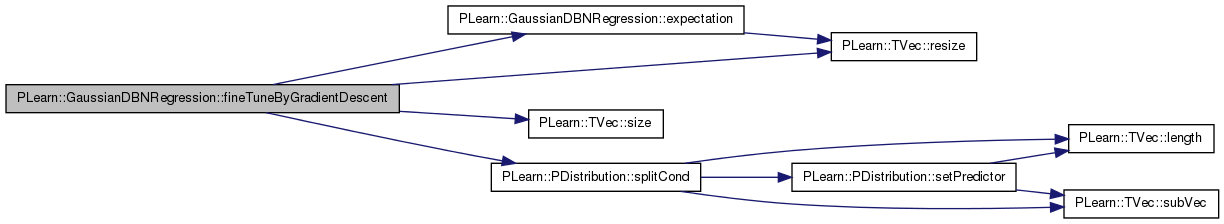
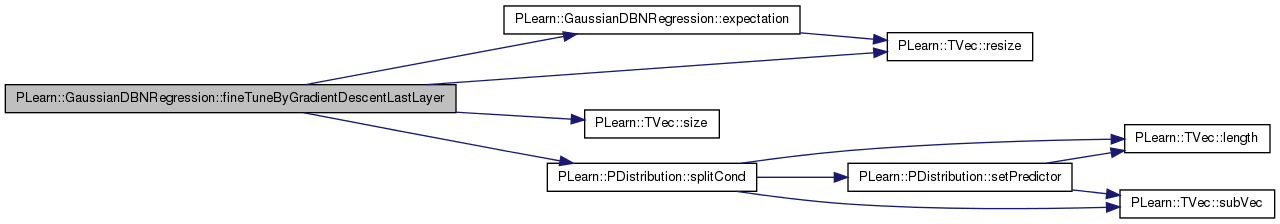
| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::fineTuneByGradientDescentLastLayer | ( | const Vec & | input | ) | [protected] |
Definition at line 756 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References activation_gradients, expectation(), expectation_gradients, i, layers, n_layers, output_gradient, PLearn::PDistribution::predicted_part, PLearn::TVec< T >::resize(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), PLearn::PDistribution::splitCond(), target_layer, and target_params.
{
// split input in predictor_part and predicted_part
splitCond(input);
// compute predicted_part expectation, conditioned on predictor_part
// (forward pass)
expectation( output_gradient );
int target_size = predicted_part.size() ;
expectation_gradients[n_layers].resize(target_size) ;
for(int i=0 ; i < target_size ; ++i) {
expectation_gradients[n_layers][i] = 2 * (output_gradient[i] - predicted_part[i]) ;
}
target_layer->bpropUpdate( target_layer->activations,
target_layer->expectation,
activation_gradients[n_layers] ,
expectation_gradients[n_layers]) ;
target_params->bpropUpdate( layers[n_layers-1]->expectation,
target_layer->activations,
expectation_gradients[n_layers-1],
activation_gradients[n_layers] );
}
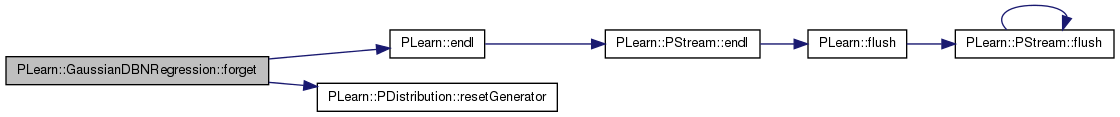
| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::forget | ( | ) | [virtual] |
(Re-)initializes the PDistribution in its fresh state (that state may depend on the 'seed' option).
And sets 'stage' back to 0 (this is the stage of a fresh learner!). ### You may remove this method if your distribution does not ### implement it.
A typical forget() method should do the following:
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 297 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References PLearn::endl(), i, input_params, layers, n_layers, params, PLearn::PDistribution::resetGenerator(), PLearn::PLearner::seed_, PLearn::PLearner::stage, target_layer, and target_params.
{
MODULE_LOG << "forget() called" << endl;
resetGenerator(seed_);
input_params->forget() ;
for( int i=1 ; i<n_layers-1 ; i++ )
params[i]->forget();
for( int i=0 ; i<n_layers ; i++ )
layers[i]->reset();
target_params->forget();
target_layer->reset();
stage = 0;
}
| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::generate | ( | Vec & | y | ) | const [virtual] |
Return a pseudo-random sample generated from the conditional distribution, of density p(y | x).
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 323 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References PLERROR.
{
PLERROR("generate not implemented for GaussianDBNRegression");
}
| OptionList & PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::getOptionList | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 59 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
| OptionMap & PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::getOptionMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 59 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
| RemoteMethodMap & PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::getRemoteMethodMap | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 59 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
| TVec< string > PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::getTestCostNames | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Return [ "NLL" ] (the only cost computed by a PDistribution).
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 861 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References PLearn::TVec< T >::append(), c, and PLearn::PDistribution::outputs_def.
{
char c = outputs_def[0];
TVec<string> result;
if( c == 'l' || c == 'd' )
result.append( "NLL" );
else if( c == 'e' )
{
result.append( "MSE" );
}
return result;
}

| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::greedyStep | ( | const Vec & | predictor, |
| int | params_index | ||
| ) | [protected, virtual] |
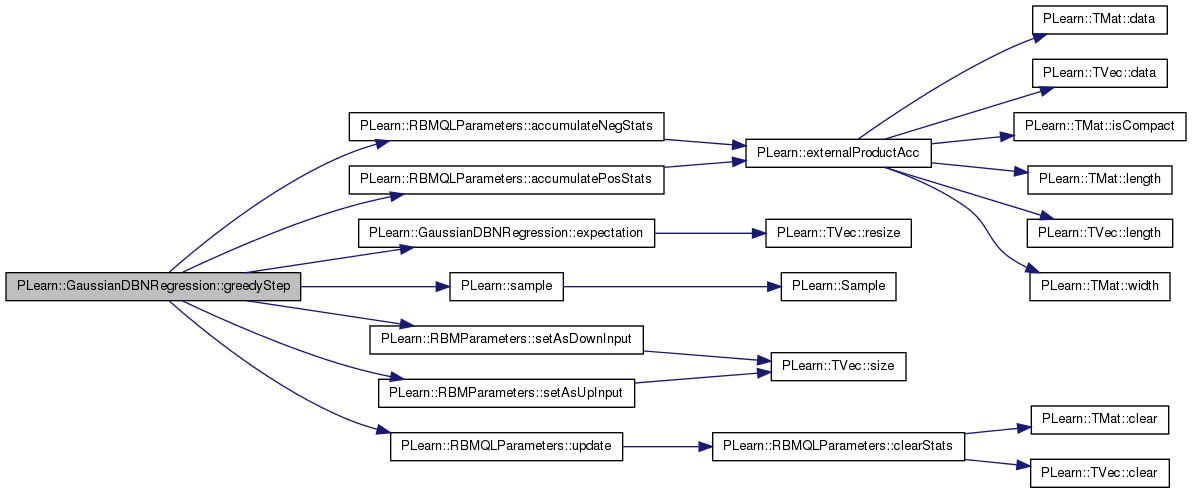
Definition at line 677 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References PLearn::RBMQLParameters::accumulateNegStats(), PLearn::RBMQLParameters::accumulatePosStats(), expectation(), i, input_params, layers, params, PLearn::sample(), PLearn::RBMParameters::setAsDownInput(), PLearn::RBMParameters::setAsUpInput(), PLearn::RBMQLParameters::update(), and use_sample_rather_than_expectation_in_positive_phase_statistics.
Referenced by train().
{
// deterministic propagation until we reach index
layers[0]->expectation << predictor;
input_params->setAsDownInput( layers[0]->expectation );
layers[1]->getAllActivations( (RBMQLParameters*) input_params );
layers[1]->computeExpectation();
for( int i=1 ; i<index ; i++ )
{
params[i]->setAsDownInput( layers[i]->expectation );
layers[i+1]->getAllActivations( (RBMLLParameters*) params[i] );
layers[i+1]->computeExpectation();
}
// positive phase
if (index == 0) {
input_params->setAsDownInput( layers[index]->expectation );
layers[index+1]->getAllActivations((RBMQLParameters*) input_params);
layers[index+1]->computeExpectation();
layers[index+1]->generateSample();
if (use_sample_rather_than_expectation_in_positive_phase_statistics)
input_params->accumulatePosStats(layers[index]->expectation,
layers[index+1]->sample );
else
input_params->accumulatePosStats(layers[index]->expectation,
layers[index+1]->expectation );
// down propagation
input_params->setAsUpInput( layers[index+1]->sample );
layers[index]->getAllActivations( (RBMQLParameters*) input_params );
// negative phase
layers[index]->generateSample();
input_params->setAsDownInput( layers[index]->sample );
layers[index+1]->getAllActivations((RBMQLParameters*) input_params);
layers[index+1]->computeExpectation();
input_params->accumulateNegStats( layers[index]->sample,
layers[index+1]->expectation );
// update
input_params->update();
}
else {
params[index]->setAsDownInput( layers[index]->expectation );
layers[index+1]->getAllActivations((RBMLLParameters*) params[index]);
layers[index+1]->computeExpectation();
layers[index+1]->generateSample();
if (use_sample_rather_than_expectation_in_positive_phase_statistics)
params[index]->accumulatePosStats(layers[index]->expectation,
layers[index+1]->sample );
else
params[index]->accumulatePosStats(layers[index]->expectation,
layers[index+1]->expectation );
// down propagation
params[index]->setAsUpInput( layers[index+1]->sample );
layers[index]->getAllActivations( (RBMLLParameters*) params[index] );
// negative phase
layers[index]->generateSample();
params[index]->setAsDownInput( layers[index]->sample );
layers[index+1]->getAllActivations((RBMLLParameters*) params[index]);
layers[index+1]->computeExpectation();
params[index]->accumulateNegStats( layers[index]->sample,
layers[index+1]->expectation );
// update
params[index]->update();
}
}

Return log of probability density log(p(y | x)).
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 389 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References density(), and pl_log.
| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy | ( | CopiesMap & | copies | ) | [virtual] |
Transforms a shallow copy into a deep copy.
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 413 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References PLearn::deepCopyField(), input_params, last_layer, layers, PLearn::PDistribution::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), params, target_layer, target_params, and training_schedule.
{
inherited::makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(copies);
deepCopyField(layers, copies);
deepCopyField(last_layer, copies);
deepCopyField(target_layer, copies);
deepCopyField(params, copies);
deepCopyField(input_params, copies);
deepCopyField(target_params, copies);
deepCopyField(training_schedule, copies);
}

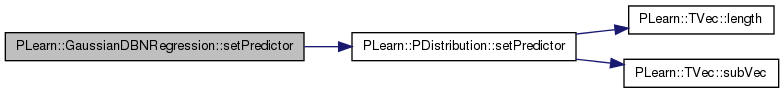
| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::setPredictor | ( | const Vec & | predictor, |
| bool | call_parent = true |
||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Set the value for the predictor part of a conditional probability.
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 429 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References PLearn::PDistribution::setPredictor().
{
if (call_parent)
inherited::setPredictor(predictor, true);
// ### Add here any specific code required by your subclass.
}
| bool PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::setPredictorPredictedSizes | ( | int | the_predictor_size, |
| int | the_predicted_size, | ||
| bool | call_parent = true |
||
| ) | [virtual] |
Generates a pseudo-random sample x from the reversed conditional distribution, of density p(x | y) (and NOT p(y | x)).
i.e., generates a "predictor" part given a "predicted" part, regardless of any previously set predictor. Set the 'predictor' and 'predicted' sizes for this distribution.
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 440 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References layers, PLearn::PDistribution::n_predicted, PLearn::PDistribution::n_predictor, PLERROR, PLearn::PDistribution::setPredictorPredictedSizes(), PLearn::TVec< T >::size(), and target_layer.
Referenced by build_layers().
{
bool sizes_have_changed = false;
if (call_parent)
sizes_have_changed = inherited::setPredictorPredictedSizes(
the_predictor_size, the_predicted_size, true);
// ### Add here any specific code required by your subclass.
if( the_predictor_size >= 0 && the_predictor_size != layers[0]->size ||
the_predicted_size >= 0 && the_predicted_size != target_layer->size )
PLERROR( "GaussianDBNRegression::setPredictorPredictedSizes - \n"
"n_predictor should be equal to layer[0]->size (%d)\n"
"n_predicted should be equal to target_layer->size (%d).\n",
layers[0]->size, target_layer->size );
n_predictor = layers[0]->size;
n_predicted = target_layer->size;
// Returned value.
return sizes_have_changed;
}


Return survival function: P(Y>y | x).
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 397 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References PLERROR.
{
PLERROR("survival_fn not implemented for GaussianDBNRegression"); return 0;
}
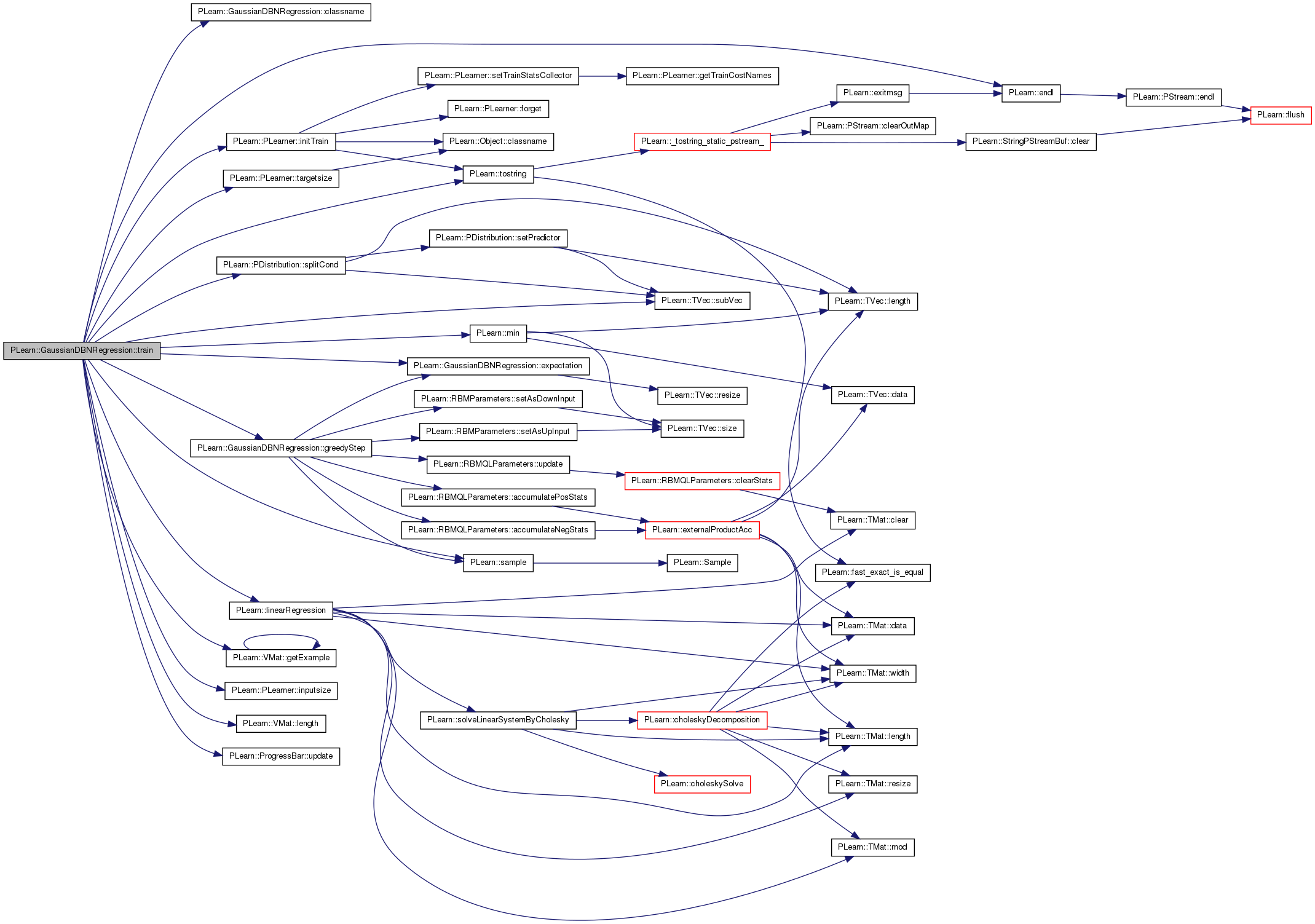
| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::train | ( | ) | [virtual] |
The role of the train method is to bring the learner up to stage == nstages, updating the train_stats collector with training costs measured on-line in the process.
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 468 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References classname(), PLearn::endl(), expectation(), PLearn::VMat::getExample(), greedyStep(), i, PLearn::PLearner::initTrain(), PLearn::PLearner::inputsize(), j, last_layer, PLearn::VMat::length(), PLearn::linearRegression(), PLearn::min(), n_layers, PLearn::PDistribution::n_predicted, PLearn::PDistribution::n_predictor, PLearn::PLearner::nstages, PLearn::PLearner::report_progress, PLearn::sample(), PLearn::PDistribution::splitCond(), PLearn::PLearner::stage, PLearn::TVec< T >::subVec(), target_params, PLearn::PLearner::targetsize(), PLearn::tostring(), PLearn::PLearner::train_set, PLearn::PLearner::train_stats, training_schedule, and PLearn::ProgressBar::update().
{
MODULE_LOG << "train() called" << endl;
// The role of the train method is to bring the learner up to
// stage==nstages, updating train_stats with training costs measured
// on-line in the process.
/* TYPICAL CODE:
static Vec input; // static so we don't reallocate memory each time...
static Vec target; // (but be careful that static means shared!)
input.resize(inputsize()); // the train_set's inputsize()
target.resize(targetsize()); // the train_set's targetsize()
real weight;
// This generic PLearner method does a number of standard stuff useful for
// (almost) any learner, and return 'false' if no training should take
// place. See PLearner.h for more details.
if (!initTrain())
return;
while(stage<nstages)
{
// clear statistics of previous epoch
train_stats->forget();
//... train for 1 stage, and update train_stats,
// using train_set->getExample(input, target, weight)
// and train_stats->update(train_costs)
++stage;
train_stats->finalize(); // finalize statistics for this epoch
}
*/
Vec input( inputsize() );
Vec target( targetsize() ); // unused
real weight; // unused
if( !initTrain() )
{
MODULE_LOG << "train() aborted" << endl;
return;
}
int nsamples = train_set->length();
MODULE_LOG << " nsamples = " << nsamples << endl;
// Let's define stage and nstages:
// - 0: fresh state, nothing is done
// - 1..n_layers-2: params[stage-1] is trained
// - n_layers-1: joint_params is trained (including params[n_layers-2])
// - n_layers: after the fine tuning
MODULE_LOG << "initial stage = " << stage << endl;
MODULE_LOG << "objective: nstages = " << nstages << endl;
// clear stats of previous epoch
train_stats->forget();
for(int layer=0 ; layer<n_layers-1 ; ++layer) {
MODULE_LOG << "Training parameters between layers " << layer
<< " and " << layer+1 << endl;
// this progress bar shows the number of loops through the whole
// training set
ProgressBar* pb = 0;
int end_stage = min( training_schedule[layer], nstages );
if( report_progress && stage < end_stage )
{
pb = new ProgressBar( "Training layer "+tostring(layer)+
"of" + classname(), end_stage - stage );
}
for( ; stage < end_stage ; stage++ )
{
// sample is the index in the training set
int sample = stage % train_set->length();
train_set->getExample(sample, input, target, weight);
greedyStep( input.subVec(0, n_predictor), layer );
if( pb )
{
if( layer == 0 )
pb->update(stage + 1);
else
pb->update(stage - training_schedule[layer-1] + 1);
}
Mat inputs(train_set.length() , n_predictor) ;
Mat outputs(train_set.length() , n_predicted);
Mat theta(1 + n_predictor , n_predicted) ;
Vec output_value(n_predicted) ;
for(int i=0 ; i<train_set.length() ; ++i) {
train_set->getExample(i, input, target, weight);
// split input in predictor_part and predicted_part
splitCond(input);
// compute predicted_part expectation, conditioned on predictor_part
// (forward pass)
expectation( output_value );
for(int j=0 ; j<n_predictor ; ++j) {
inputs[i][j] = last_layer->expectation[j] ;
// cout << last_layer->expectation[j] << " " ;
}
for(int j=0 ; j<n_predicted ; ++j) {
outputs[i][j] = input[j+n_predictor] ;
}
}
// pout << "inputs " << endl << inputs << endl ;
// pout << "outputs " << endl << outputs << endl ;
linearRegression(inputs,outputs,0.0,theta);
// init the a_i term
target_params->up_units_params[1].fill(1) ;
// pout << "Theta" << theta << endl ;
// set the bias (b_i)
for(int i=0 ; i<n_predicted ; ++i) {
target_params->up_units_params[0][i] = - 2.0 * theta[i][0] ;
}
for(int i=0 ; i<n_predicted ; ++i) {
for(int j=0 ; j<n_predictor ; ++j) {
target_params->weights[i][j] = -2.0 * theta[j][i+1] ;
}
}
}
}
/*
MODULE_LOG << "Fine-tuning all parameters, using method "
<< fine_tuning_method << endl;
if( fine_tuning_method == "" ) // do nothing
sample += n_samples_to_see;
else if( fine_tuning_method == "EGD" )
{
if( report_progress )
pb = new ProgressBar( "Training all " + classname()
+ " parameters by fine tuning",
n_samples_to_see );
*/
/*
pout << "==================" << endl
<< "Before update:" << endl
<< "up: " << joint_params->up_units_params << endl
<< "weights: " << endl << joint_params->weights << endl
<< "down: " << joint_params->down_units_params << endl
<< endl;
// */
// linear regression for last weights
/*
int begin_sample = sample;
int end_sample = begin_sample + n_samples_to_see;
for( ; sample < end_sample ; sample++ )
{
// sample is the index in the training set
int i = sample % train_set->length();
train_set->getExample(i, input, target, weight);
fineTuneByGradientDescentLastLayer( input );
if( pb )
pb->update( sample - begin_sample + 1 );
}
sample = begin_sample ;
for( ; sample < 100 ; sample++ )
{
// sample is the index in the training set
int i = sample % train_set->length();
train_set->getExample(i, input, target, weight);
fineTuneByGradientDescent( input );
if( pb )
pb->update( sample - begin_sample + 1 );
}
*/
/*
pout << "-------" << endl
<< "After update:" << endl
<< "up: " << joint_params->up_units_params << endl
<< "weights: " << endl << joint_params->weights << endl
<< "down: " << joint_params->down_units_params << endl
<< endl;
// */
train_stats->finalize(); // finalize statistics for this epoch
MODULE_LOG << endl;
}
| void PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::variance | ( | Mat & | cov | ) | const [virtual] |
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 405 of file GaussianDBNRegression.cc.
References PLERROR.
{
PLERROR("variance not implemented for GaussianDBNRegression");
}
Reimplemented from PLearn::PDistribution.
Definition at line 232 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
TVec< Vec > PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::activation_gradients [mutable, protected] |
gradients of cost wrt the activations (output of params)
Definition at line 248 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by build_params(), fineTuneByGradientDescent(), and fineTuneByGradientDescentLastLayer().
TVec< Vec > PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::expectation_gradients [mutable, protected] |
gradients of cost wrt the expectations (output of layers)
Definition at line 251 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by build_params(), fineTuneByGradientDescent(), and fineTuneByGradientDescentLastLayer().
Method for fine-tuning the whole network after greedy learning.
One of:
Definition at line 117 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by build_(), and declareOptions().
The method used to initialize the weights:
Definition at line 81 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by build_(), build_params(), and declareOptions().
Parameters linking input layer[0] and layer[1].
Definition at line 102 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by build_params(), declareOptions(), expectation(), fineTuneByGradientDescent(), forget(), greedyStep(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
last_layer is layer[n_layers-1]
Definition at line 92 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by build_layers(), build_params(), expectation(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), and train().
Layers that learn representations of the input, layers[0] is input layer, layers[n_layers-1] is last layer.
Definition at line 89 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by build_(), build_layers(), build_params(), declareOptions(), expectation(), fineTuneByGradientDescent(), fineTuneByGradientDescentLastLayer(), forget(), greedyStep(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), and setPredictorPredictedSizes().
### declare public option fields (such as build options) here Start your comments with Doxygen-compatible comments such as //!
The learning rate
Definition at line 71 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by build_params(), and declareOptions().
Number of layers, including input layer and last layer, but not target layer.
Definition at line 85 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by build_(), build_layers(), build_params(), declareOptions(), expectation(), fineTuneByGradientDescent(), fineTuneByGradientDescentLastLayer(), forget(), and train().
Vec PLearn::GaussianDBNRegression::output_gradient [mutable, protected] |
gradient wrt output activations
Definition at line 254 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by build_params(), fineTuneByGradientDescent(), and fineTuneByGradientDescentLastLayer().
RBMParameters linking the unsupervised layers.
params[i] links layers[i] and layers[i+1], i>0
Definition at line 99 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by build_params(), declareOptions(), expectation(), fineTuneByGradientDescent(), forget(), greedyStep(), and makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy().
Target (or label) layer.
Definition at line 95 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by build_layers(), build_params(), declareOptions(), expectation(), fineTuneByGradientDescent(), fineTuneByGradientDescentLastLayer(), forget(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), and setPredictorPredictedSizes().
Parameters linking target_layer and last_layer.
Definition at line 105 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by build_params(), declareOptions(), expectation(), fineTuneByGradientDescent(), fineTuneByGradientDescentLastLayer(), forget(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), and train().
Number of examples to use during each of the different greedy steps of the training phase.
Definition at line 109 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by build_(), declareOptions(), makeDeepCopyFromShallowCopy(), and train().
Definition at line 119 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by declareOptions(), and greedyStep().
The weight decay.
Definition at line 74 of file GaussianDBNRegression.h.
Referenced by declareOptions().
 1.7.4
1.7.4